Preface: SCTP is used mostly in the telecom area. Traditionally, telecom switches use SS7 (Signaling System No. 7) to interconnect different entities in the telecom network.
From technical point of view, IP network is open and not reliable. This is why SCTP was developed.
SCTP design objective:
- Emulate the advantages of the SS7 network accumulated over the decades.
- Create a connection-oriented protocol better than TCP in speed, security, and redundancy.
Background: SCTP is a message oriented, reliable transport protocol with direct support for multihoming that runs on top of ip(7), and supports both v4 and v6 versions. Like TCP, SCTP provides reliable, connection oriented data delivery with congestion control.Unlike TCP, SCTP also provides message boundary preservation, ordered and unordered message delivery, multi-streaming and multi-homing.
Stream Control Transmission Protocol over User Datagram Protocol (SCTP over UDP, also known as UDP encapsulation of SCTP) is a feature defined in RFC6951 and implemented in the Linux kernel space since 5.11. 0. It is planned to be supported by Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 8.5. 0 and 9.0.
SCTP is a reliable message-oriented protocol. It preserves the message boundaries, and at the same time, detects lost data, duplicate data, and out-of-order data. It also has congestion control and flows control mechanisms.
About the SCTP sender’s port number. It can be used by the receiver in combination with the source IP address, the SCTP destination port and possibly the destination IP address to identify the association to which this packet belongs. The port number 0 MUST NOT be used. Destination Port Number is 16 bits (unsigned integer).This is the SCTP port number to which this packet is destined.
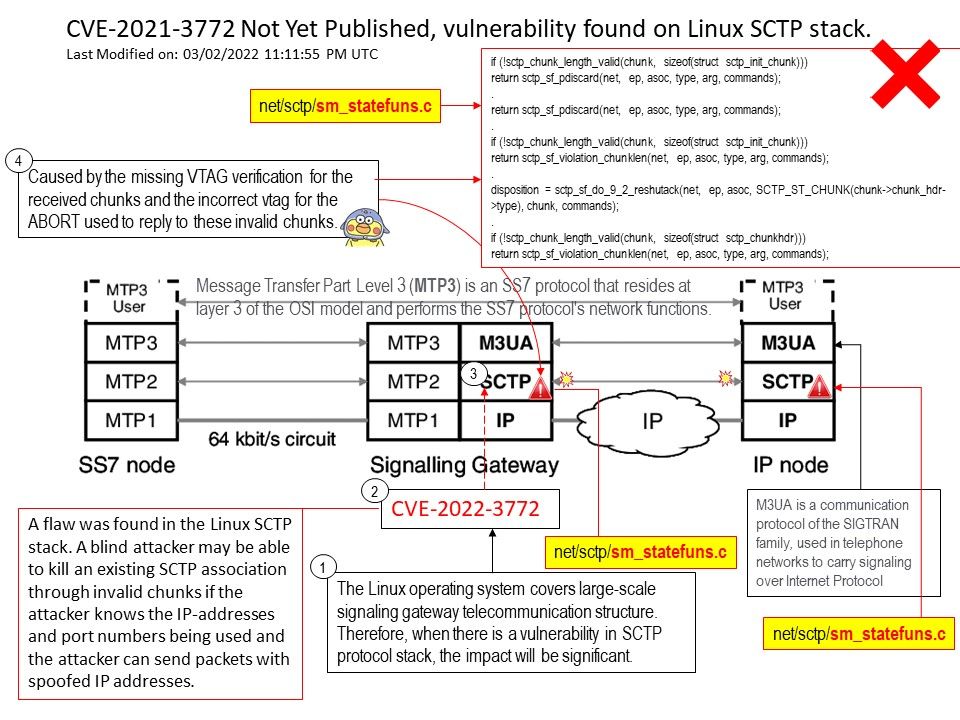
Vulnerability details: A flaw was found in the Linux SCTP stack. A blind attacker may be able to kill an existing SCTP association through invalid chunks if the attacker knows the IP-addresses and port numbers being used and the attacker can send packets with spoofed IP addresses.
Remedy:
- Make sure sctp_vtag_verify() is called firstly to verify the vtag from the received chunk and discard this – chunk if it fails.
- Always use the vtag from the received INIT chunk to make the response ABORT in sctp_ootb_pkt_new().
- Fix the order for some checks and add some missing checks for the received chunk.
Official announcement (From the Ubuntu security team) – For more details, please refer to the link – https://ubuntu.com/security/CVE-2021-3772