Preface: If you have fgfmsd (TCP/541 / TCP/542) public-facing and have not upgraded to a fixed release, perhaps you should consider the workaround by vendor.
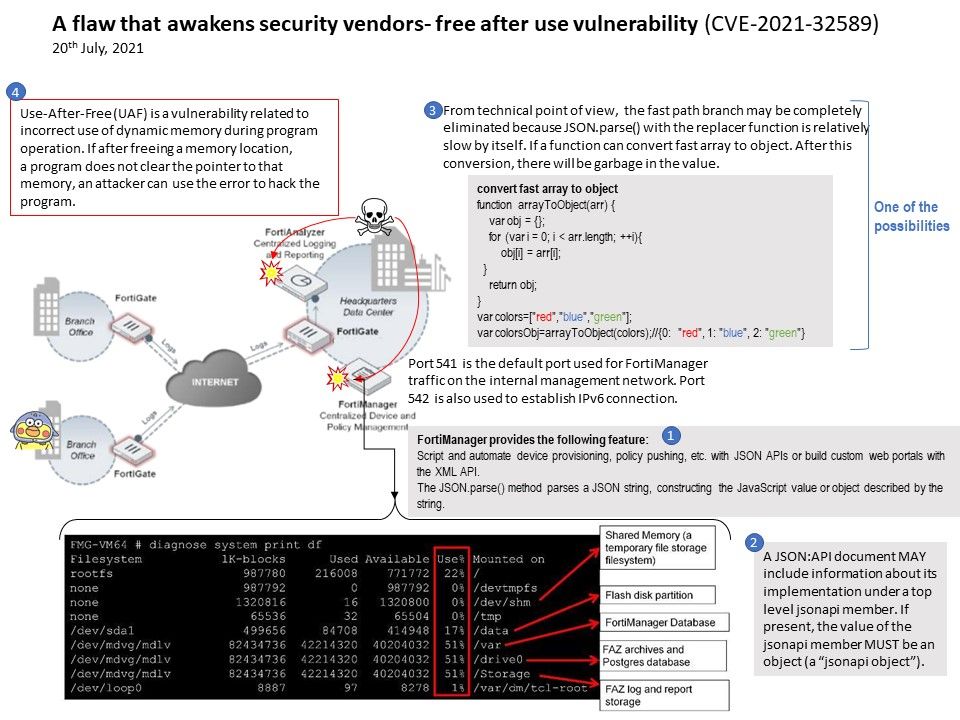
Background: The FGFM protocol runs over SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) using TCP port 541 under IPv4. Both FortiGate and FortiManager units have a ‘FGFM’ daemon running exclusively for FortiGate to FortiManager communication. The FortiManager unit listens on TCP port 541 for an incoming session request. The FortiGate unit establishes an SSL session with the FortiManager. Both units use TCP port 541 for sending and receiving messages.
You can add FortiAnalyzer devices to FortiManager and manage them. When you add a FortiAnalyzer device to FortiManager, FortiManager automatically enables FortiAnalyzer features. FortiAnalyzer and FortiManager must be running the same OS version, at least 5.6 or later.
Vulnerability details: The vulnerability exists due to a use-after-free error within the fgfmsd daemon. A remote non-authenticated attacker can send a specially crafted request to port 541/tcp (IPv4) or 542/tcp (IPv6), trigger a use-after-free error and execute arbitrary code on the system with root privileges.
Workaround: Disable FortiManager features on the FortiAnalyzer unit using the command below:
– config system global
– set fmg-status disable <— Disabled by default.
– end
Official announcement – https://www.fortiguard.com/psirt/FG-IR-21-067