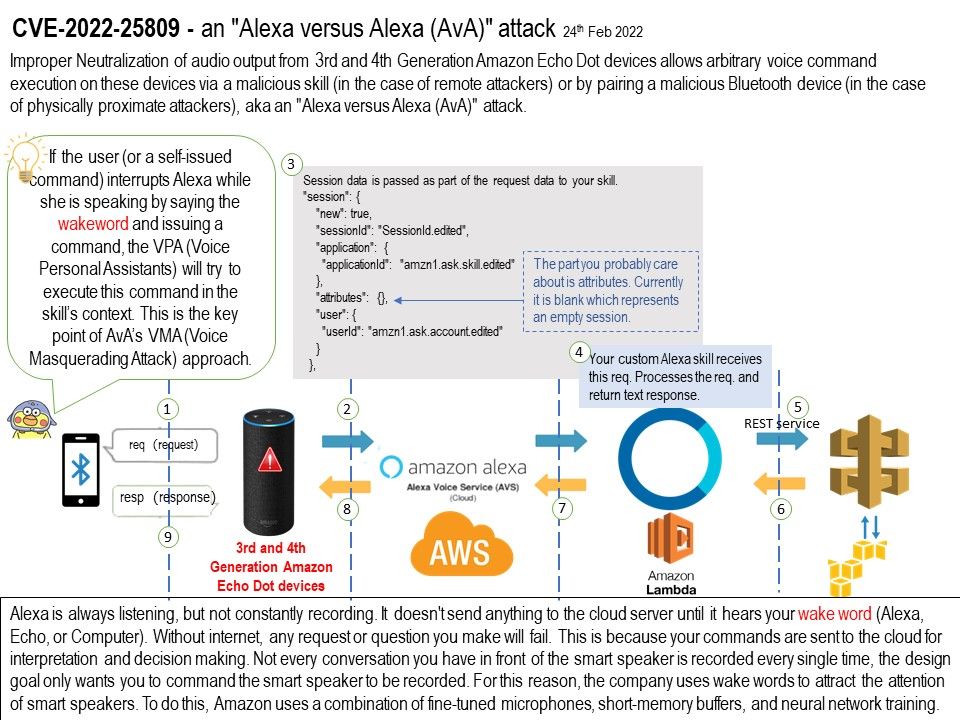
.jpg?width=1920&height=1080&fit=bounds)
Preface: The registration of CVE records is largely out of sync with the time of the event. Perhaps the new release of CVE record by today, however it was happened few weeks or months ago. But with reference of these vulnerabilities records. Vulnerability scanner can precisely provide a result to you after scan.
Background: Generally, suppliers have the right to keep design defect information from being released to the public. This CVE record was publicly released on March 9, 2022. But if you try to look in the local Windows directory (c:\windows\system32). You found that at least two of the[ .] dlls have been updated. They are hal[.]dll and ci[.]dll. Both files are closely related to ntoskrnl[.]exe. My guess is more based on this design limitation of ci[.]dll .
Ci[.] dll runs a feature that validates the integrity of a system file or drive whenever it is loaded into memory. This is an important Windows component and should not be removed. The Microsoft Windows operating system exhibits a graphical user interface and made its first appearance in November, 1985.
Virtual Secure Mode (VSM) has to be enabled in a special policy in the Group Policy Editor (gpedit[. ]msc): Computer Configuration -> Administrative templates -> System -> Device Guard -> Turn on Virtualization Based Security. Enable this policy and select Secure Boot option in Select Platform security level.
Vulnerability details: Certain versions of Windows from Microsoft contain the following vulnerability: Windows NT OS Kernel Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability.
Official announcement – https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/vulnerability/CVE-2022-23298

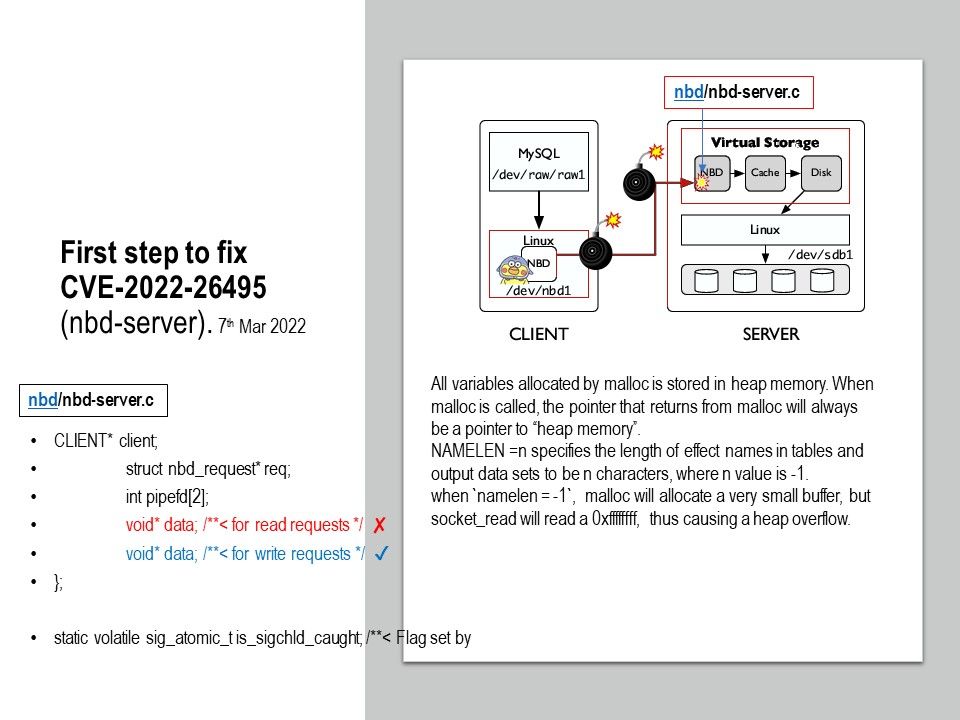

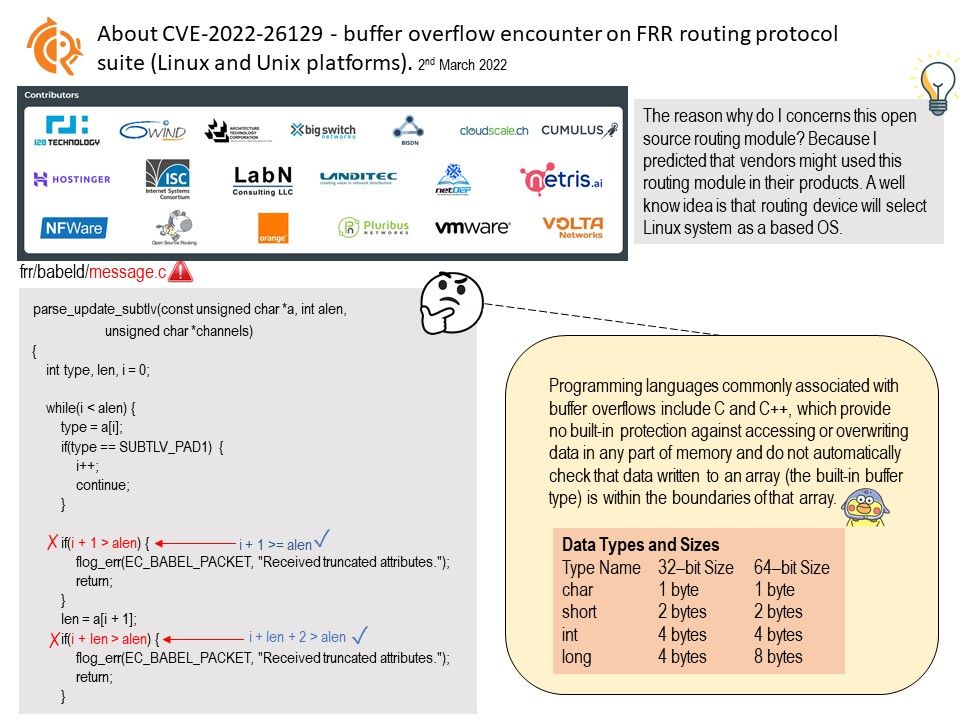
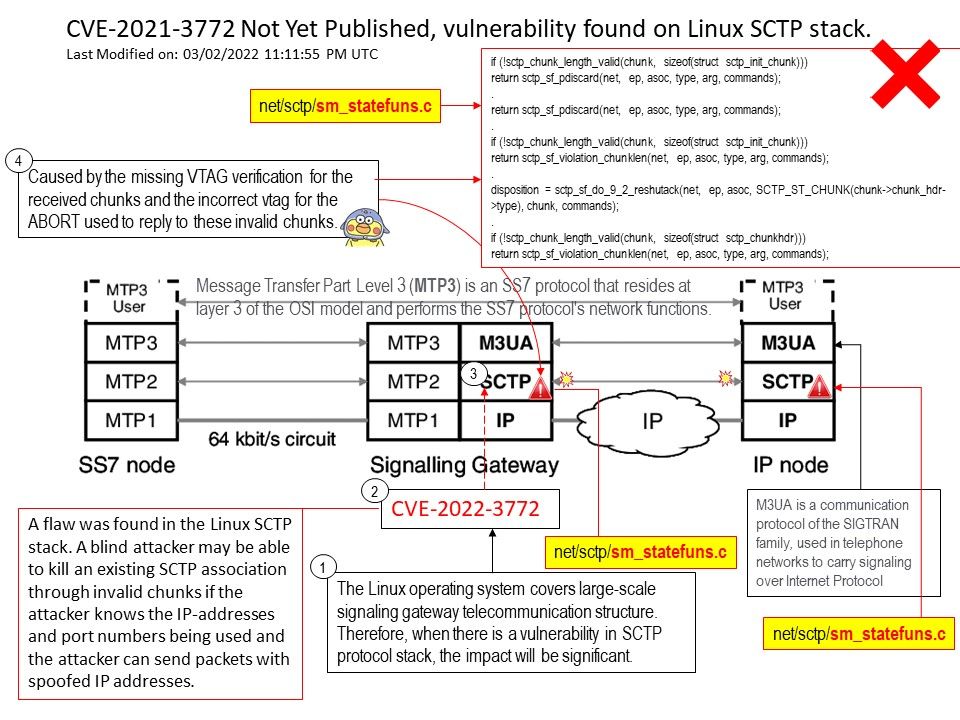
.jpg?width=1920&height=1080&fit=bounds)

.jpg?width=1920&height=1080&fit=bounds)