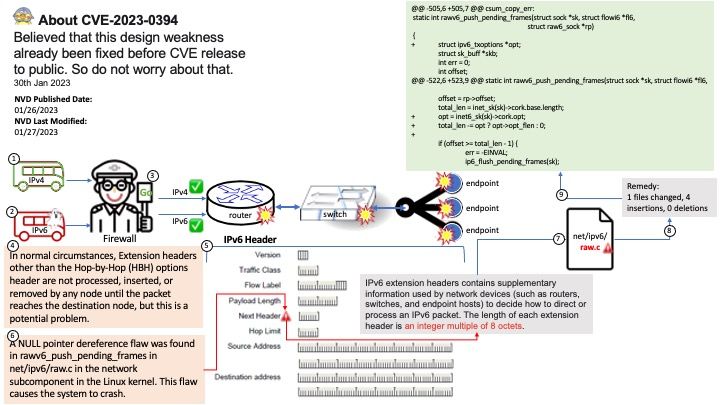
Preface: Believed that this design weakness already been fixed before CVE release to public. So do not worry about that.
To become secure, since a known Potential issues of IPv6 extension headers. Therefore , both stateful and stateless firewalls should do a deep inspection. Otherwise, it can do the evasion silently.
Background: From an early deployment aspect, IPv6 is seen as mandatory for specific 5G traffic flows, such as the 5G Control Plane (CP) and the 5G User Plane (UP). For the Management Plane (MP) and IPSec, IPv6 deployment in the early phase is not seen as mandatory but optional if available. But time will tell, IPv6 will have a major role to play in 5G, as IPv4 addresses, which are already in short supply, could never suffice the ever-growing connection demand further down the road.
IPv6 extension headers contains supplementary information used by network devices (such as routers, switches, and endpoint hosts) to decide how to direct or process an IPv6 packet. The length of each extension header is an integer multiple of 8 octets.
Vulnerability Details: A NULL pointer dereference flaw was found in rawv6_push_pending_frames in net/ipv6/raw.c in the network subcomponent in the Linux kernel. This flaw causes the system to crash.
Ref:In normal circumstances, Extension headers other than the Hop-by-Hop (HBH) options header are not processed, inserted, or removed by any node until the packet reaches the destination node, but this is a potential problem.
For the official announcement, please refer to the following URL: https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2023-0394