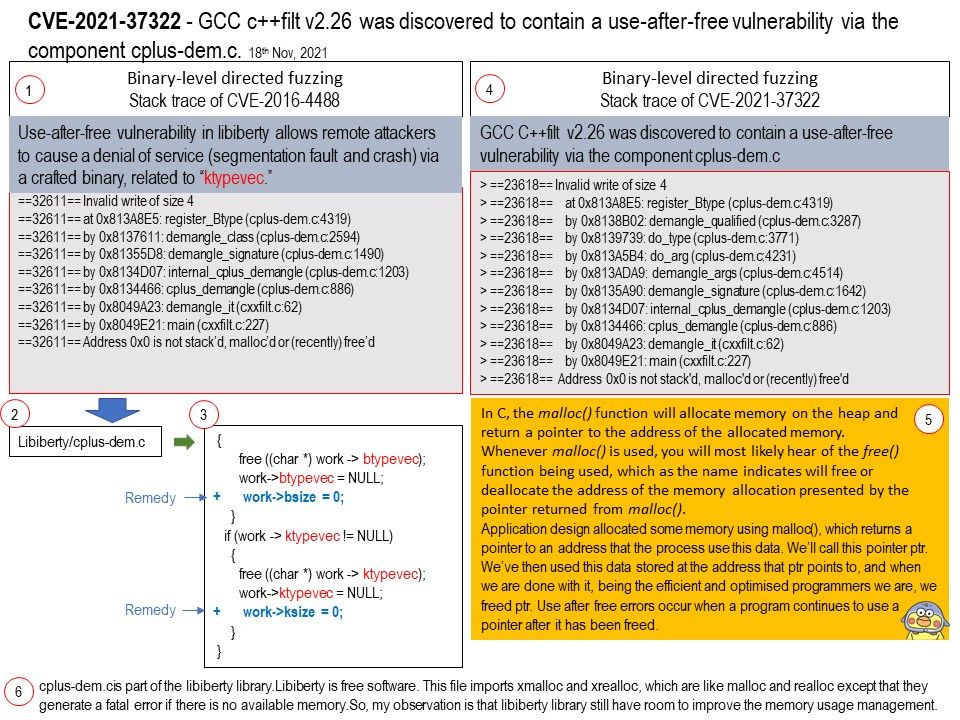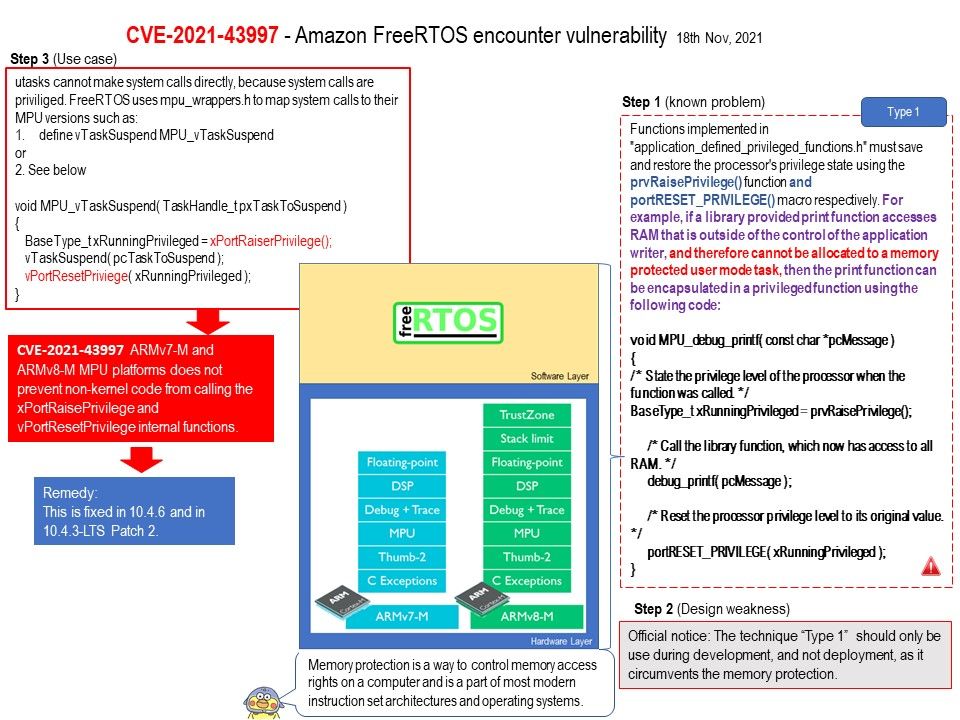
Preface: If a network interface controller is intended to be used as a boot device for a UEFI operating system or UEFI applications, then a UEFI Driver must be implemented that produces Network Interface Identifier Protocol and UNDI, the Simple Network Protocol, or the Managed Network Protocol.
Background: Tianocore EDK II is the UEFI reference implementation by Intel. EDK is the abbreviation for EFI Development Kit and is developed by the TianoCore community.
UEFI stands for Unified Extensible Firmware Interface. It does the same job as a BIOS, but with difference. It stores all data about initialization and startup. UEFI supports drive sizes upto 9 zettabytes, whereas BIOS only supports 2.2 terabytes. UEFI provides faster boot time.
UEFI also includes TCP (the latest version of UEFI from IIRC supports booting via HTTP, similar to iPXE).
Disadvantages of UEFI?
- 64-bit are necessary.
- Virus and Trojan threat due to network support, since UEFI doesn’t have anti-virus software.
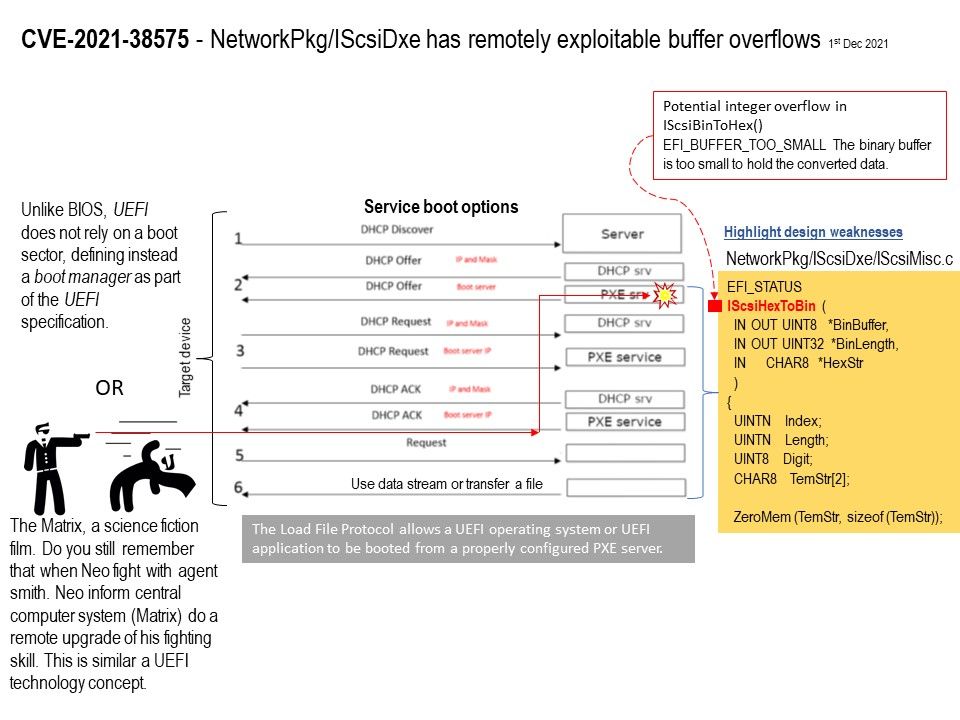
Vulnerability details: Certain versions of EDK II from TianoCore contain vulnerability (NetworkPkg/IScsiDxe has remotely exploitable buffer overflows). The fact is that potential integer overflow in IScsiBinToHex().
Reason: EFI_BUFFER_TOO_SMALL The binary buffer is too small to hold the converted data.
Official details: Please refer to the link – https://bugzilla.tianocore.org/show_bug.cgi?id=3356
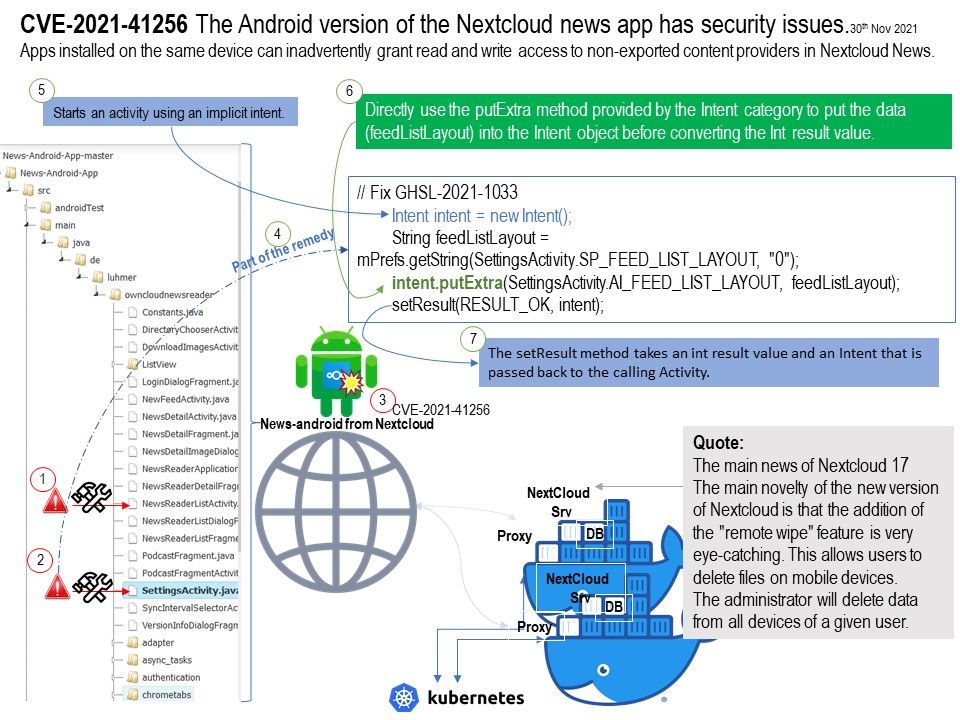
.jpg)