Preface: NetScaler was initially developed in 1997 by Michel K Susai and acquired by Citrix Systems in 2005. What is the difference between NetScaler ADC and NetScaler gateway? NetScaler ADC is an application delivery controller. NetScaler Gateway (formerly Citrix Gateway) is an access gateway with SSL VPN solution, providing single sign-on (SSO) and authentication for remote end users of network assets.
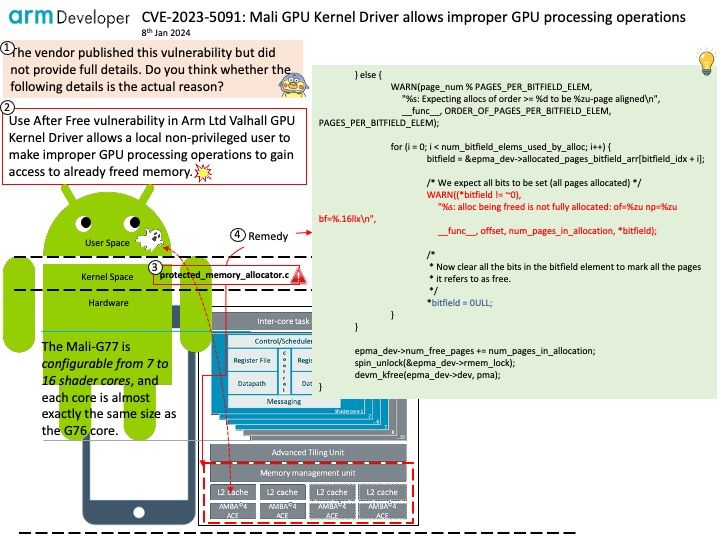
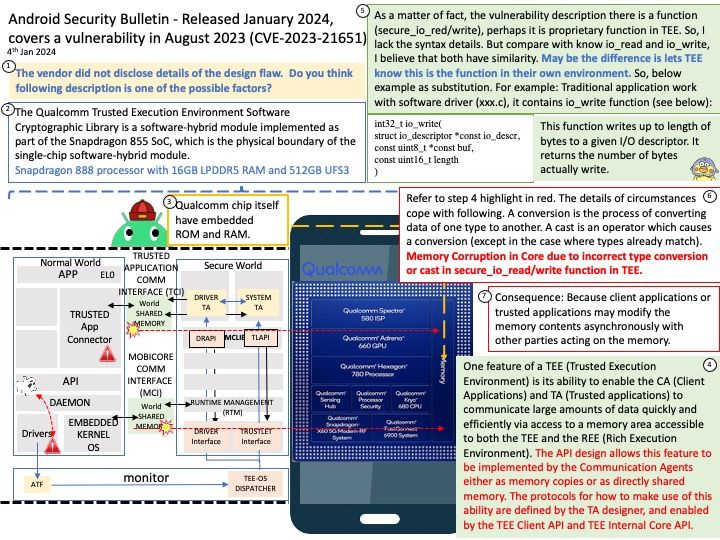
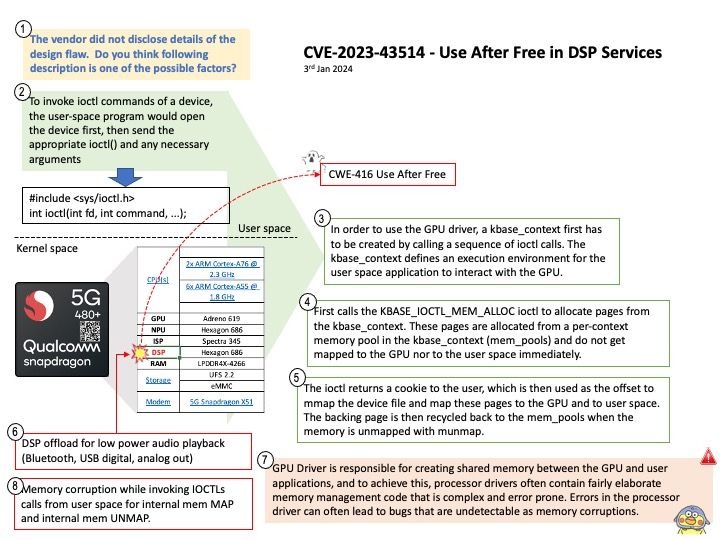
Background: A cross-site scripting (XSS) attack is a type of injection attack in which malicious script is injected into an otherwise benign and trusted website. The risk of XSS comes from the ability to execute arbitrary JS within the current user context.
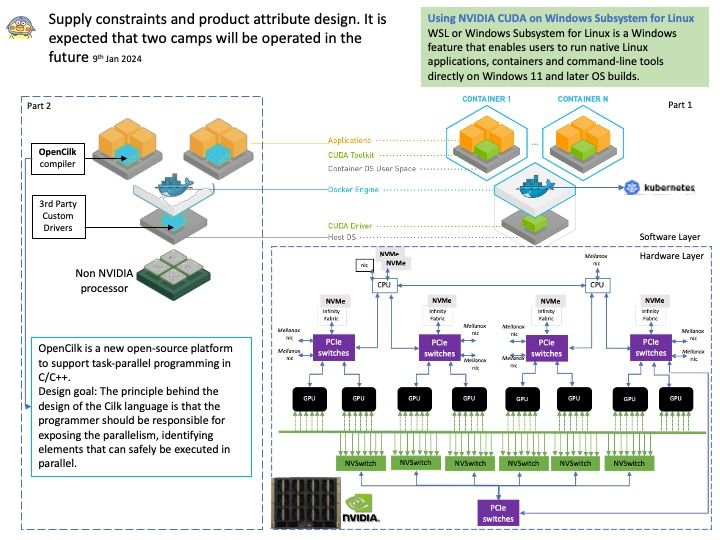
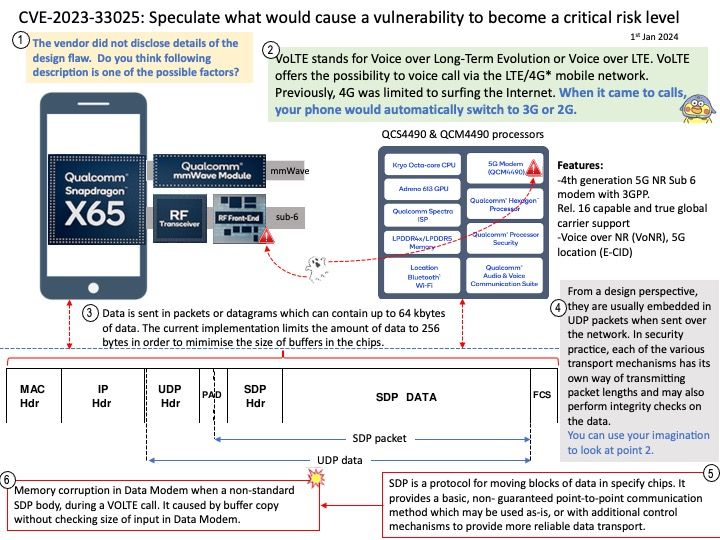
UDP is common, but it has inherent vulnerabilities that make it prone to attacks, such as limited packet verification, IP spoofing and DoS attacks.
Ref:
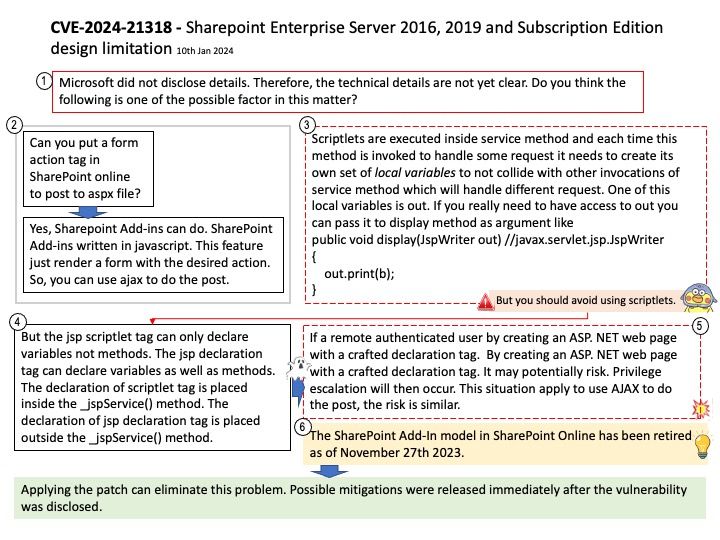
#NSIP address – The management IP address for NetScaler Gateway that is used for all management‑related access to the appliance. NetScaler Gateway also uses the NSIP address for authentication
#Subnet IP (SNIP) address – The IP address that represents the user device by communicating with a server on a secondary network
#Cluster management IP (CLIP) address
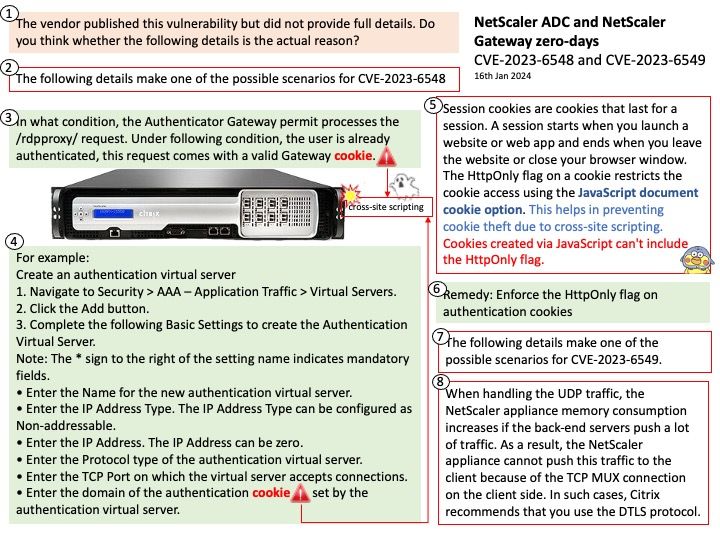
Vulnerability details:
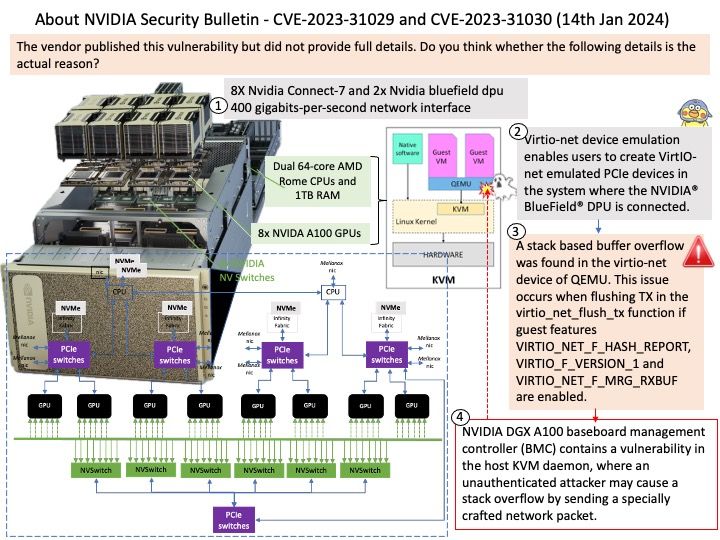
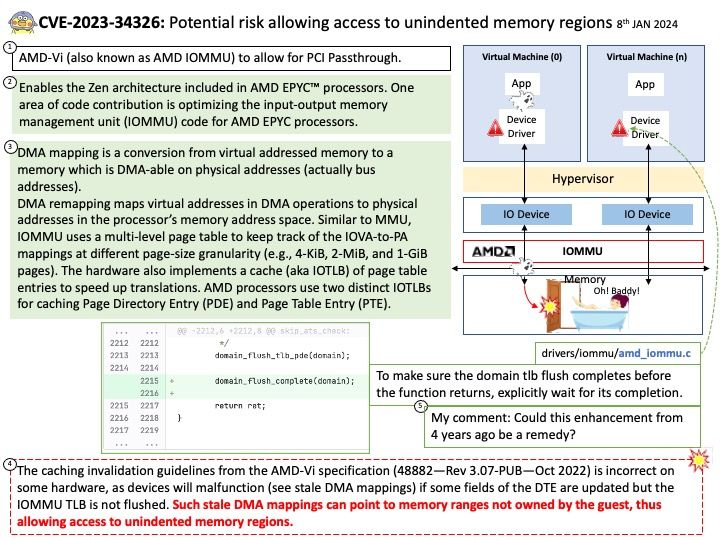
CVE-2023-6548 is a RCE vulnerability in the NetScaler ADC and Gateway appliances. An authenticated attacker with low level privileges could exploit this vulnerability if they are able to access NetScaler IP (NSIP), Subnet IP (SNIP), or cluster management IP (CLIP) with access to the appliance’s management interface.
CVE-2023-6549 is a denial of service (DoS) vulnerability in the NetScaler ADC and Gateway appliances. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability when a vulnerable appliance has been configured as a Gateway (e.g. VPN, ICA Proxy, CVPN, RDP Proxy) or as a AAA virtual server.
Official announcement: Please refer to the link for details – https://support.citrix.com/article/CTX584986/netscaler-adc-and-netscaler-gateway-security-bulletin-for-cve20236548-and-cve20236549