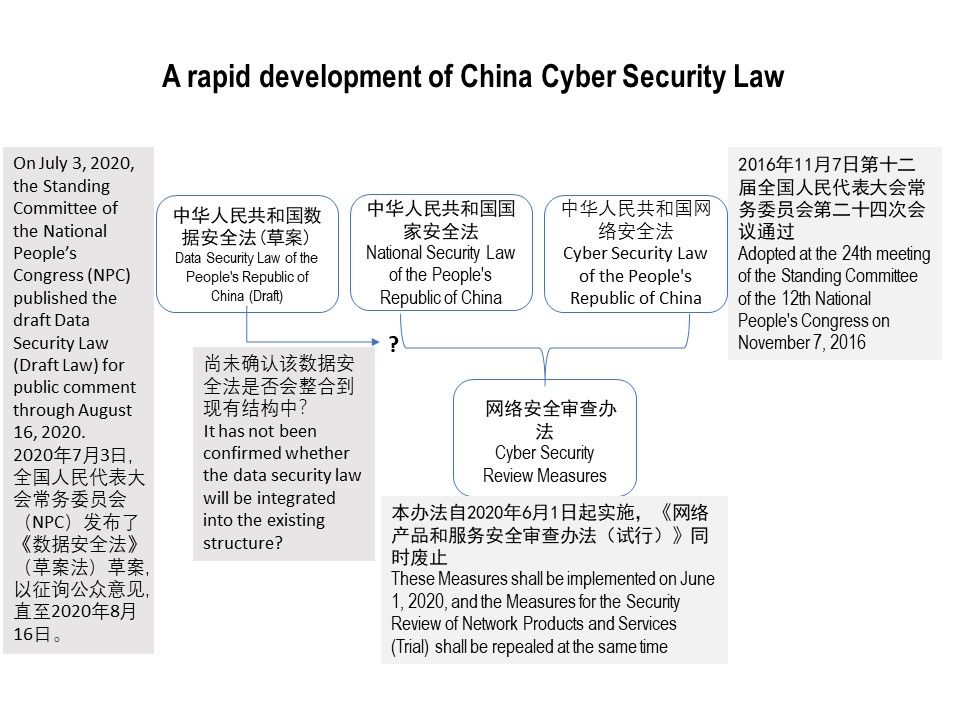
Preface:
It make foreign countries enterprise firm nervous that new cyber security law with effective 1st June 2017. The Article 5 looks with powerful privileges which causes solicitor, data privacy expert headache!
Let take a closer look of Article 5 (see below):
Article 5 The state shall take measures to monitor, defend against and deal with cybersecurity risks and threats from both inside and outside the territory of the People’s Republic of China, protect critical information infrastructure from attack, intrusion, interference and damage, punish illegal criminal activities on the network in accordance with the law, and maintain cyberspace security and order.
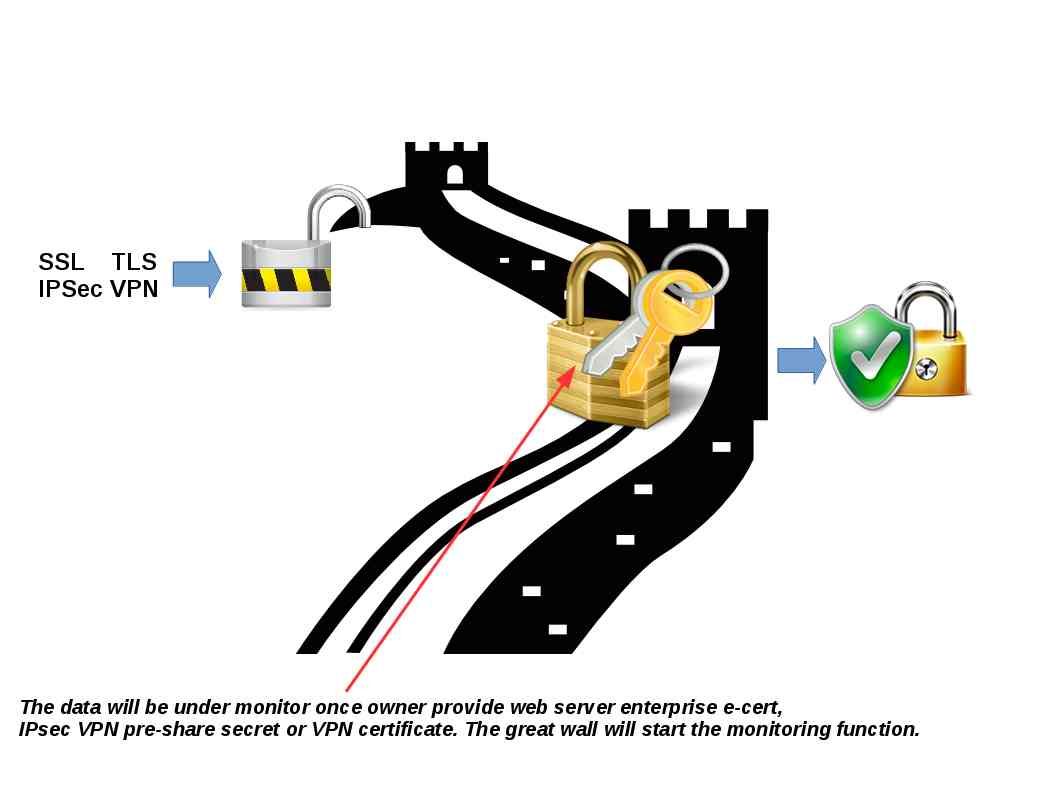
Techincal view point: In the sense that even though your web hosting not located in Greater China area once there is one endpoint located in Greater China the computer owner require to follow the new law.
Technical support criteria: Such surveillance process not difficult to do. A common network break through technique is man-in-the-middle. The data will be under monitor once owner provide web server enterprise e-cert, IPsec VPN pre-share secret or VPN certificate. The great wall will start the monitoring function.
Not surprised! It required to follow their law once you are going to do the business in China! Below is the cyber security law details for your reference.
2017 cyber security law for reference
General Provisions – 總則
Article 1 This Law is developed for the purposes of guaranteeing cybersecurity, safeguarding cyberspace sovereignty, national security and public interest, protecting the lawful rights and interests of citizens, legal persons and other organizations, and promoting the sound development of economic and social informatization.
第一條 為了保障網絡安全,維護網絡空間主權和國家安全、社會公共利益,保護公民、法人和其他組織的合法權益,促進經濟社會信息化健康發展,制定本法。
Article 2 This Law shall apply to the construction, operation, maintenance and use of the network as well as the supervision and administration of cybersecurity within the territory of the People’s Republic of China.
第二條 在中華人民共和國境內建設、運營、維護和使用網絡,以及網絡安全的監督管理,適用本法。
Article 3 The state shall lay equal stress on cybersecurity and information-based development, follow the guidelines of positive use, scientific development, legal management and security guarantee, promote the construction of network infrastructure and interconnection, encourage the innovation and application of network technologies, support the cultivation of cybersecurity talents, establish and improve the cybersecurity guarantee system, and enhance the capability to protect cybersecurity.
第三條國家堅持網絡安全與信息化發展並重,遵循積極利用、科學發展、依法管理、確保安全的方針,推進網絡基礎設施建設和互聯互通,鼓勵網絡技術創新和應用,支持培養網絡安全人才,建立健全網絡安全保障體系,提高網絡安全保護能力。
Article 4 The state shall develop and continuously improve cybersecurity strategies, specify the basic requirements and major objectives for guaranteeing cybersecurity, and propose cybersecurity policies, work tasks and measures in key fields.
第四條 國家製定並不斷完善網絡安全戰略,明確保障網絡安全的基本要求和主要目標,提出重點領域的網絡安全政策、工作任務和措施。
Article 5 The state shall take measures to monitor, defend against and deal with cybersecurity risks and threats from both inside and outside the territory of the People’s Republic of China, protect critical information infrastructure from attack, intrusion, interference and damage, punish illegal criminal activities on the network in accordance with the law, and maintain cyberspace security and order.
第五條國家採取措施,監測、防禦、處置來源於中華人民共和國境內外的網絡安全風險和威脅,保護關鍵信息基礎設施免受攻擊、侵入、干擾和破壞,依法懲治網絡違法犯罪活動,維護網絡空間安全和秩序。
Article 6 The state shall advocate honest, faithful, healthy and civilized network conduct, advance the spreading of core socialist values, and take measures to enhance the awareness and level of cybersecurity of the entire society, so as to form a favorable environment for promoting cybersecurity with the participation of the entire society.
第六條 國家倡導誠實守信、健康文明的網絡行為,推動傳播社會主義核心價值觀,採取措施提高全社會的網絡安全意識和水平,形成全社會共同參與促進網絡安全的良好環境。
Article 7 The state shall actively carry out international exchange and cooperation in terms of cyberspace governance, research and development of network technologies, formulation of standards thereof, and crackdown on illegal crimes committed on the network and other aspects, promote the construction of a peaceful, safe, open and cooperative cyberspace, and establish a multilateral, democratic and transparent system for cyber governance.
第七條國家積極開展網絡空間治理、網絡技術研發和標準制定、打擊網絡違法犯罪等方面的國際交流與合作,推動構建和平、安全、開放、合作的網絡空間,建立多邊、民主、透明的網絡治理體系。
Article 8 The national cyberspace administration shall be responsible for the overall planning and coordination of cybersecurity work and relevant supervision and administration. The competent telecommunications department of the State Council, public security departments and other relevant authorities shall be responsible for cybersecurity protection, supervision and administration within the scope of their respective functions in accordance with the provisions of this Law and other relevant laws and administrative regulations.
第八條 國家網信部門負責統籌協調網絡安全工作和相關監督管理工作。國務院電信主管部門、公安部門和其他有關機關依照本法和有關法律、行政法規的規定,在各自職責範圍內負責網絡安全保護和監督管理工作。
Article 9 Network operators shall, when conducting business operations and providing services, abide by laws and administrative regulations, respect social morality, observe business ethics, have good faith, perform the cybersecurity protection obligation, accept supervision by the government and the public, and undertake social responsibilities.
第九條 網絡運營者開展經營和服務活動,必須遵守法律、行政法規,尊重社會公德,遵守商業道德,誠實信用,履行網絡安全保護義務,接受政府和社會的監督,承擔社會責任
Article 10 For the construction and operation of the network or the provision of services through the network, technical measures and other necessary measures shall be taken in accordance with the provisions of laws and administrative regulations and the compulsory requirements of national standards to ensure the safe and stable operation of the network, effectively respond to cybersecurity incidents, prevent illegal criminal activities committed on the network, and maintain the integrity, confidentiality and availability of network data.
第十條建設、運營網絡或者通過網絡提供服務,應當依照法律、行政法規的規定和國家標準的強制性要求,採取技術措施和其他必要措施,保障網絡安全、穩定運行,有效應對網絡安全事件,防範網絡違法犯罪活動,維護網絡數據的完整性、保密性和可用性。
Article 11 Network-related industry organizations shall, in accordance with their charters, intensify industry self-discipline, formulate codes of conduct on cybersecurity, direct their members to strengthen cybersecurity protection, raise the level of cybersecurity protection, and promote the sound development of the industry.
第十一條 網絡相關行業組織按照章程,加強行業自律,制定網絡安全行為規範,指導會員加強網絡安全保護,提高網絡安全保護水平,促進行業健康發展。
Article 12 The state shall protect the rights of citizens, legal persons and other organizations to use the network in accordance with the law, promote the popularity of network access, provide better network services, provide the public with safe and convenient network services, and guarantee the orderly and free flow of network information in accordance with the law. Any individual or organization using the network shall comply with the Constitution and laws, follow public order and respect social morality, shall not endanger cybersecurity, and shall not use the network to conduct any activity that endangers national security, honor and interest, incites to subvert the state power or overthrow the socialist system, incites to split the country or undermine national unity, advocates terrorism or extremism, propagates ethnic hatred or discrimination, spreads violent or pornographic information, fabricates or disseminates false information to disrupt the economic and social order, or infringes upon the reputation, privacy, intellectual property rights or other lawful rights and interests of any other person.
第十二條 國家保護公民、法人和其他組織依法使用網絡的權利,促進網絡接入普及,提升網絡服務水平,為社會提供安全、便利的網絡服務,保障網絡信息依法有序自由流動。任何個人和組織使用網絡應當遵守憲法法律,遵守公共秩序,尊重社會公德,不得危害網絡安全,不得利用網絡從事危害國家安全、榮譽和利益,煽動顛覆國家政權、推翻社會主義制度,煽動分裂國家、破壞國家統一,宣揚恐怖主義、極端主義,宣揚民族仇恨、民族歧視,傳播暴力淫穢色情信息,編造、傳播虛假信息擾亂經濟秩序和社會秩序,以及侵害他人名譽、隱私、知識產權和其他合法權益等活動。
Article 13 The state shall support the research and development of network products and services that are conducive to the healthy growth of minors, legally punish the activities that damage the physical and mental health of minors by using the network, and provide a safe and healthy network environment for minors.
第十三條 國家支持研究開發有利於未成年人健康成長的網絡產品和服務,依法懲治利用網絡從事危害未成年人身心健康的活動,為未成年人提供安全、健康的網絡環境。
Article 14 Any individual or organization shall have the right to report the conduct that endangers cybersecurity to the cyberspace administration, telecommunications department, public security authority, and other departments. The department that receives the report shall handle such a report in a timely manner in accordance with the law, or transfer the report to the competent department in a timely manner if it falls outside its responsibility. The relevant department shall keep confidential the information on the informant, and protect the informant’s lawful rights and interests.
第十四條 任何個人和組織有權對危害網絡安全的行為向網信、電信、公安等部門舉報。收到舉報的部門應當及時依法作出處理;不屬於本部門職責的,應當及時移送有權處理的部門。有關部門應當對舉報人的相關信息予以保密,保護舉報人的合法權益
Cybersecurity Support and Promotion – 網絡安全支持與促進
Article 15 The state shall establish and improve the system of cybersecurity standards. The standardization administrative department of the State Council and other relevant departments of the State Council shall, according to their respective functions, organize the formulation of and revise at appropriate time national and industry standards relating to cybersecurity administration and the security of network products, services and operations. The state shall support enterprises, research institutions, institutions of higher learning, and network-related industry organizations in participating in the formulation of national and industry standards on cybersecurity.
第十五條 國家建立和完善網絡安全標準體系。國務院標準化行政主管部門和國務院其他有關部門根據各自的職責,組織製定並適時修訂有關網絡安全管理以及網絡產品、服務和運行安全的國家標準、行業標準。國家支持企業、研究機構、高等學校、網絡相關行業組織參與網絡安全國家標準、行業標準的製定。
Article 16 The State Council and people’s governments of provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government shall make overall planning, increase input, support key cybersecurity technology industries and projects, support the research, development and application of cybersecurity technologies, popularize safe and reliable network products and services, protect the intellectual property rights of network technologies, and support enterprises, research institutions, and institutions of higher learning, among others, in participating in national innovation projects on cybersecurity technologies.
第十六條國務院和省、自治區、直轄市人民政府應當統籌規劃,加大投入,扶持重點網絡安全技術產業和項目,支持網絡安全技術的研究開發和應用,推廣安全可信的網絡產品和服務,保護網絡技術知識產權,支持企業、研究機構和高等學校等參與國家網絡安全技術創新項目。
Article 17 The state shall boost the construction of a socialized service system for cybersecurity, and encourage relevant enterprises and institutions to provide such security services as cybersecurity authentication, detection and risk assessment.
第十七條 國家推進網絡安全社會化服務體系建設,鼓勵有關企業、機構開展網絡安全認證、檢測和風險評估等安全服務。
Article 18 The state shall encourage the development of technologies for protecting and using network data, promote the availability of public data resources, and promote technological innovation and social and economic development. The state shall support the innovation of cybersecurity management methods and the application of new network technologies to enhance cybersecurity protection.
第十八條 國家鼓勵開發網絡數據安全保護和利用技術,促進公共數據資源開放,推動技術創新和經濟社會發展。國家支持創新網絡安全管理方式,運用網絡新技術,提升網絡安全保護水平。
Article 19 People’s governments at all levels and their relevant departments shall organize regular cybersecurity publicity and education, and direct and urge relevant entities to conduct cybersecurity publicity and education in an effective manner. Mass media shall offer pertinent cybersecurity publicity and education to the public.
第十九條 各級人民政府及其有關部門應當組織開展經常性的網絡安全宣傳教育,並指導、督促有關單位做好網絡安全宣傳教育工作。大眾傳播媒介應當有針對性地面向社會進行網絡安全宣傳教育
Article 20 The state shall provide support to enterprises, institutions of higher learning, vocational schools and other education training institutions to conduct cybersecurity-related education and training, take multiple means to cultivate cybersecurity talents, and promote the exchange of cybersecurity talents.
第二十條 國家支持企業和高等學校、職業學校等教育培訓機構開展網絡安全相關教育與培訓,採取多種方式培養網絡安全人才,促進網絡安全人才交流。
Network Operation Security – 網絡運行安全
Section 1 General Provisions – 一般規定
Article 21 The state shall implement the rules for graded protection of cybersecurity.Network operators shall, according to the requirements of the rules for graded protection of cybersecurity, fulfill the following security protection obligations, so as to ensure that the network is free from interference, damage or unauthorized access, and prevent network data from being divulged, stolen or falsified.
(1) Developing internal security management rules and operating procedures, determining the persons in charge of cybersecurity, and carrying out the responsibility for cybersecurity protection.
(2) Taking technical measures to prevent computer viruses, network attack, network intrusion and other acts endangering cybersecurity.
(3) Taking technical measures to monitor and record the status of network operation and cybersecurity incidents, and preserving relevant weblogs for not less than six months as required.
(4) Taking measures such as data categorization, and back-up and encryption of important data.
(5) Performing other obligations as prescribed by laws and administrative regulations.
第二十一條 國家實行網絡安全等級保護製度。網絡運營者應當按照網絡安全等級保護製度的要求,履行下列安全保護義務,保障網絡免受干擾、破壞或者未經授權的訪問,防止網絡數據洩露或者被竊取、
篡改:
(一)制定內部安全管理制度和操作規程,確定網絡安全負責人,落實網絡安全保護責任;
(二)採取防範計算機病毒和網絡攻擊、網絡侵入等危害網絡安全行為的技術措施;
(三)採取監測、記錄網絡運行狀態、網絡安全事件的技術措施,並按照規定留存相關的網絡日誌不少於六個月;
(四)採取數據分類、重要數據備份和加密等措施;
(五)法律、行政法規規定的其他義務。
Article 22 Network products and services shall comply with the compulsory requirements of relevant national standards. Providers of network products and services shall not install malware. When a provider discovers any risk such as security defect and vulnerability of its network products or services, it shall immediately take remedial measures, inform users in a timely manner, and report it to the competent department in accordance with relevant provisions. Providers of network products and services shall continuously provide security maintenance for their products and services, and shall not terminate the provision of security maintenance within the stipulated period or the period agreed upon by the parties. Where network products and services have the function of collecting users’ information, their providers shall explicitly notify their users and obtain their consent. If any user’s personal information is involved, the provider shall also comply with this Law and the provisions of relevant laws and administrative regulations on the protection of personal information.
第二十二條 網絡產品、服務應當符合相關國家標準的強制性要求。網絡產品、服務的提供者不得設置惡意程序;發現其網絡產品、服務存在安全缺陷、漏洞等風險時,應當立即採取補救措施,按照規定及時告知用戶並向有關主管部門報告。網絡產品、服務的提供者應當為其產品、服務持續提供安全維護;在規定或者當事人約定的期限內,不得終止提供安全維護。網絡產品、服務具有收集用戶信息功能的,其提供者應當向用戶明示並取得同意;涉及用戶個人信息的,還應當遵守本法和有關法律、行政法規關於個人信息保護的規定。
Article 23 Key network equipment and specialized cybersecurity products shall, in accordance with the compulsory requirements of relevant national standards, pass the security certification conducted by qualified institutions or meet the requirements of security detection before being sold or provided. The national cyberspace administration shall, in conjunction with relevant departments of the State Council, develop and release the catalogue of key network equipment and specialized cybersecurity products, and promote the mutual recognition of security certification and security detection results to avoid repeated certification and detection.
第二十三條 網絡關鍵設備和網絡安全專用產品應當按照相關國家標準的強制性要求,由具備資格的機構安全認證合格或者安全檢測符合要求後,方可銷售或者提供。國家網信部門會同國務院有關部門製定、公佈網絡關鍵設備和網絡安全專用產品目錄,並推動安全認證和安全檢測結果互認,避免重複認證、檢測。
Article 24 Where network operators provide network access and domain registration services for users, handle network access formalities for fixed-line or mobile phone users, or provide users with information release services, instant messaging services and other services, they shall require users to provide true identity information when signing agreements with users or confirming the provision of services. If any user fails to provide his or her true identify information, the network operator shall not provide him or her with relevant services. The state shall implement the strategy of credible identity in cyberspace, support the research and development of safe and convenient technologies for electronic identity authentication, and promote mutual recognition among different electronic identity authentication technologies.
第二十四條網絡運營者為用戶辦理網絡接入、域名註冊服務,辦理固定電話、移動電話等入網手續,或者為用戶提供信息發布、即時通訊等服務,在與用戶簽訂協議或者確認提供服務時,應當要求用戶提供真實身份信息。用戶不提供真實身份信息的,網絡運營者不得為其提供相關服務。國家實施網絡可信身份戰略,支持研究開發安全、方便的電子身份認證技術,推動不同電子身份認證之間的互認。
Article 25 Network operators shall make emergency response plans for cybersecurity incidents, and deal with system bugs, computer viruses, network attack, network intrusion and other security risks in a timely manner. When any incident endangering cybersecurity occurs, the relevant operator shall immediately initiate the emergency response plan, take corresponding remedial measures, and report it to the competent department in accordance with relevant provisions.
第二十五條網絡運營者應當制定網絡安全事件應急預案,及時處置系統漏洞、計算機病毒、網絡攻擊、網絡侵入等安全風險;在發生危害網絡安全的事件時,立即啟動應急預案,採取相應的補救措施,並按照規定向有關主管部門報告。
Article 26 Such activities as cybersecurity authentication, detection and risk assessment shall be conducted, and cybersecurity information on system bugs, computer viruses, network attack, and network intrusion, among others, shall be released to the public in accordance with relevant provisions of the state.
第二十六條 開展網絡安全認證、檢測、風險評估等活動,向社會發布系統漏洞、計算機病毒、網絡攻擊、網絡侵入等網絡安全信息,應當遵守國家有關規定。
Article 27 No individual or organization may conduct any activity endangering cybersecurity, such as illegally intruding into any other person’s network, interfering with the normal functions of any other person’s network, and stealing network data, or provide programs or tools specifically used for conducting activities endangering cybersecurity, such as network intrusion, interference with normal functions and protective measures of the network, and stealing of network data. Whoever knows that any other person conducts any activity endangering cybersecurity shall not provide technical support, advertising promotion,payment and settlement services or any other assistance to such a person.
第二十七條任何個人和組織不得從事非法侵入他人網絡、干擾他人網絡正常功能、竊取網絡數據等危害網絡安全的活動;不得提供專門用於從事侵入網絡、干擾網絡正常功能及防護措施、竊取網絡數據等危害網絡安全活動的程序、工具;明知他人從事危害網絡安全的活動的,不得為其提供技術支持、廣告推廣、支付結算等幫助。