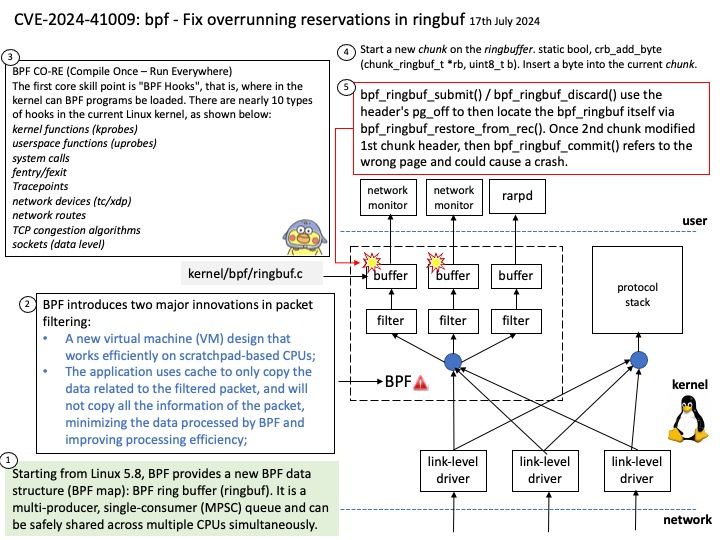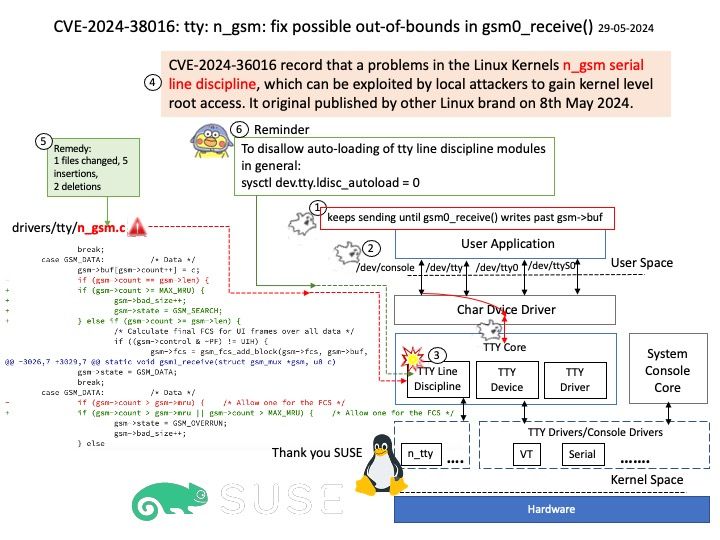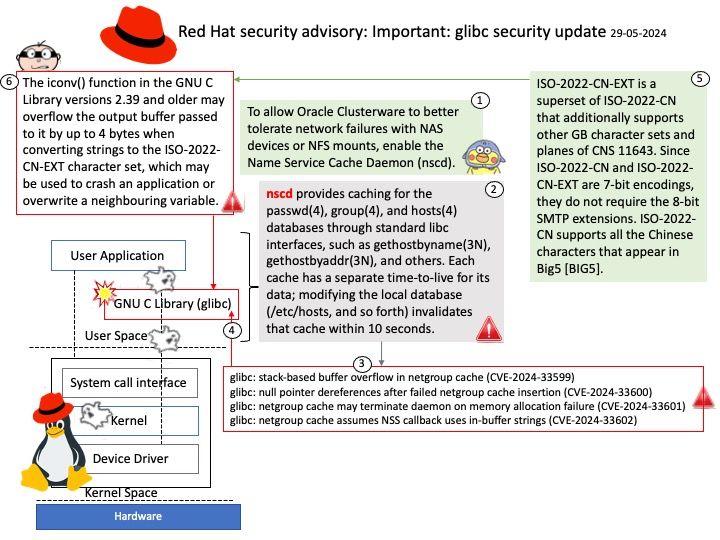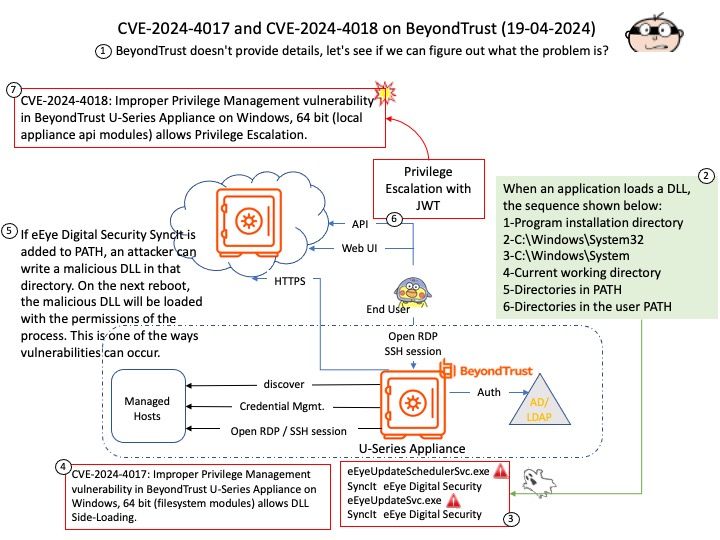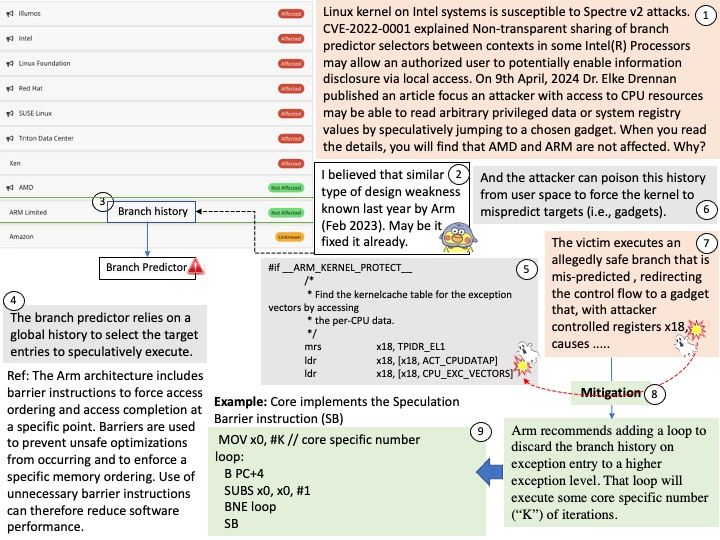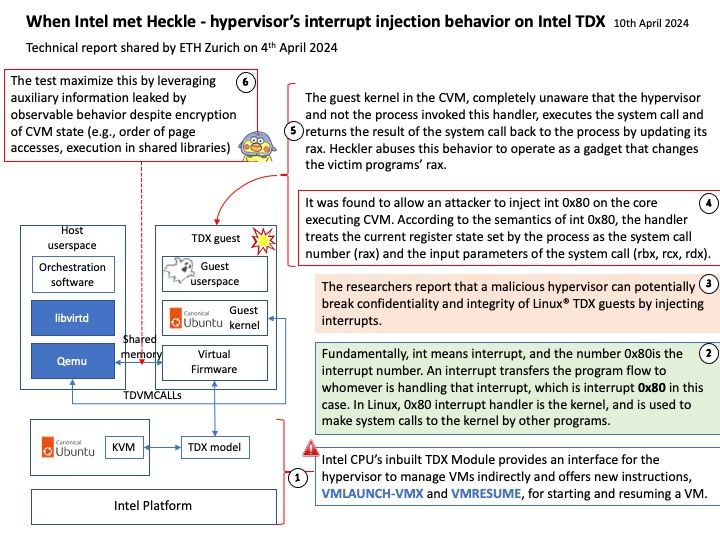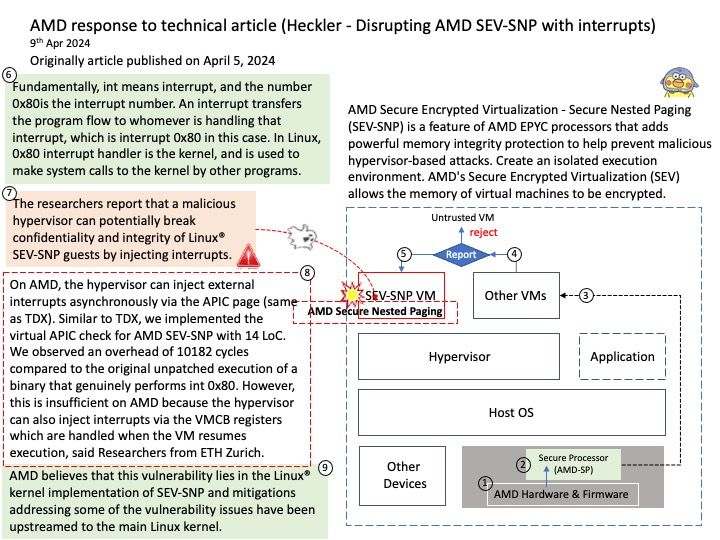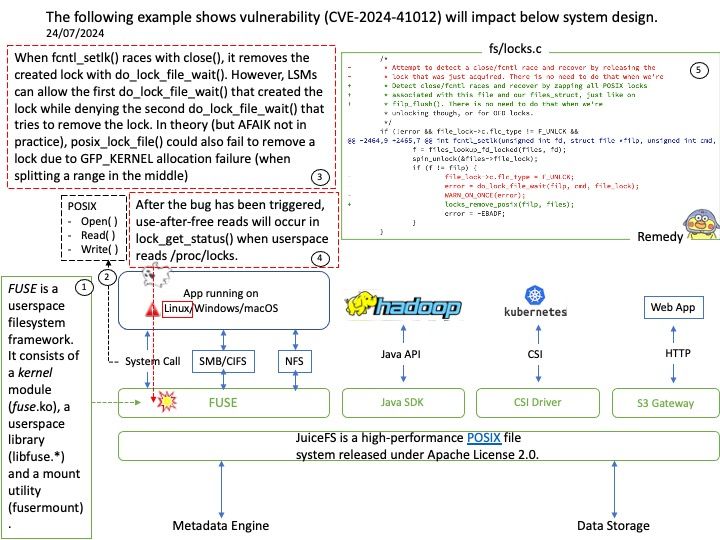
In the Linux kernel, design weakness (CVE-2024-41012) has been resolved.
Preface: The GFP acronym stands for “get free pages”, the underlying memory allocation function. Diversity of the allocation APIs combined with the numerous GFP flags makes the question “How should I allocate memory?” not that easy to answer, although very likely you should use. kzalloc(<size>, GFP_KERNEL);
Background: You can build a 64-bit POSIX-compliant tick-less kernel with a Linux-compatible syscall implementation using Go.
Vulnerability details: When fcntl_setlk() races with close(), it removes the created lock with do_lock_file_wait(). However, LSMs can allow the first do_lock_file_wait() that created the lock while denying the second do_lock_file_wait() that tries to remove the lock. In theory (but AFAIK not in practice), posix_lock_file() could also fail to remove a lock due to GFP_KERNEL allocation failure (when splitting a range in the middle).
After the bug has been triggered, use-after-free reads will occur in lock_get_status() when userspace reads /proc/locks. This can likely be used to read arbitrary kernel memory, but can’t corrupt kernel memory. This only affects systems with SELinux / Smack / AppArmor / BPF-LSM in enforcing mode and only works from some security contexts.
Official announcement: Please refer to the official announcement for details – https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-41012