Preface: What is an example of autonomous AI?
Autonomous intelligence is artificial intelligence (AI) that can act without human intervention, input, or direct supervision. It’s considered the most advanced type of artificial intelligence. Examples may include smart manufacturing robots, self-driving cars, or care robots for the elderly.
Background: What is Jetson AGX Xavier used for?
As the world’s first computer designed specifically for autonomous machines, Jetson AGX Xavier has the performance to handle the visual odometry, sensor fusion, localization and mapping, obstacle detection, and path-planning algorithms that are critical to next-generation robots.
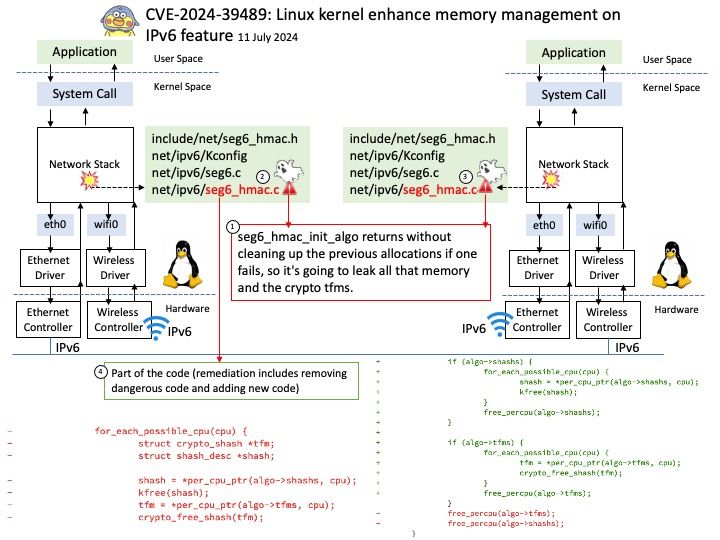
Vulnerability details: NVIDIA Jetson Linux contains a vulnerability in NvGPU where error handling paths in GPU MMU mapping code fail to clean up a failed mapping attempt. A successful exploit of this vulnerability may lead to denial of service, code execution, and escalation of privileges.
Official announcement: Please refer to the official announcement for details – https://nvidia.custhelp.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/5555