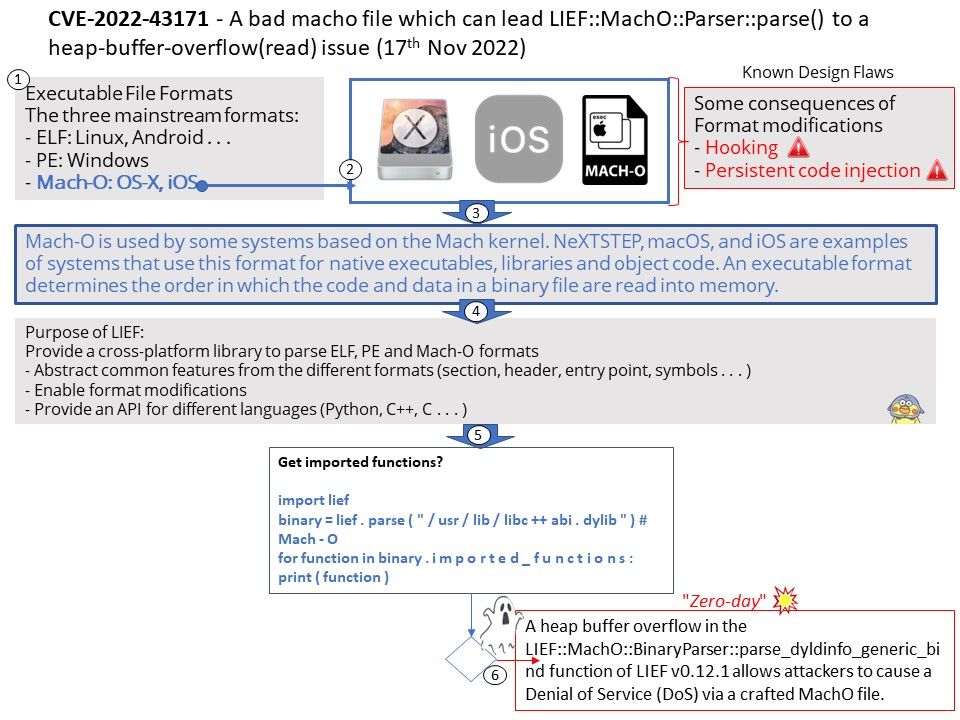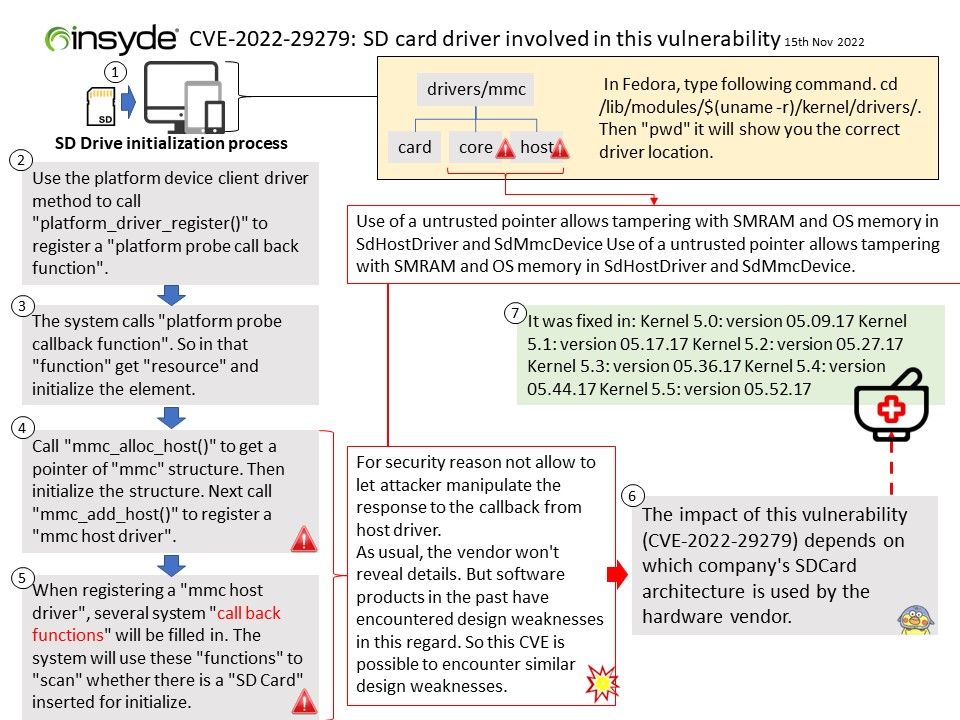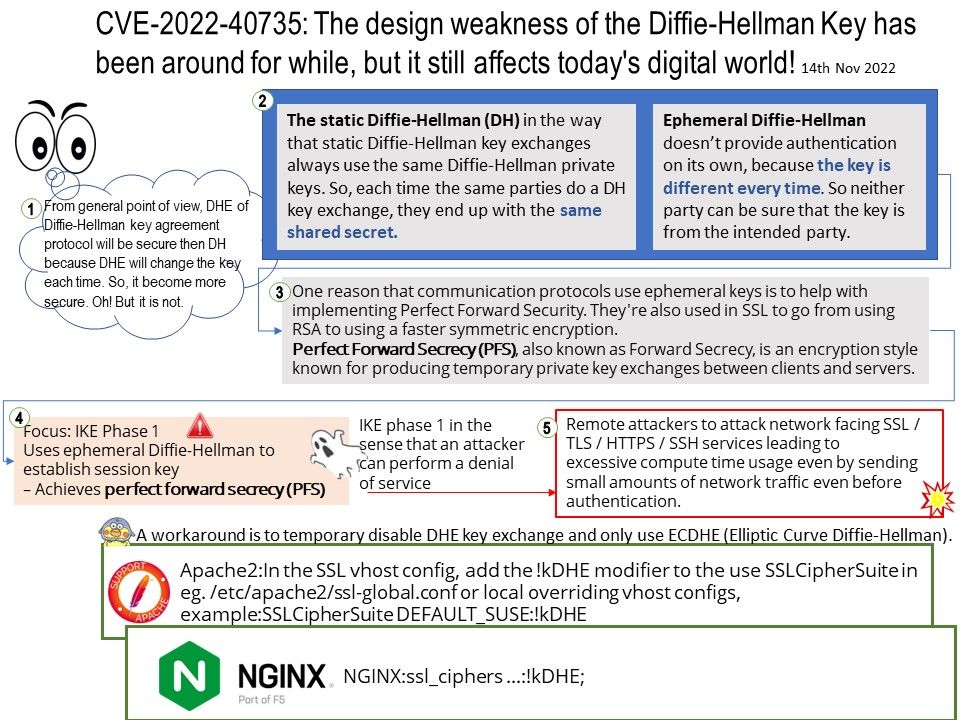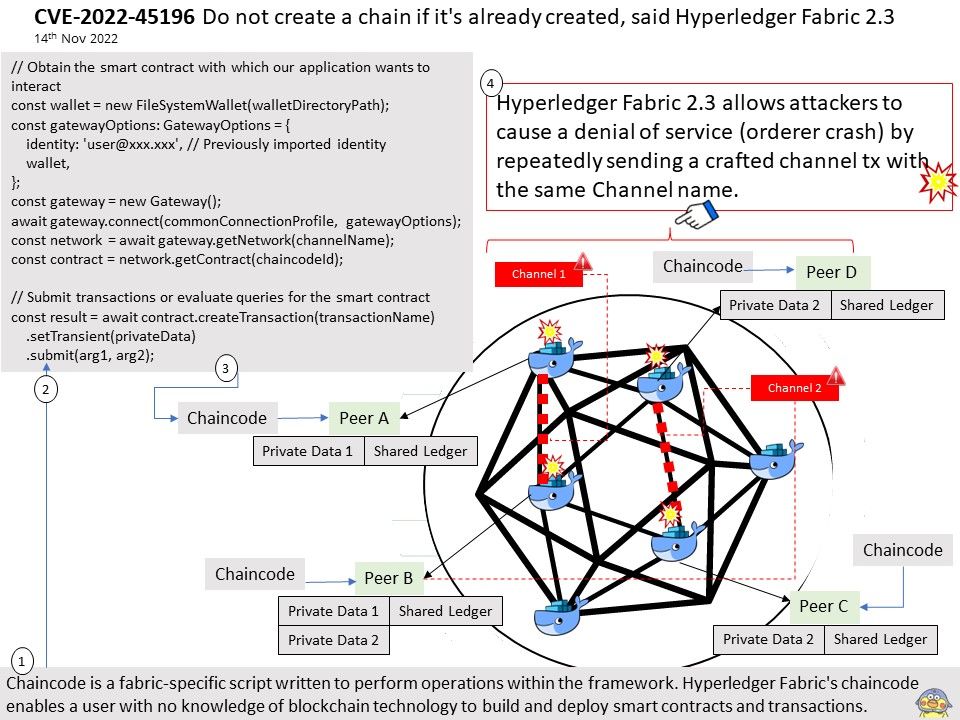
Preface: Different functional logics are encapsulated into different components/subsystems. From the perspective of the system level, gralloc belongs to the lowest HAL layer module and provides services for the upper-level libui and libgui libraries.
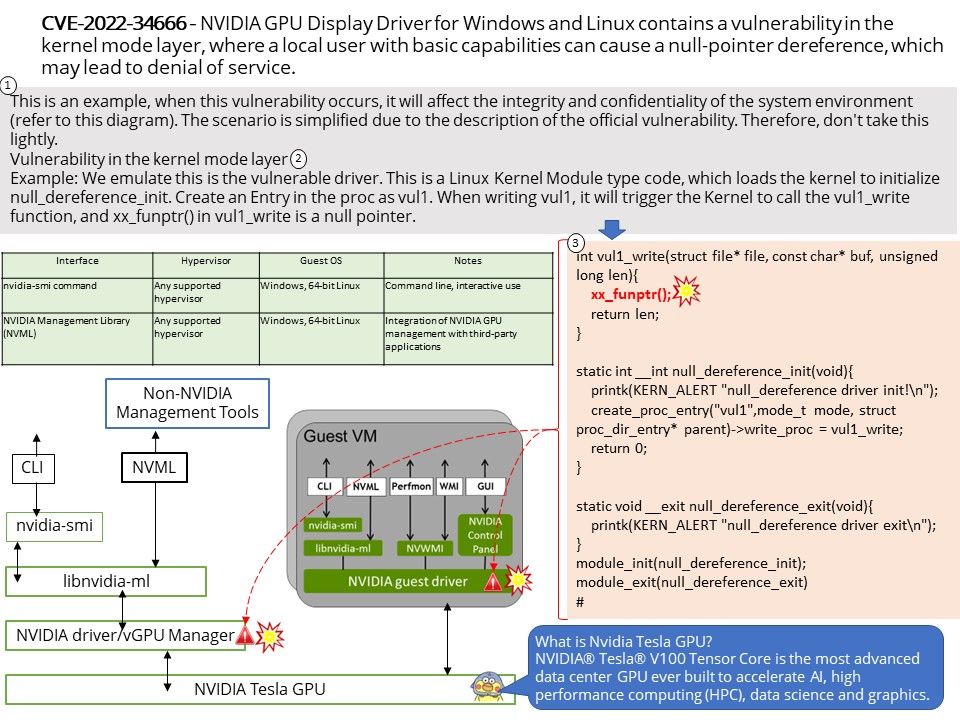
The Gralloc4Allocator in the libui library of the Android framework layer is used as a proxy and encapsulates its functions.
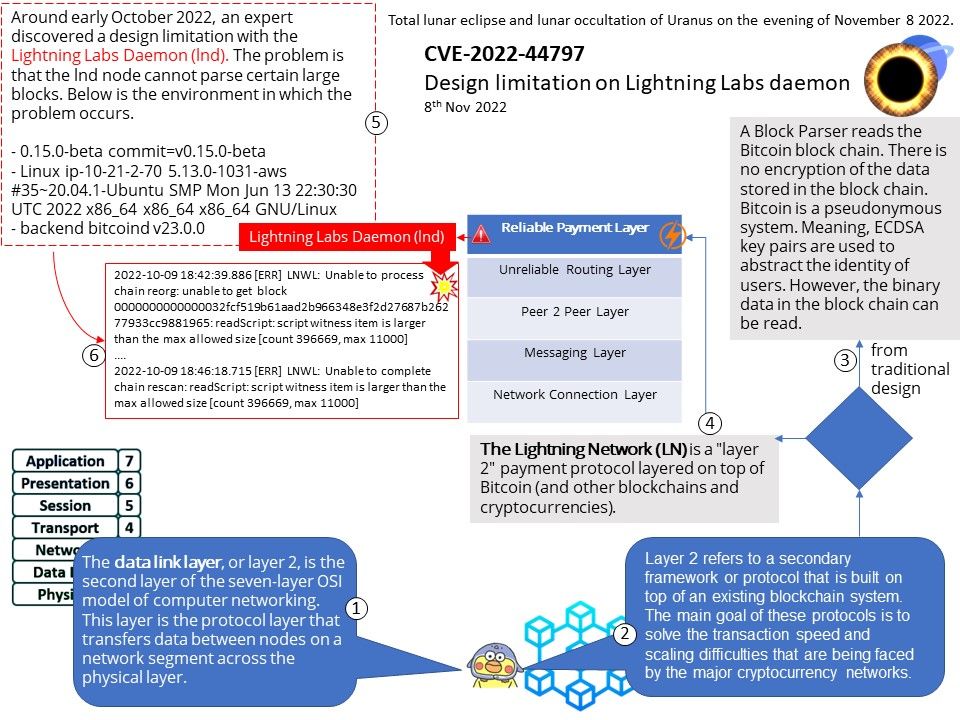
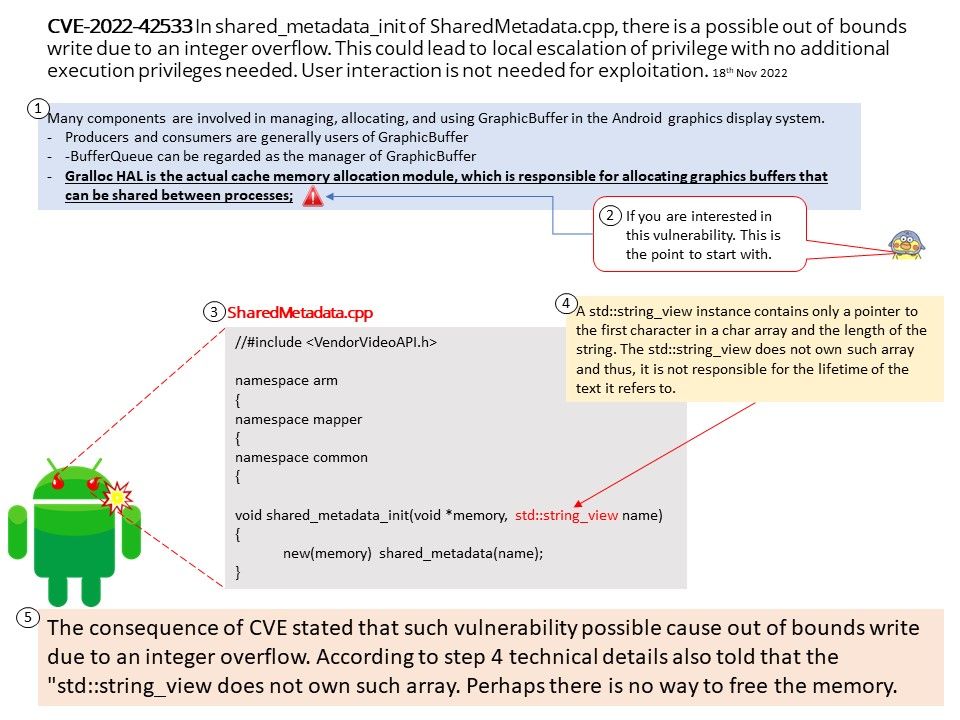
Background: Many components are involved in managing, allocating, and using GraphicBuffer in the Android graphics display system
- Producers and consumers are generally users of GraphicBuffer, either writing data or reading data;
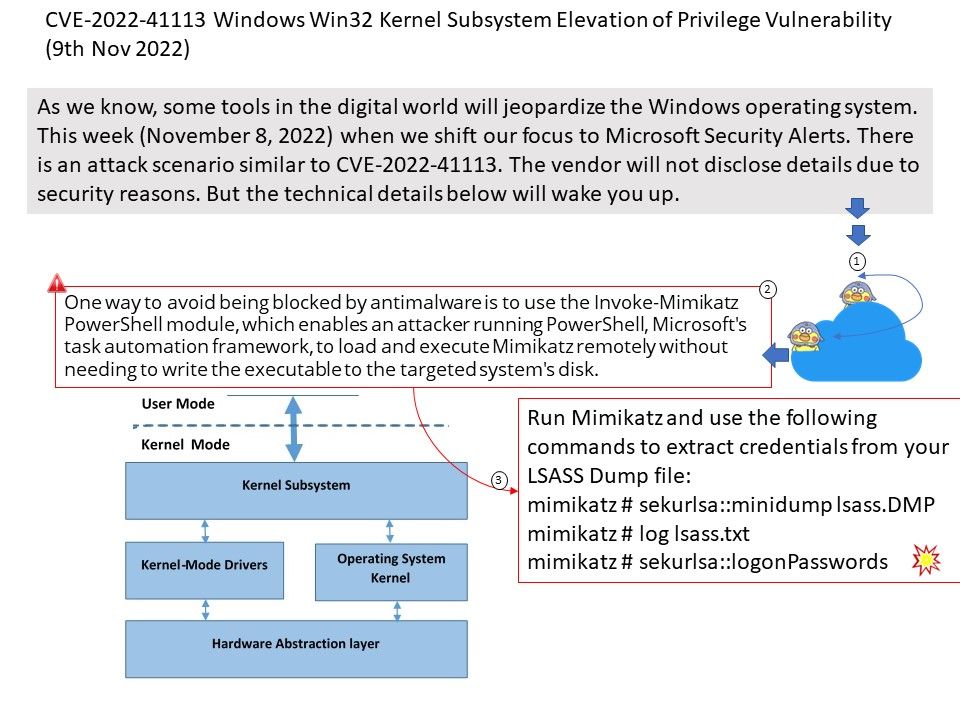
- BufferQueue can be regarded as the manager of GraphicBuffer, which handles requests from users in a unified way, so as to manage the allocation, release and transfer of GraphicBuffer in a unified way;
- Gralloc HAL is the actual cache memory allocation module, which is responsible for allocating graphics buffers that can be shared between processes.
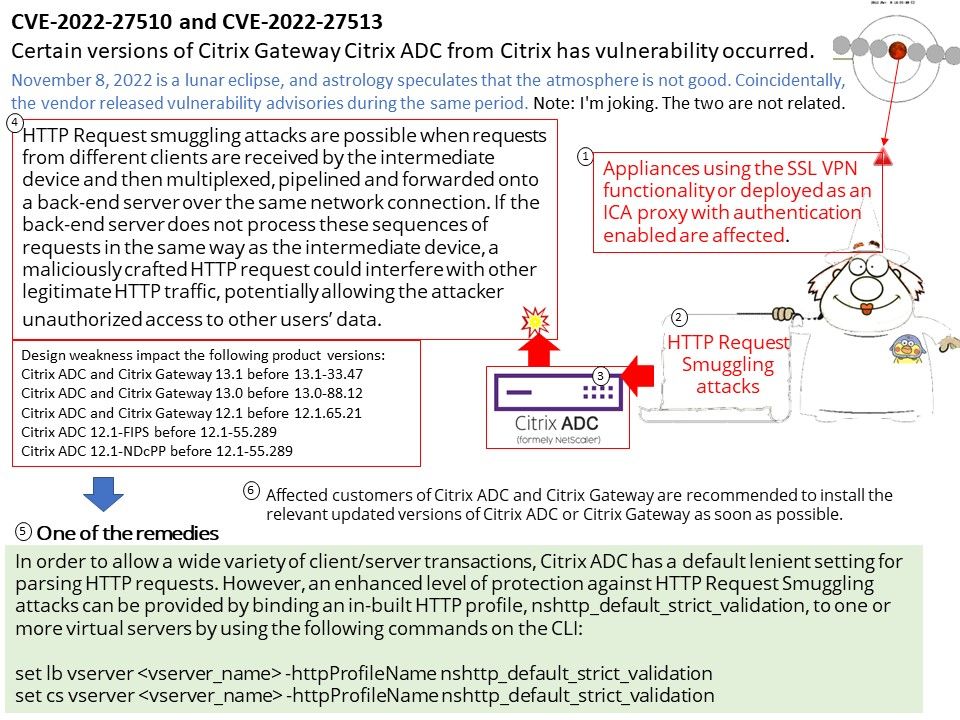
Vulnerability details: In shared_metadata_init of SharedMetadata[.]cpp, there is a possible out of bounds write due to an integer overflow. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation.
To read more about std::string_view, please refer to the link for details – https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/string/basic_string_view
Official announcement: Please refer to the link for details – https://source.android.com/docs/security/bulletin/pixel/2022-11-01