Preface: Microsoft has been a mainstay of the computer systems world for more than four decades. At the same time, it also promotes the development of the Internet and other technologies. About fifteen years ago, virtual machines led the way, bringing the concept into the business world and successfully fending off mainstream cybersecurity attacks. It seems that the computer system has quietly transformed into a virtual world. Maybe you will say because of cloud technology. The collaboration between network technology and cloud computing creates another potential opportunity for open source network software to jump into the competition.
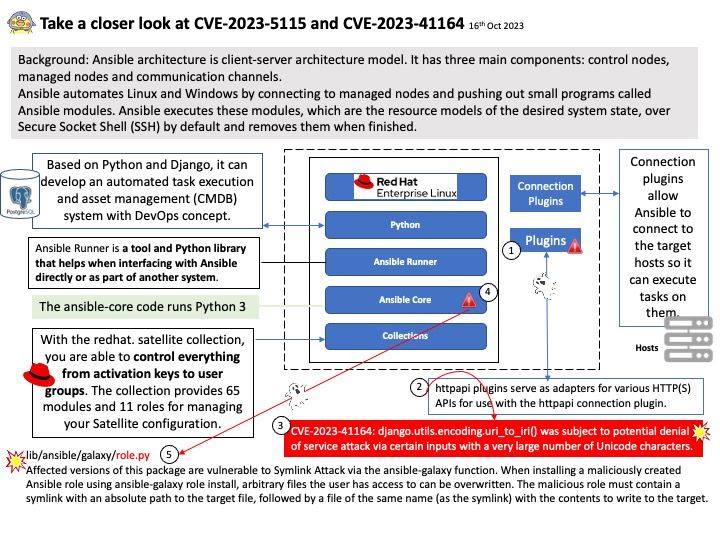
Background: FRRouting (FRR) is a free and open source Internet routing protocol suite for Linux and Unix platforms. It implements BGP, OSPF, RIP, IS-IS, PIM, LDP, BFD, Babel, PBR, OpenFabric and VRRP, with alpha support for EIGRP and NHRP.
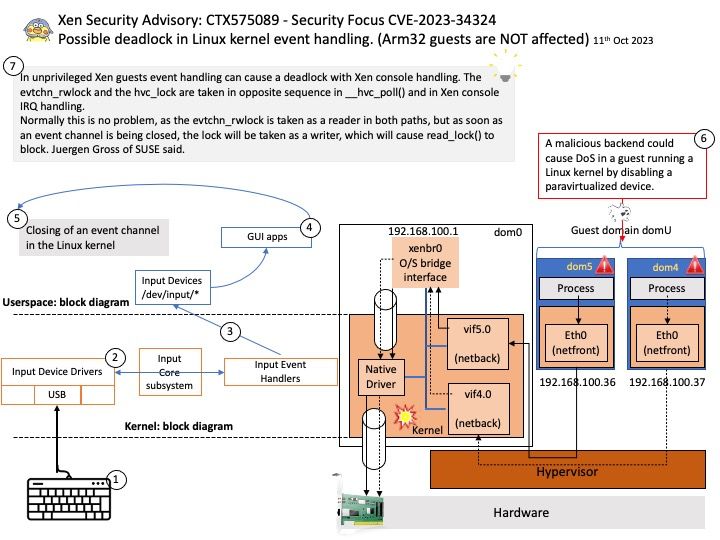
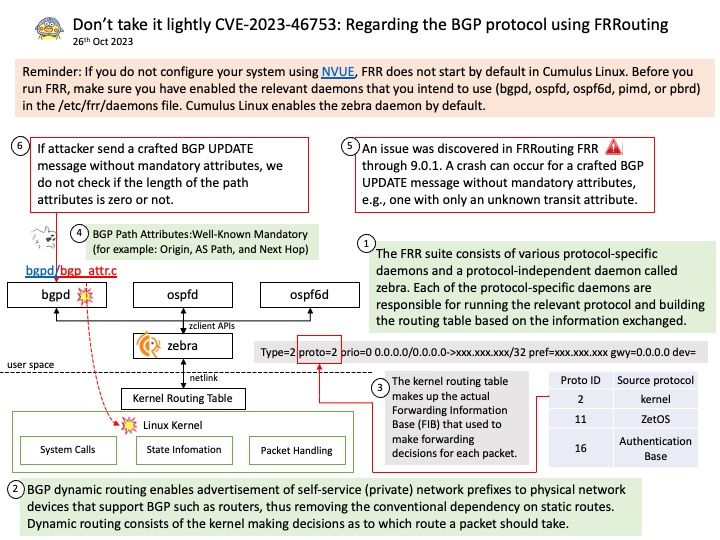
The FRR suite consists of various protocol-specific daemons and a protocol-independent daemon called zebra. Each of the protocol-specific daemons are responsible for running the relevant protocol and building the routing table based on the information exchanged.
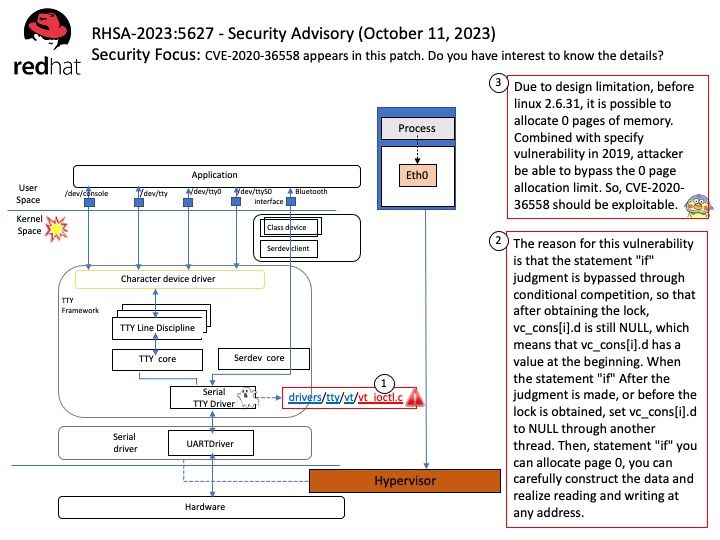
Remark: zebra is an IP routing manager. It provides kernel routing table updates, interface lookups, and redistribution of routes between different routing protocols.
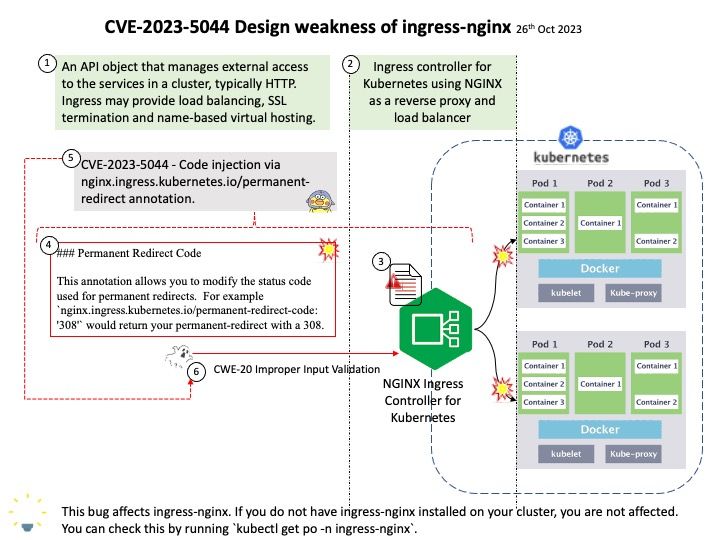
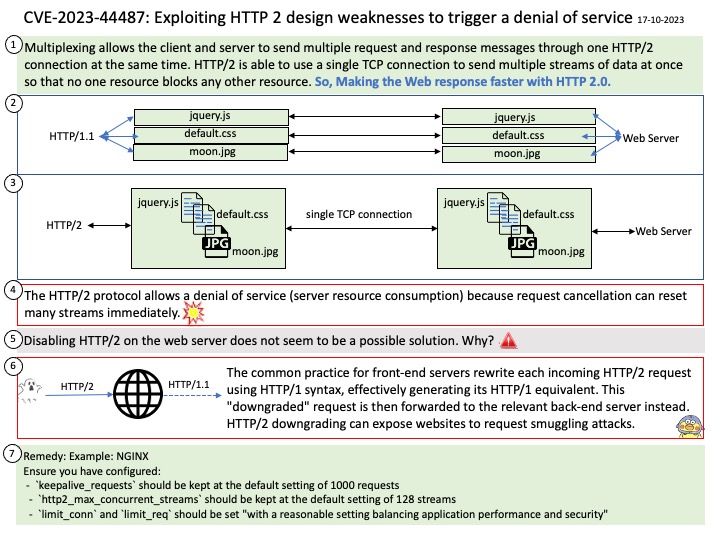
Vulnerability details: An issue was discovered in FRRouting FRR through 9.0.1. A crash can occur for a crafted BGP UPDATE message without mandatory attributes, e.g., one with only an unknown transit attribute.
Official announcement: Please refer to the link for details – https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2023-46753