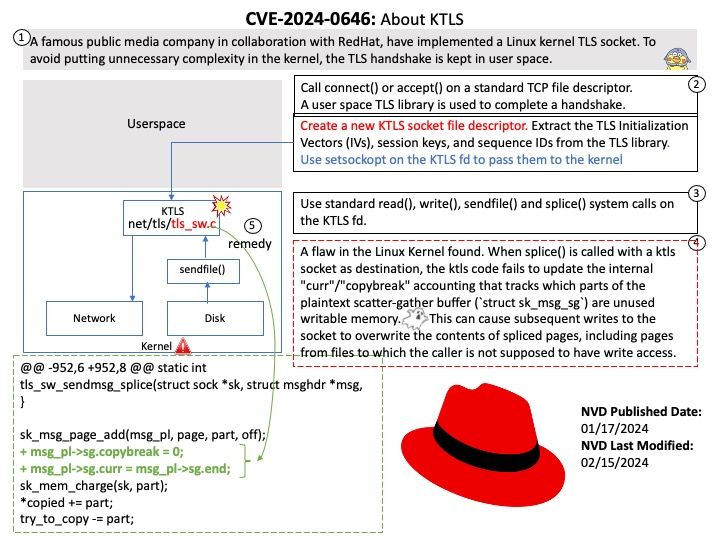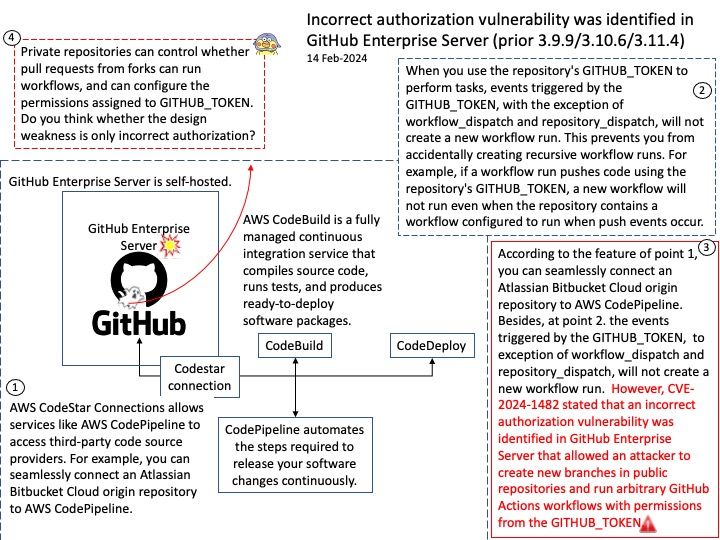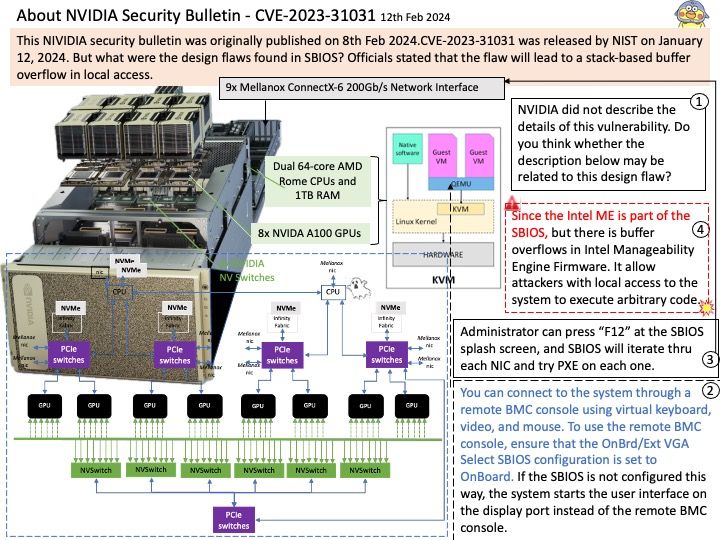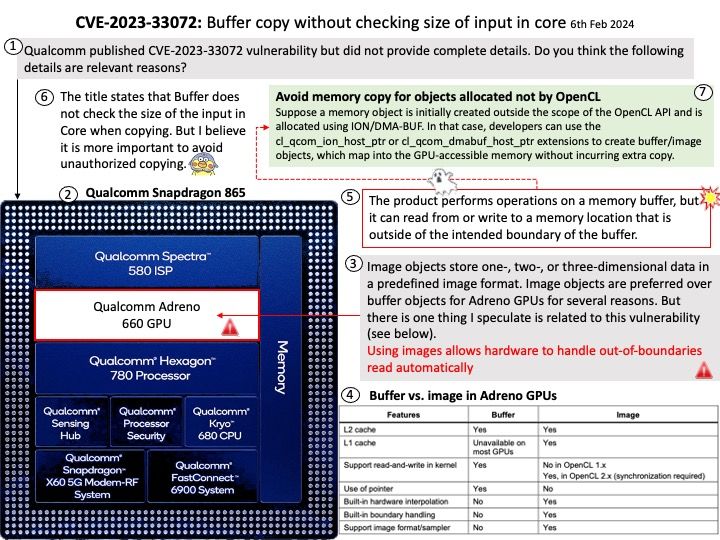
This announcement original published on 20th Feb 2024
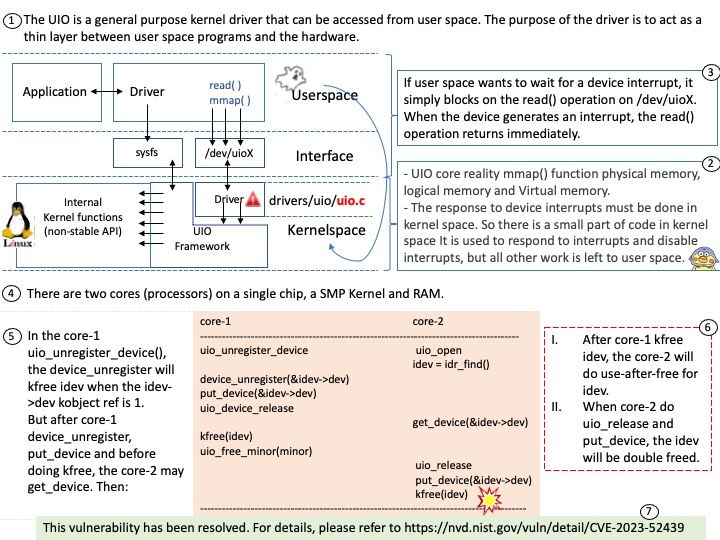
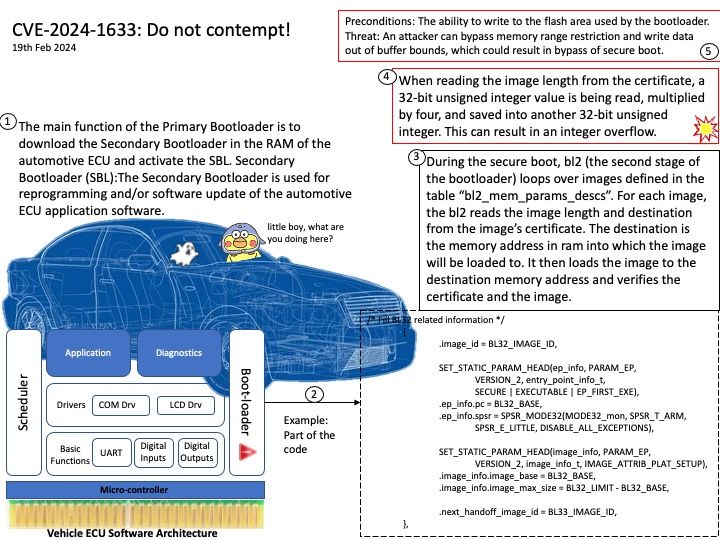
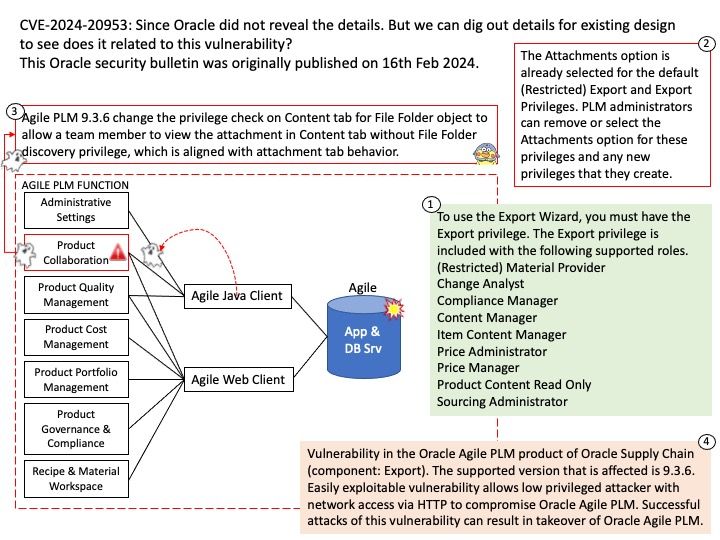
Preface: When two components have problems in the same place. If vendor did not specify the details in clear. In this circumstances, the design weakness looks the same.
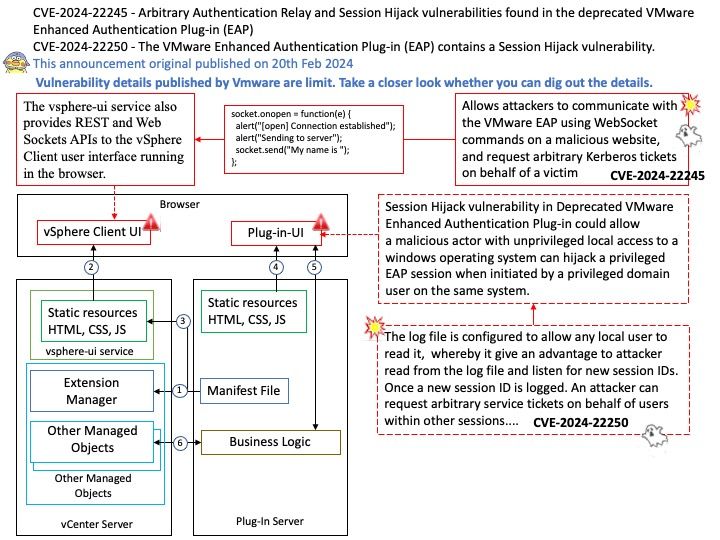
Background: The Enhanced Authentication Plugin (EAP) is an extra software package that doesn’t come pre-installed. Administrators need to install it on client computers used for administration to allow direct login when using the VMware vSphere Client through a web browser.
The VMware EAP is a deprecated browser plugin that enables seamless single sign-on (SSO) to vSphere’s management interface from client workstations. It is an optional feature that stopped receiving support with the release of VMware vCenter Server 7.0.0u2 in March 2021.
Vulnerability details:
Session Hijack Vulnerability in Deprecated EAP Browser Plugin (CVE-2024-22250) – The VMware Enhanced Authentication Plug-in (EAP) contains a Session Hijack vulnerability. VMware has evaluated the severity of this issue to be in the Important severity range with a maximum CVSSv3 base score of 7.8.
Arbitrary Authentication Relay Vulnerability in Deprecated EAP Browser Plugin (CVE-2024-22245) – The VMware Enhanced Authentication Plug-in (EAP) contains an Arbitrary Authentication Relay vulnerability. VMware has evaluated the severity of this issue to be in the Critical severity range with a maximum CVSSv3 base score of 9.6.
Official announcement: Please refer to the link for details – https://www.vmware.com/security/advisories/VMSA-2024-0003.html