Preface: Encryption uses a key to ensure the ciphertext cannot be deciphered by anyone but the authorized recipient. Signing of data works to authenticate the sender of the data and tends to implement a form of encryption in its process.
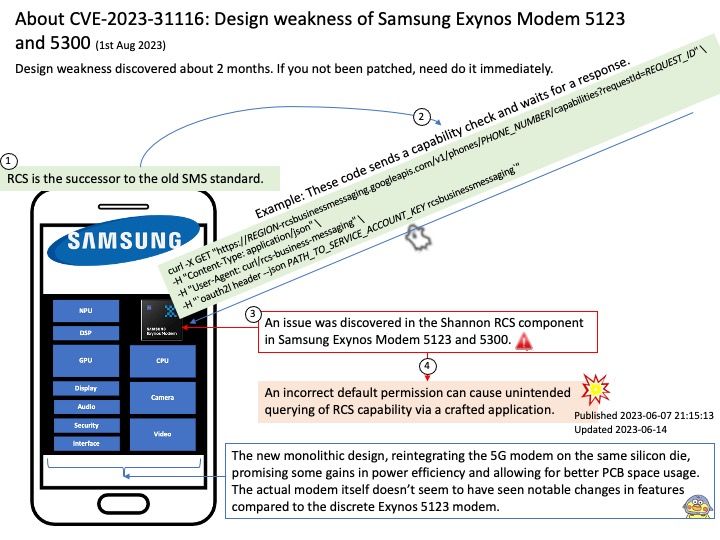
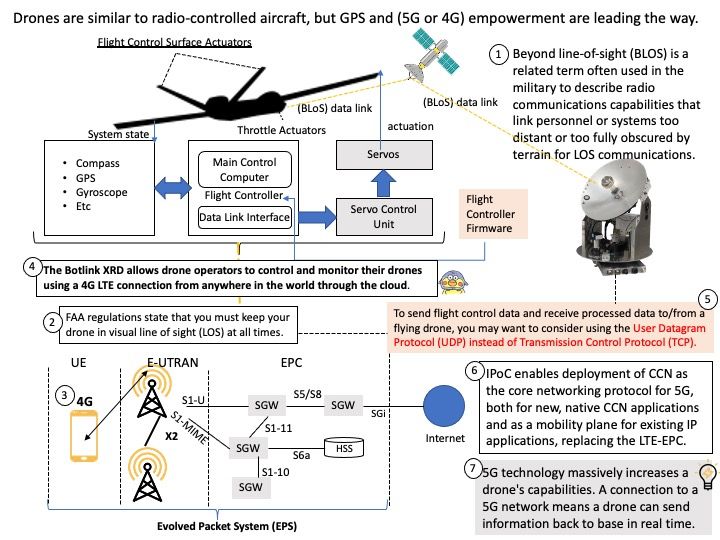
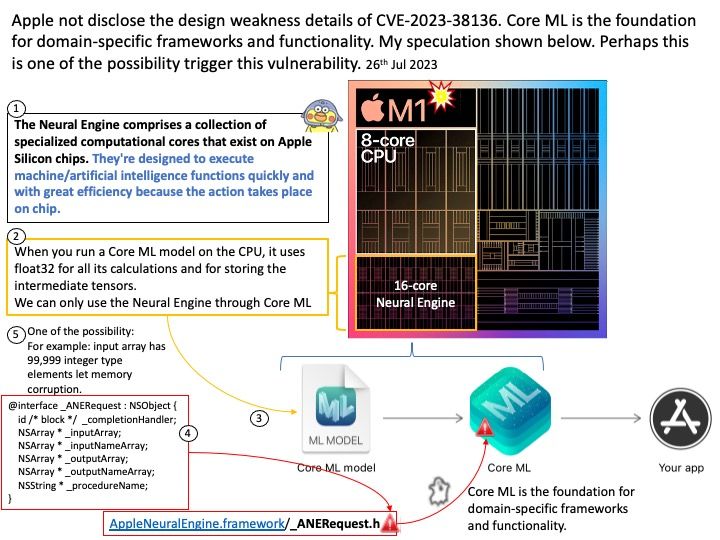
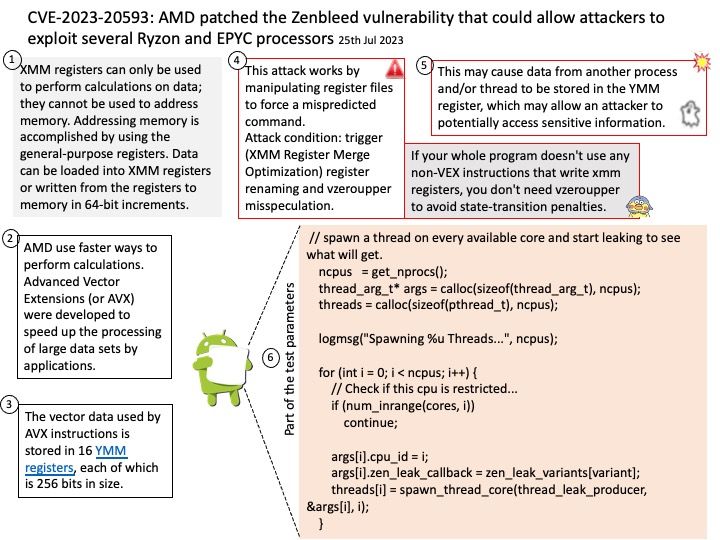
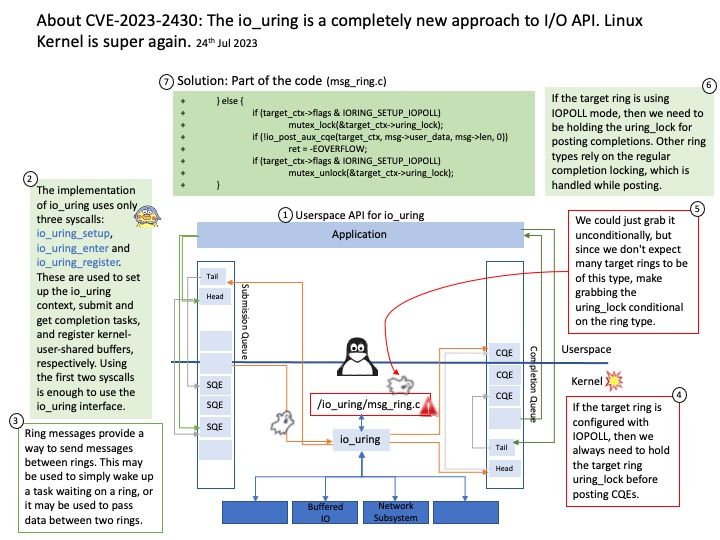
Background: JSON Object Signing and Encryption (JOSE) is the set of software technologies standardized by the IETF to represent encrypted and/or sign content as JSON data. The technologies include JSON Web Signatures (JWS), JSON Web Encryption (JWE), JSON Web Key (JWK), and JSON Web Algorithms (JWA).
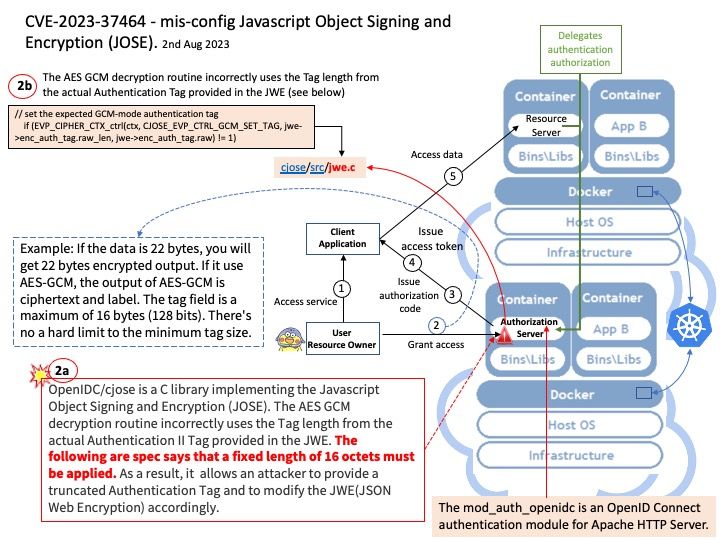
Vulnerability details: OpenIDC/cjose is a C library implementing the Javascript Object Signing and Encryption (JOSE). The AES GCM decryption routine incorrectly uses the Tag length from the actual Authentication II Tag provided in the JWE. The following are spec says that a fixed length of 16 octets must be applied. Therefore this bug allows an attacker to provide a truncated Authentication Tag and to modify the JWE accordingly.
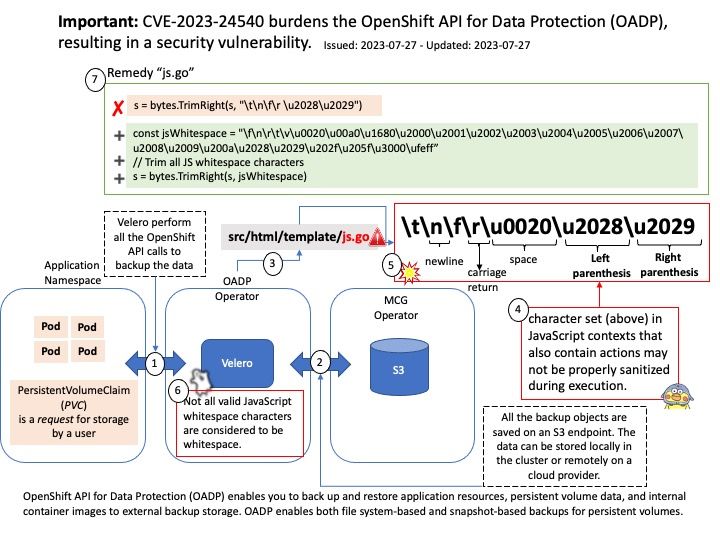
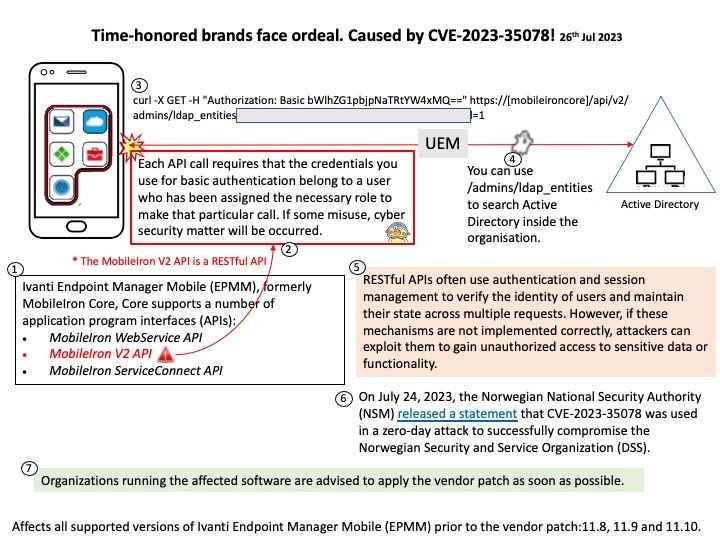
Remediation: Users should upgrade to a version >= 0.6.2.2
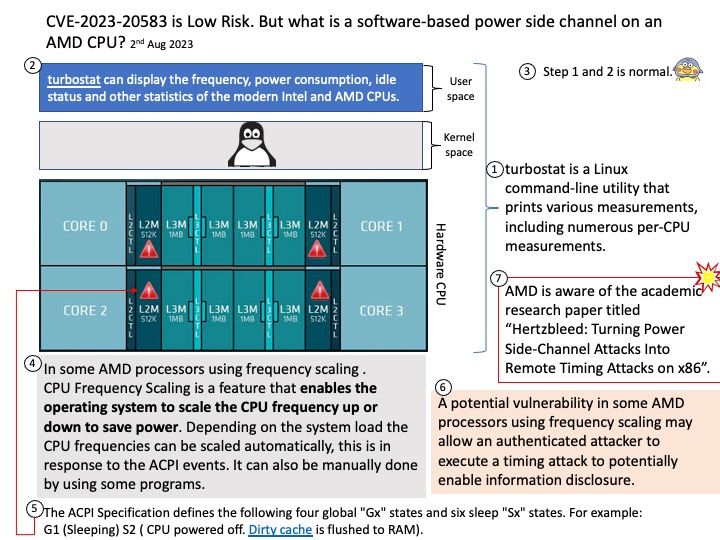
Official announcement: For details, please refer to the link – https://access.redhat.com/errata/RHSA-2023:4410