Preface: Forward proxy is used to forward traffic from a client to the internet, while a reverse proxy is used to forward traffic from the internet to a web server.
Background: A reverse proxy is a server, app, or cloud service that sits in front of one or more web servers to intercept and inspect incoming client requests before forwarding them to the web server and subsequently returning the server’s response to the client.
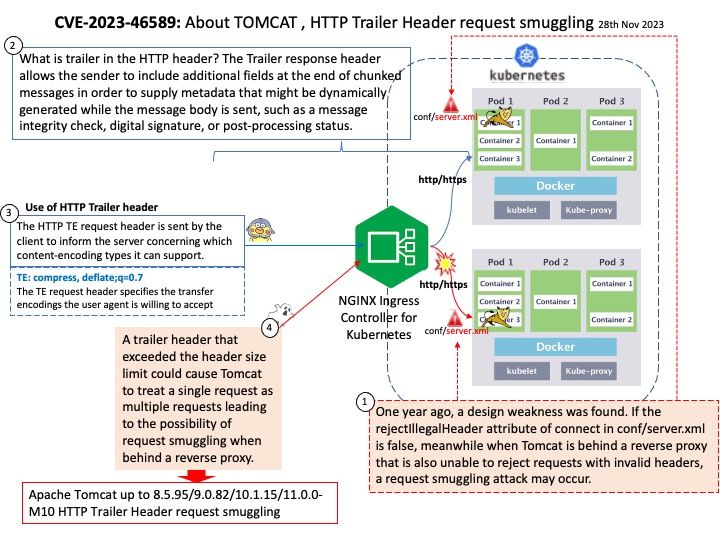
The HTTP specification provides two different ways to specify the end of a request: Content-Length and Transfer-Encoding. Classic request smuggling attacks involve placing both the Content-Length header and the Transfer-Encoding header into a single HTTP/1 request and manipulating these so that the front-end and back-end servers process the request differently.
Vulnerability details: Improper Input Validation vulnerability in Apache Tomcat. Tomcat from 11.0.0-M1 through 11.0.0-M10, from 10.1.0-M1 through 10.1.15, from 9.0.0-M1 through 9.0.82 and from 8.5.0 through 8.5.95 did not correctly parse HTTP trailer headers. A trailer header that exceeded the header size limit could cause Tomcat to treat a single request as multiple requests leading to the possibility of request smuggling when behind a reverse proxy.
Remedy: Upgrading to version 8.5.96, 9.0.83, 10.1.16 or 11.0.0-M11 eliminates this vulnerability.
Official announcement: Please refer to the link for details – https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2023-46589