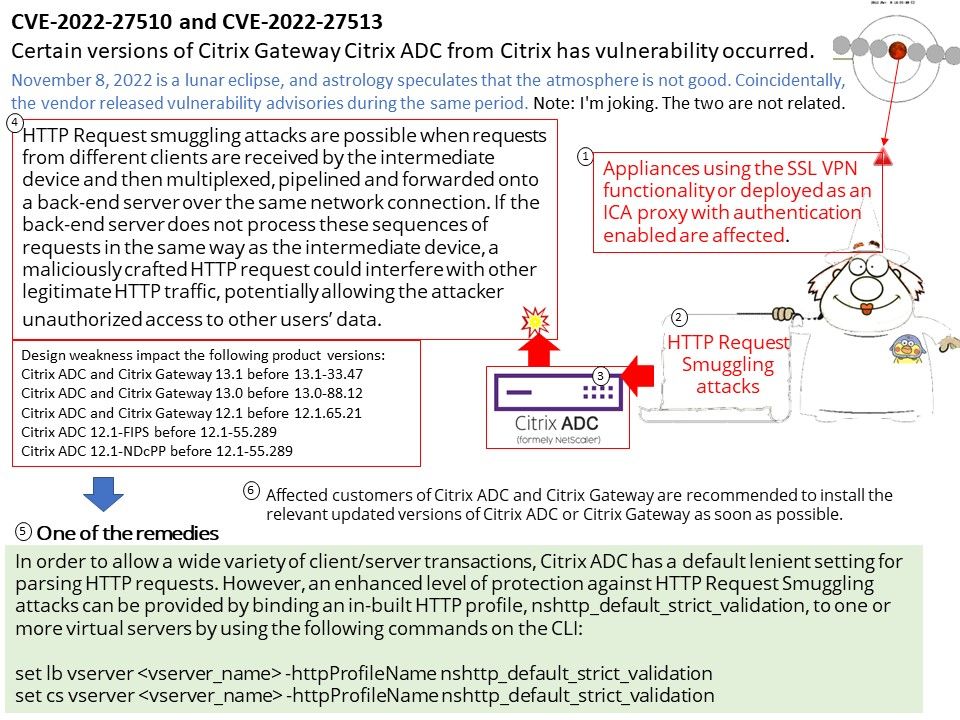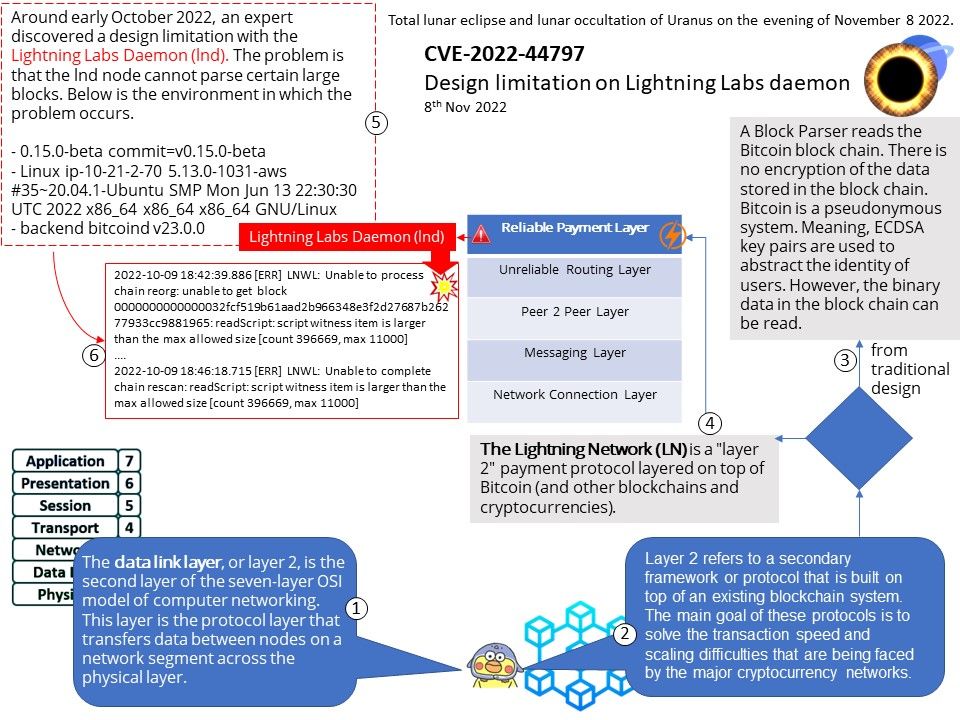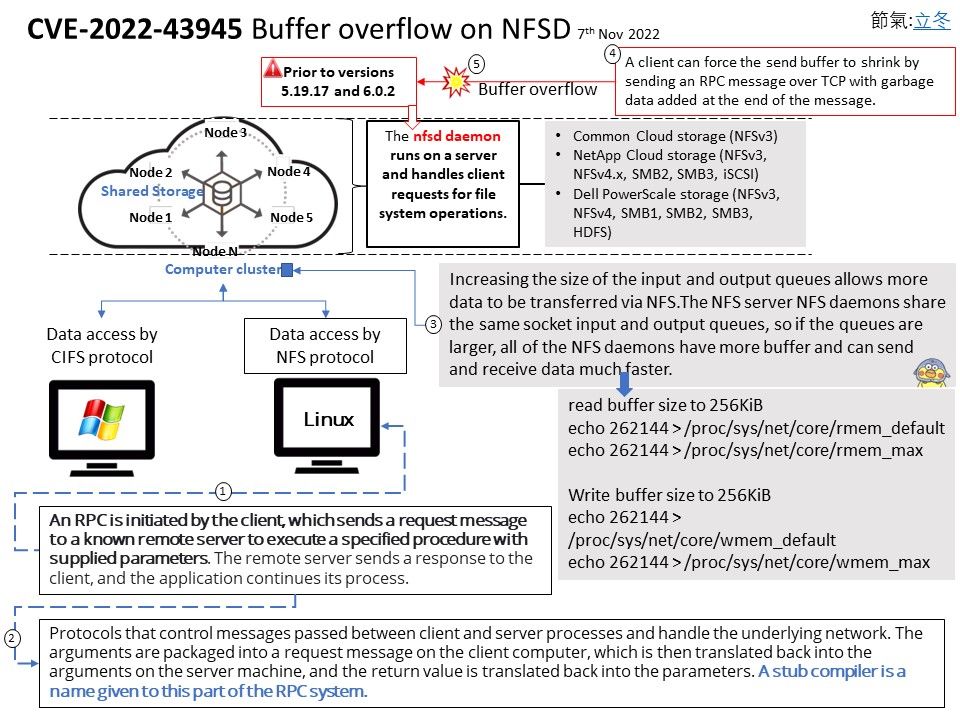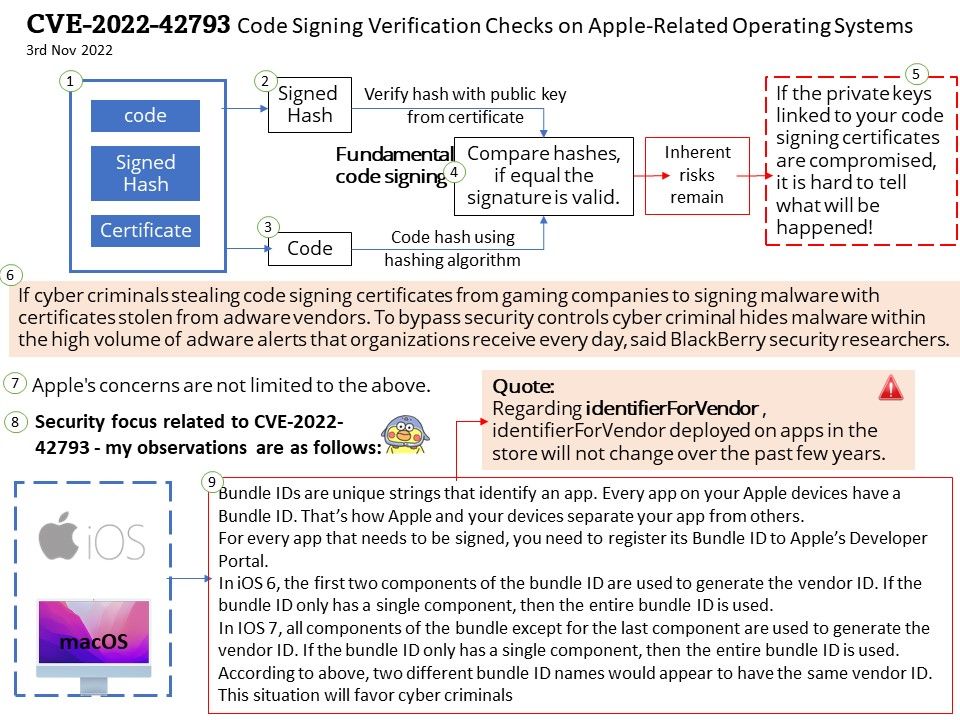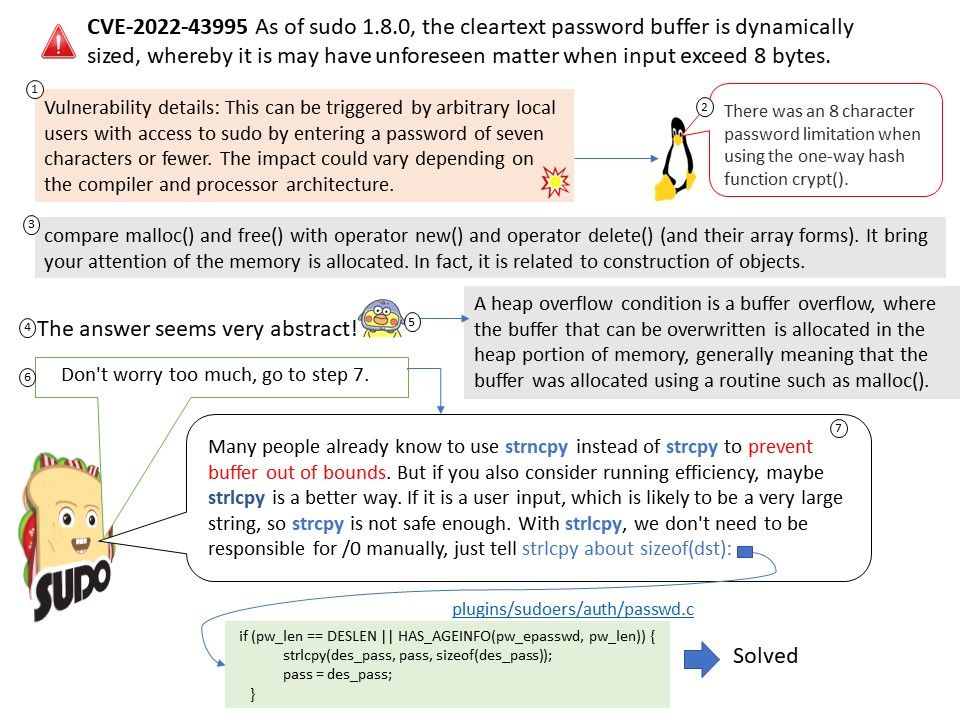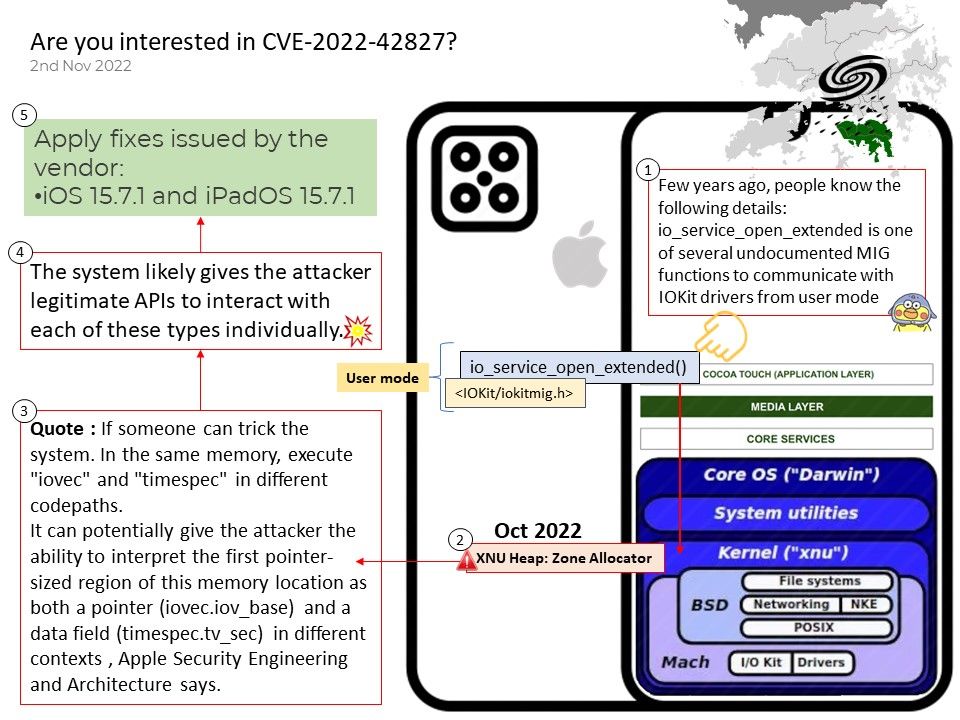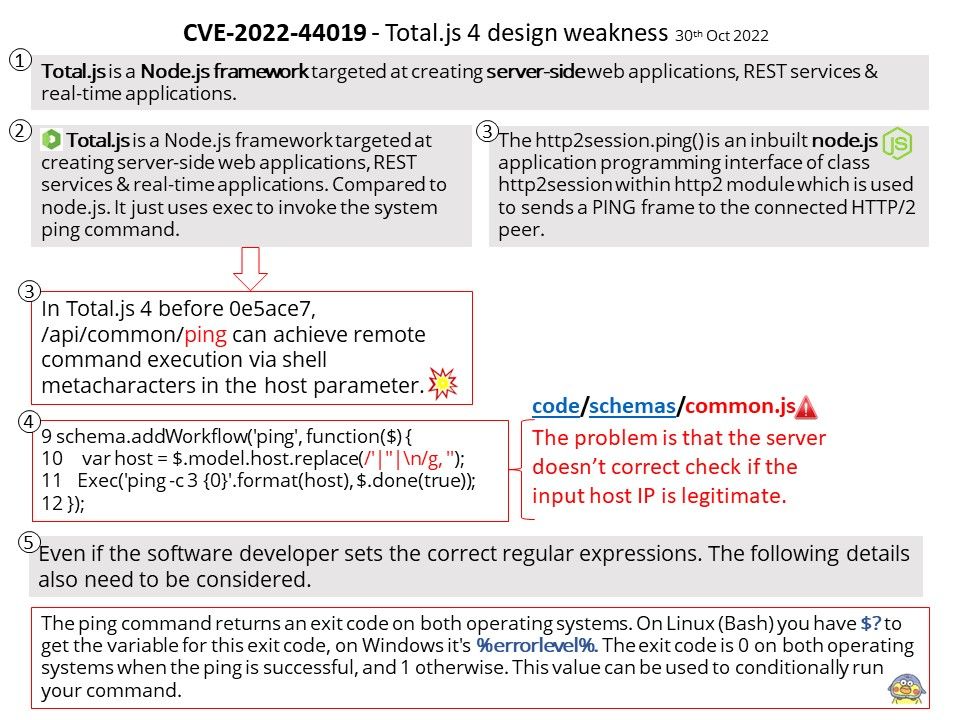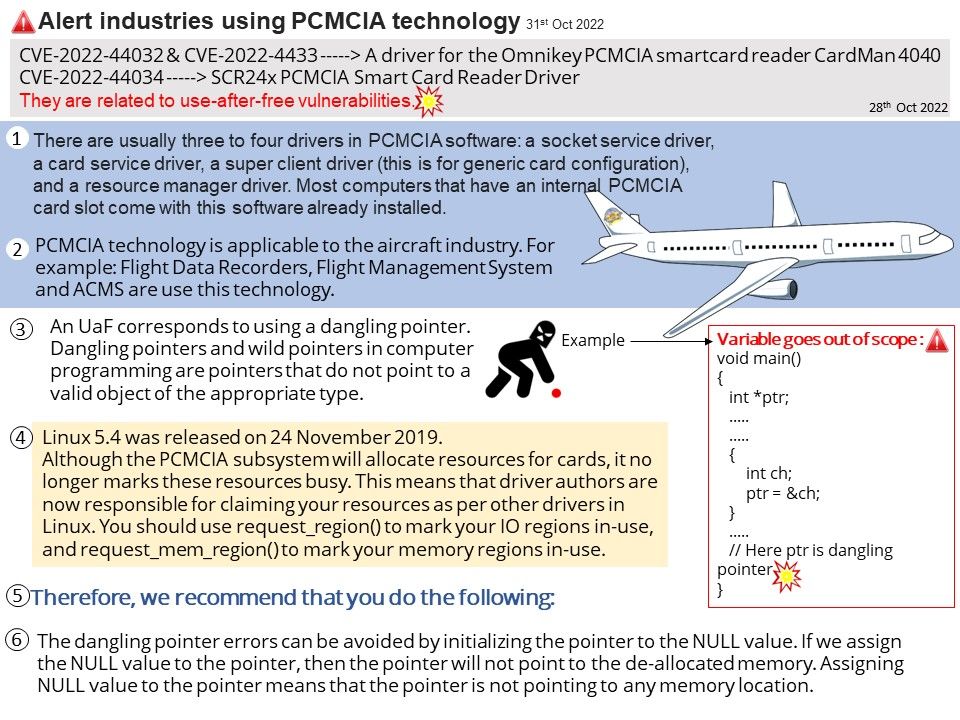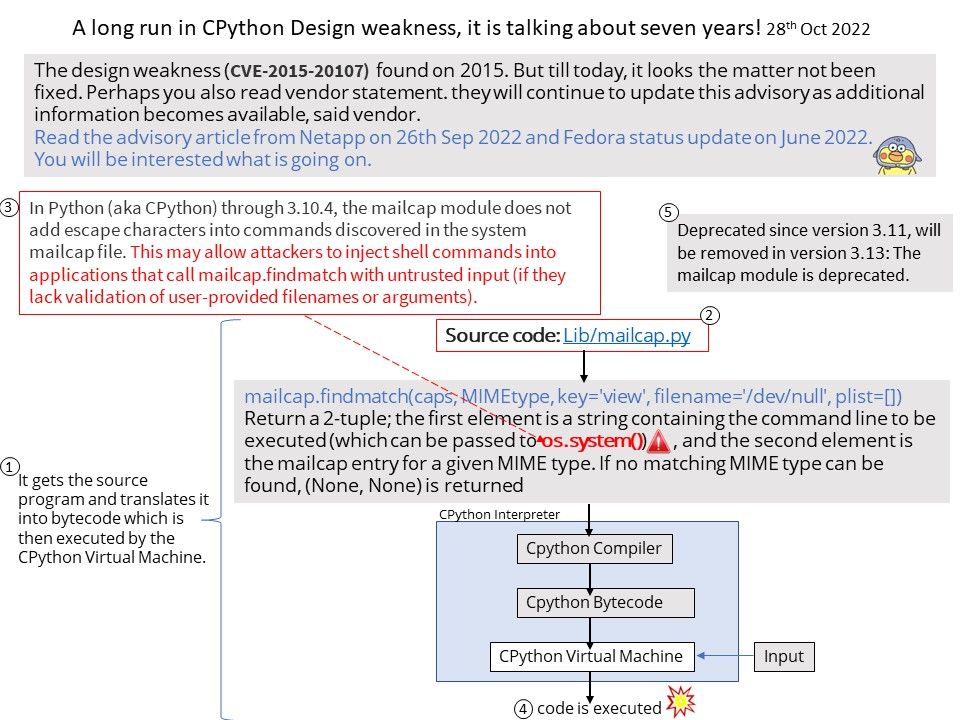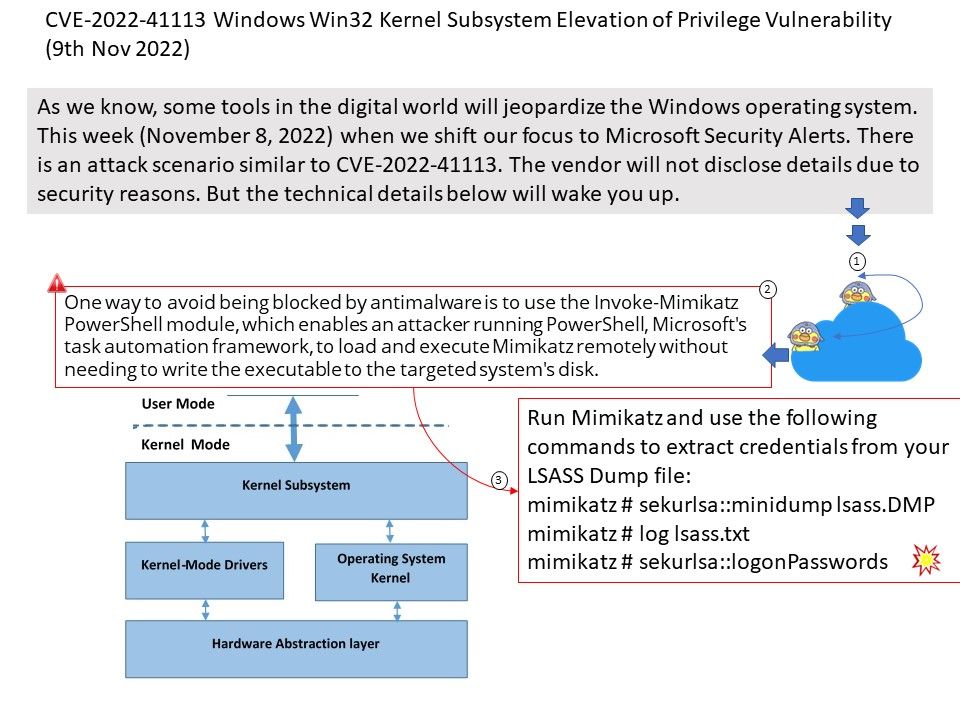
Preface: As we know, some tools in the digital world will jeopardize the Windows operating system. This week (November 8, 2022) when we shift our focus to Microsoft Security Alerts. There is an attack scenario similar to CVE-2022-41113. The vendor will not disclose details due to security reasons. But the technical details below will wake you up.
Background: Local Security Authority Server Service (LSASS) is a process in Microsoft Windows operating systems that is responsible for enforcing the security policy on the system. It verifies users logging on to a Windows computer or server, handles password changes, and creates access tokens.
Domain, local usernames, and passwords that are stored in the memory space of a process are named LSASS (Local Security Authority Subsystem Service).
Vulnerability details: This week (November 8, 2022) when we shift our focus to Microsoft Security Alerts. There is an attack scenario similar to CVE-2022-41113. The vendor will not disclose details due to security reasons. But the technical details below will wake you up.
Assigner: Microsoft
Published: 2022-11-09
Updated: 2022-11-09
Windows Win32 Kernel Subsystem Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability.
One of the possible paths an attacker would take.
Mimikatz, how it collect Windows passwords, credentials
One way to avoid being blocked by antimalware is to use the Invoke-Mimikatz PowerShell module, which enables an attacker running PowerShell, Microsoft’s task automation framework, to load and execute Mimikatz remotely without needing to write the executable to the targeted system’s disk.
Run Mimikatz and use the following commands to extract credentials from your LSASS Dump file:
mimikatz # sekurlsa::minidump lsass[.]DMP
mimikatz # log lsass[.]txt
mimikatz # sekurlsa::logonPasswords
Remedy:
- On x86-based or x64-based devices using Secure Boot and UEFI or not
- enable LSA protection on a single computer
- Using Local Group Policy on Windows 11, 22H2 (Configure LSASS to run as a protected process)
Official announcement: Please refer to the link for details – https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/en-US/vulnerability/CVE-2022-41113