Preface: Samsung Electronics has started the development of IoT.js on 2015, a platform for IoT applications written in JavaScript, and JerryScript, a JavaScript engine for small, embedded devices.
Background: JerryScript is an ultra-lightweight JavaScript engine for the Internet of things. It is capable of executing ECMAScript 5.1 source code on devices with less than 64 KB of memory.
JerryScript Engine can be embedded into any application, providing the way to run JavaScript in a large range of environments – from desktops to low-memory microcontrollers.
Ref: IoT devices come with severe constraints in terms of CPU performance and memory footprint. Because of that, Samsung has designed the JerryScript engine to run in less than 64KB or RAM and the entire code fits in less than 200KB of ROM.
Vulnerability details: CVE-2022-22895 – The following vulnerability was found:
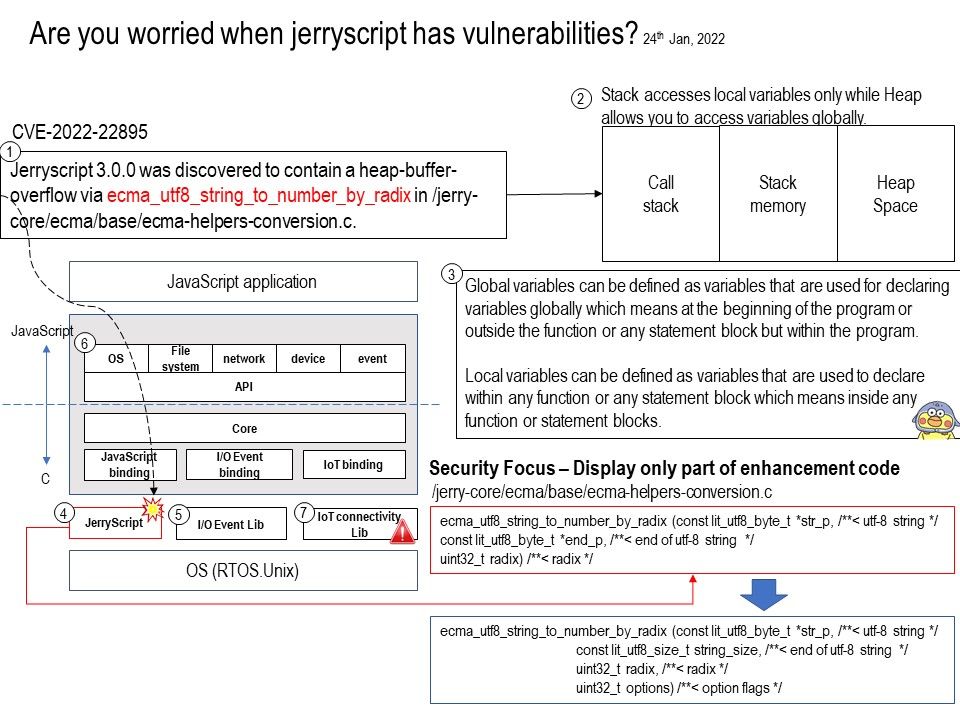
Jerryscript 3.0.0 was discovered to contain a heap-buffer-overflow via ecma_utf8_string_to_number_by_radix in /jerry-core/ecma/base/ecma-helpers-conversion[.]c.
Why are we interested in CVE-2022-22893? Here’s why:
Stack is a linear data structure whereas Heap is a hierarchical data structure. Stack memory will never become fragmented whereas Heap memory can become fragmented as blocks of memory are first allocated and then freed. Stack accesses local variables only while Heap allows you to access variables globally.
See whether the attached diagram give you a quick idea of the vulnerability? Also, some vulnerabilities were found in jerryscript. See below for details:
CVE-2022-22894 – The following vulnerability was found:
Jerryscript 3.0.0 was discovered to contain a stack overflow via ecma_lcache_lookup in /jerry-core/ecma/base/ecma-lcache[.]c.
CVE-2022-22893 – The following vulnerability was found:
Jerryscript 3.0.0 was discovered to contain a stack overflow via vm_loop.lto_priv.304 in /jerry-core/vm/vm[.]c.
CVE-2022-22891 – The following vulnerability was found:
Jerryscript 3.0.0 was discovered to contain a SEGV vulnerability via ecma_ref_object_inline in /jerry-core/ecma/base/ecma-gc[.]c.
Remedy: Please refer to Github.
.jpg?width=1920&height=1080&fit=bounds)