Preface: The basic idea behind AIO is to allow a process to initiate a number of I/O operations without having to block or wait for any to complete.
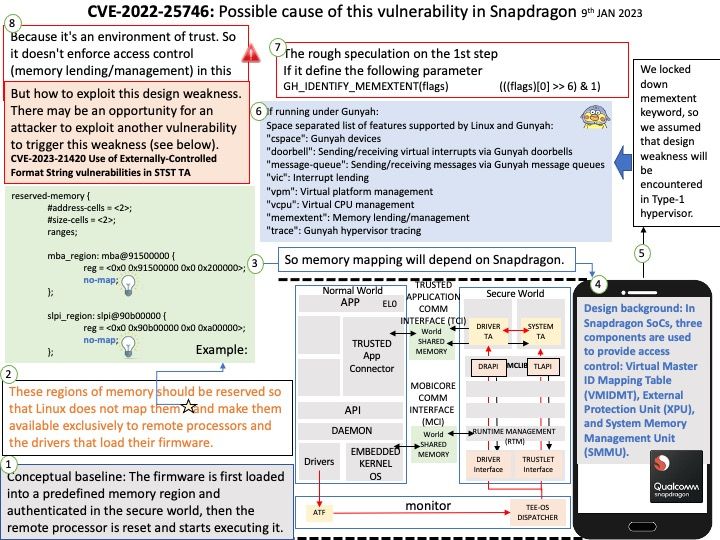
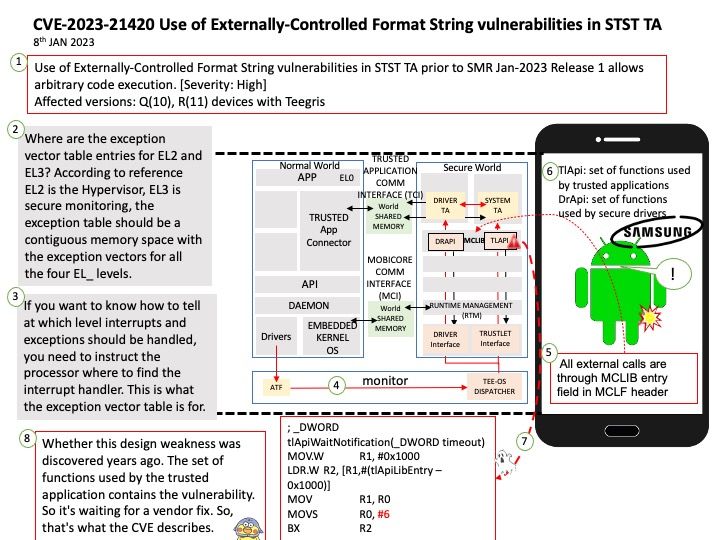
Background: System calls are how a program enters the kernel to perform some task. Programs use system calls to perform a variety of operations such as: creating processes, doing network , file IO,…etc.
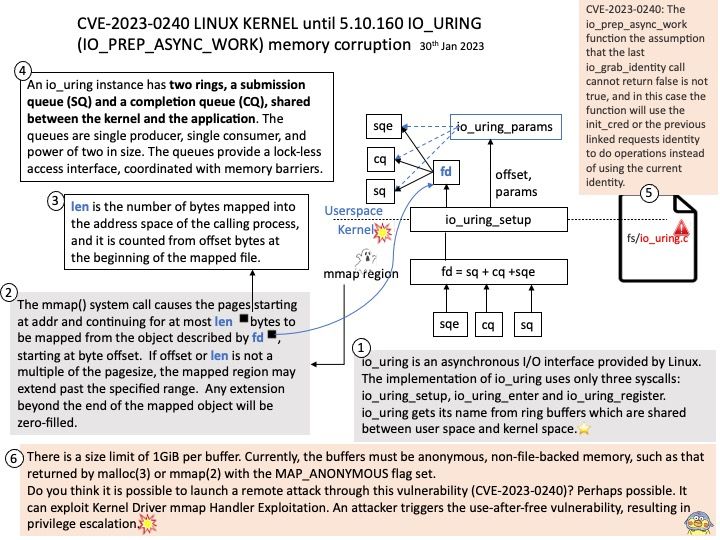
io_uring is an asynchronous I/O interface provided by Linux. The implementation of io_uring uses only three syscalls: io_uring_setup, io_uring_enter and io_uring_register.
io_uring gets its name from ring buffers which are shared between user space and kernel space.
There is a size limit of 1GiB per buffer. Currently, the buffers must be anonymous, non-file-backed memory, such as that returned by malloc(3) or mmap(2) with the MAP_ANONYMOUS flag set.
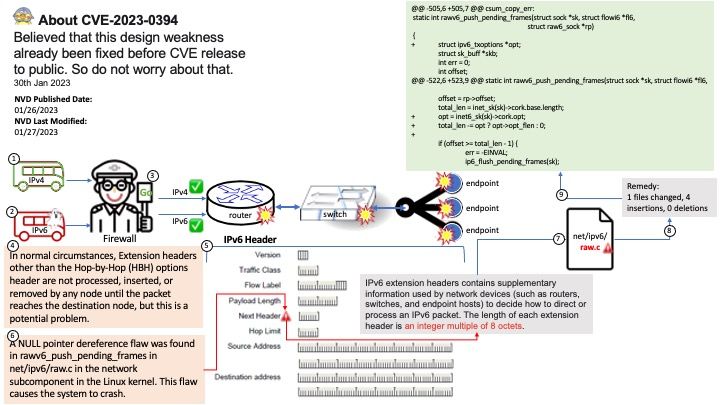
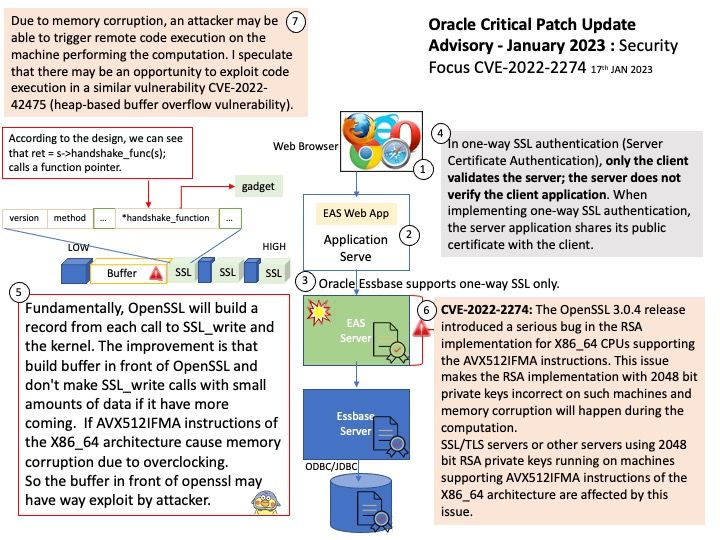
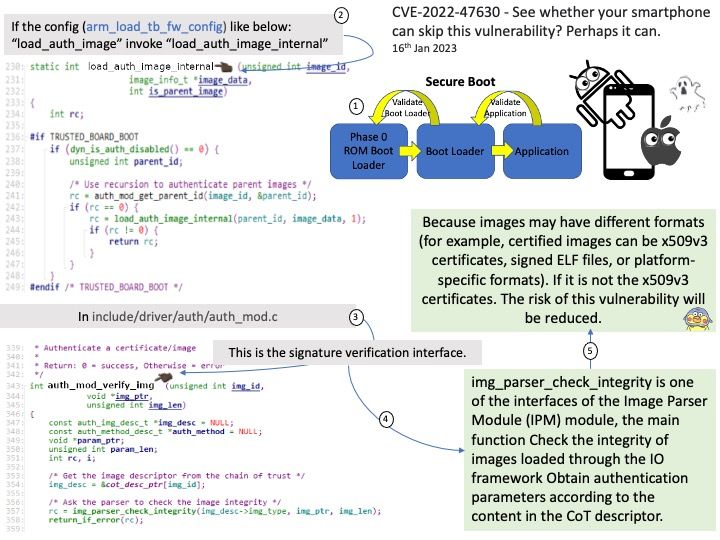
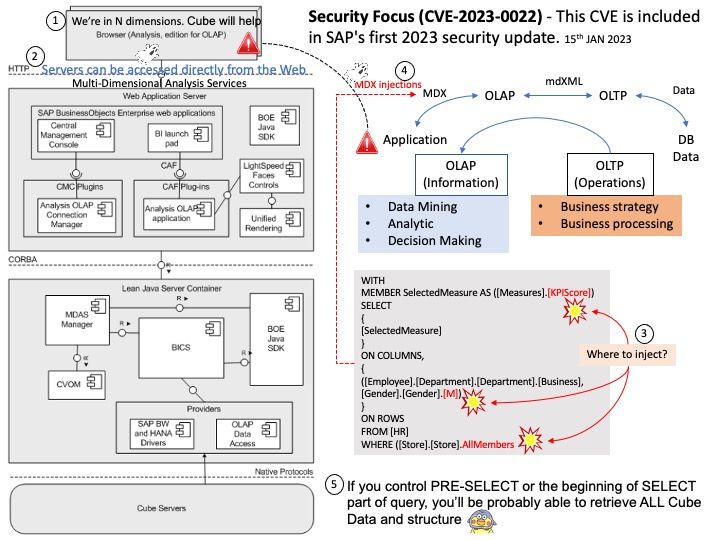
Do you think it is possible to launch a remote attack through this vulnerability (CVE-2023-0240)? Perhaps possible. It can exploit Kernel Driver mmap Handler Exploitation.
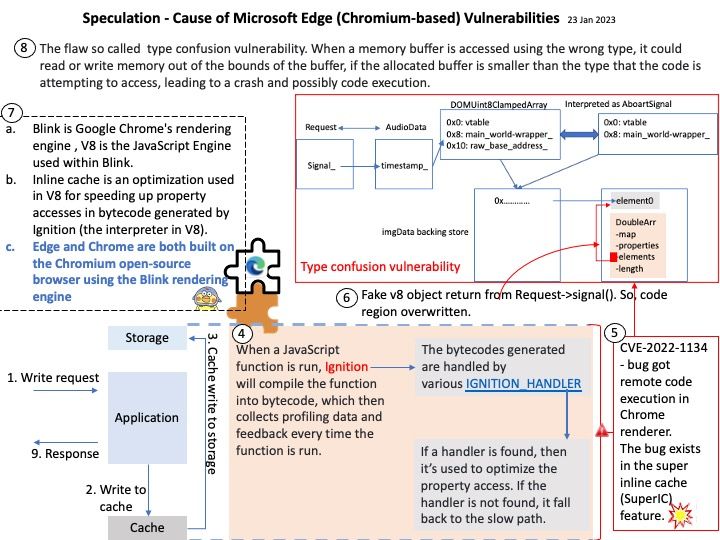
Ref: The use-after-free vulnerability exploits a mistake made by the original author of a software and can result in devastating effects that range from remote code execution to the leaking of sensitive data.
Vulnerability details: There is a logic error in io_uring’s implementation which can be used to trigger a use-after-free vulnerability leading to privilege escalation. In the io_prep_async_work function the assumption that the last io_grab_identity call cannot return false is not true, and in this case the function will use the init_cred or the previous linked requests identity to do operations instead of using the current identity. This can lead to reference counting issues causing use-after-free. We recommend upgrading past version 5.10.161.
Official announcement: For details, please refer to the URL – https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2023-0240

-10thJan2023.jpg)