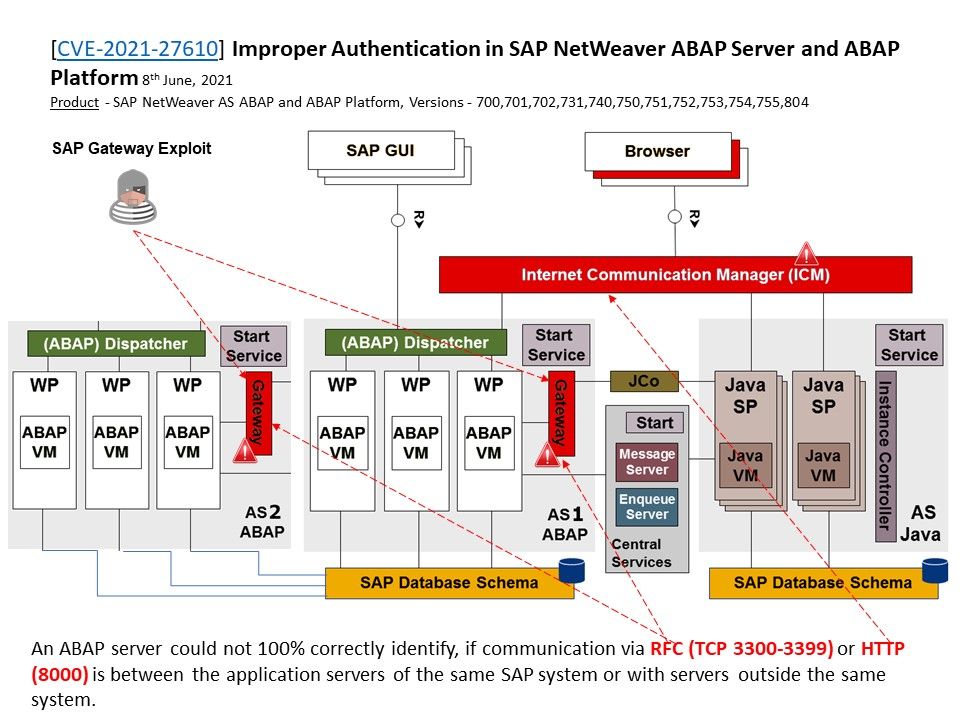
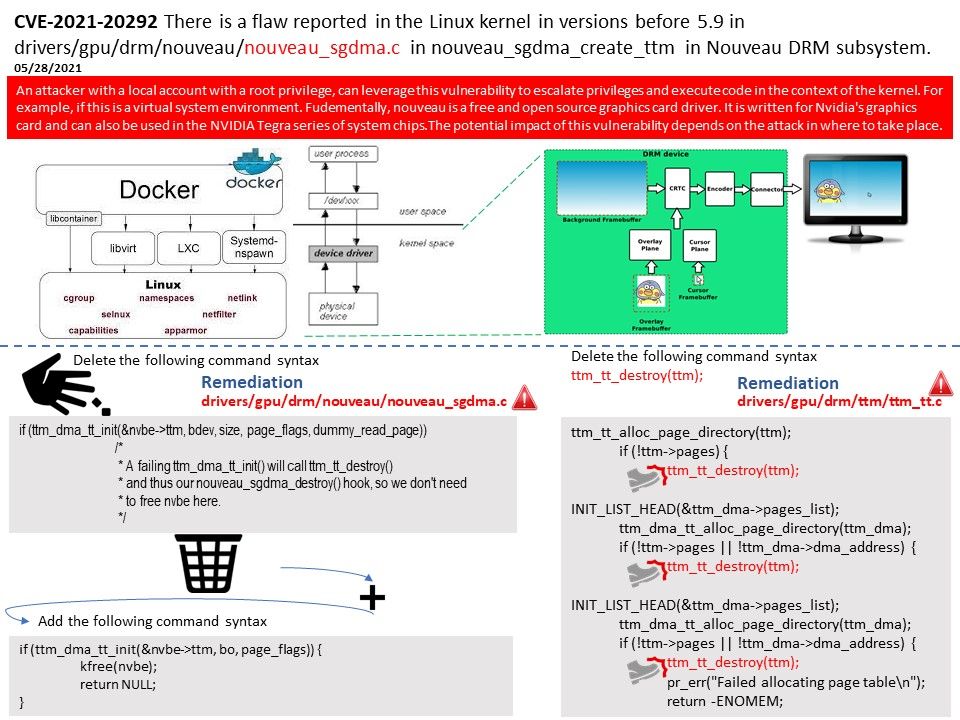
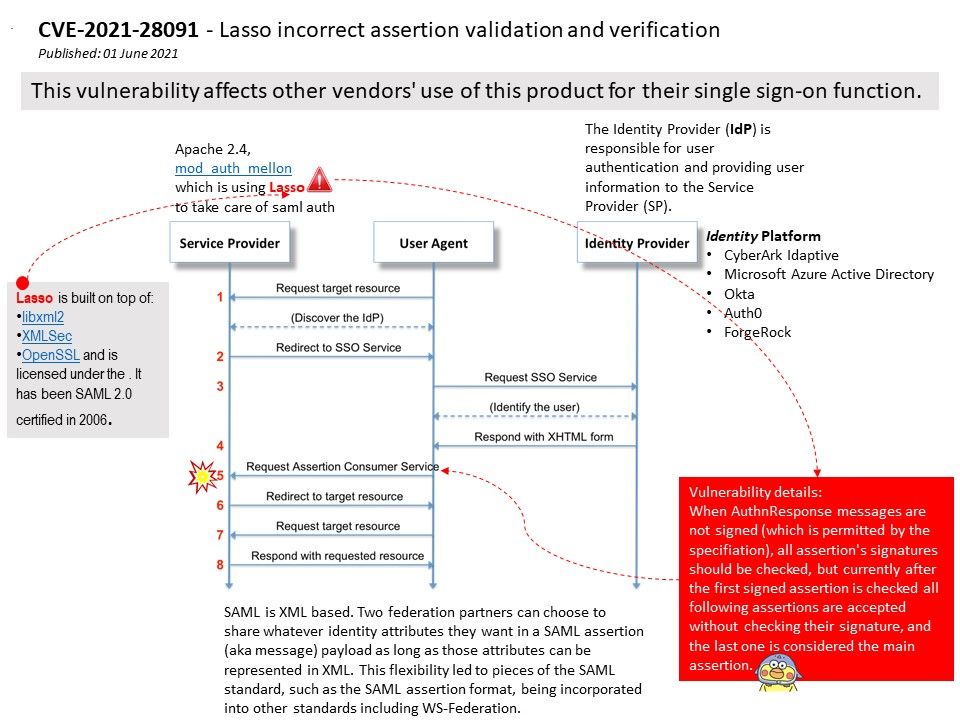
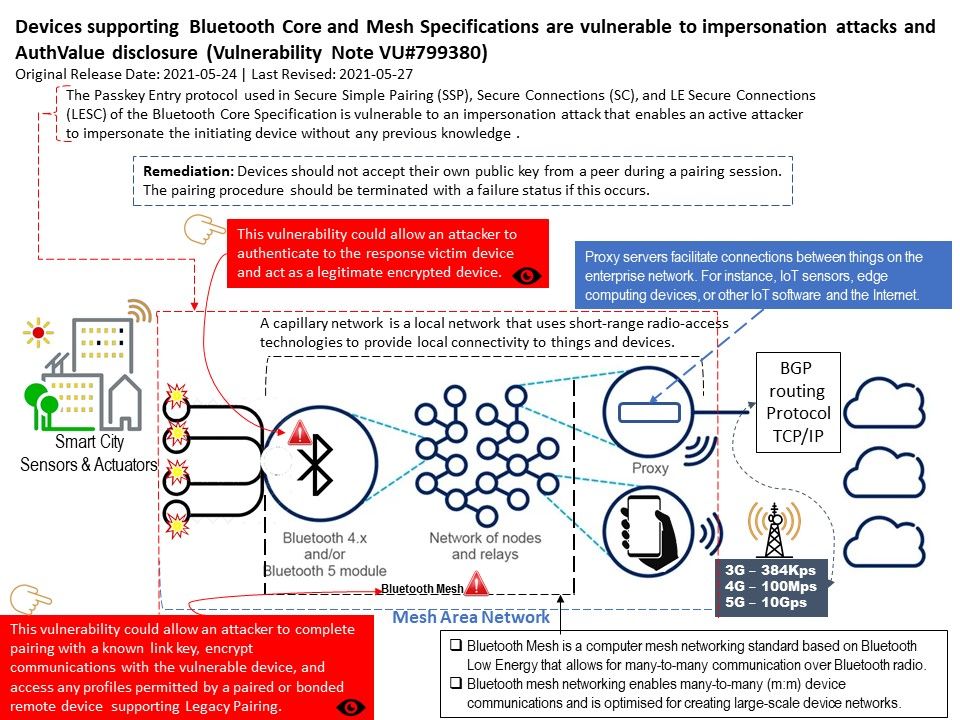
.jpg?width=1920&height=1080&fit=bounds)
Preface: When the TCP/IP network protocol replaces the classic MODBUS protocol on a large scale. At the same time, there is a large demand for the deployment of Windows operating system servers and workstations. From the perspective of cyber security, information technology and operational technology are the same.
Synopsis: On May (9th May 2021), 2017, the WannaCry ransomware attack show to the world of their power. They can easily halted the entire DHS medical service in England. Recently, Ransomware attack shuts down biggest U.S. gasoline pipeline.
Contingency plan focus: In fact, according to official recommendations, payment of ransom is not recommended. This is because even if you pay, there is no guarantee that your system and data will be 100% fully restored. Therefore, an effective backup solution combined with business contingency plans is the correct way to solve this problem. However, the service interruption caused by ransomware is different from the traditional disaster recovery concept. The traditional DR concept assuming hardware or software failure. But it can resume operation through hot standby or cold standby facilities.
A gap was found here: In fact, the contingency plan for ransomware attacks is slightly different from the traditional disaster recovery plan. Because traditional DR will replicate two equivalent functional sites for DR. However, if the DR site contains design weaknesses similar to the production site. Maybe your DR environmental risk level will increase! Because it is a ransomware attack.
CISA recommends based on this matter: https://www.cisa.gov/sites/default/files/publications/CISA_Fact_Sheet-Rising_Ransomware_Threat_to_OT_Assets_508C.pdf