Preface: How fast are the Voyager computers?
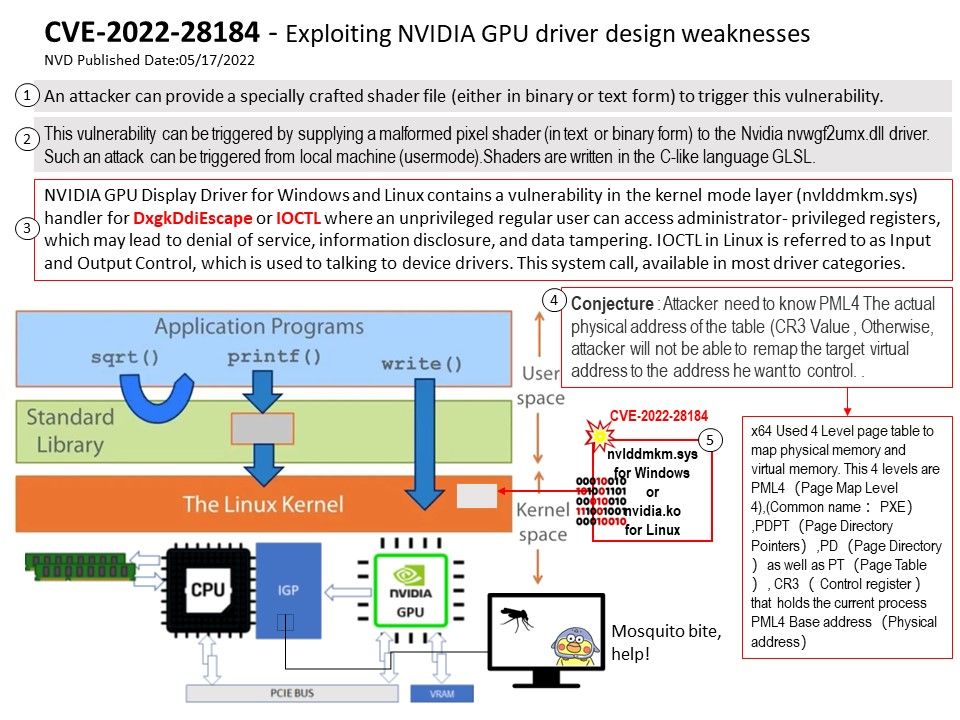
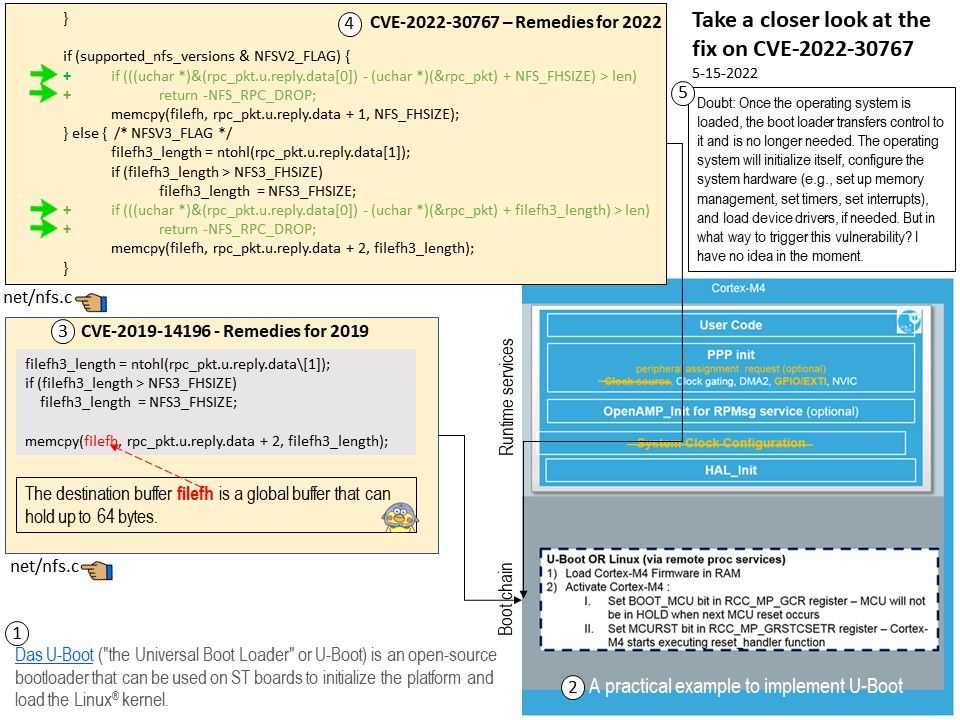
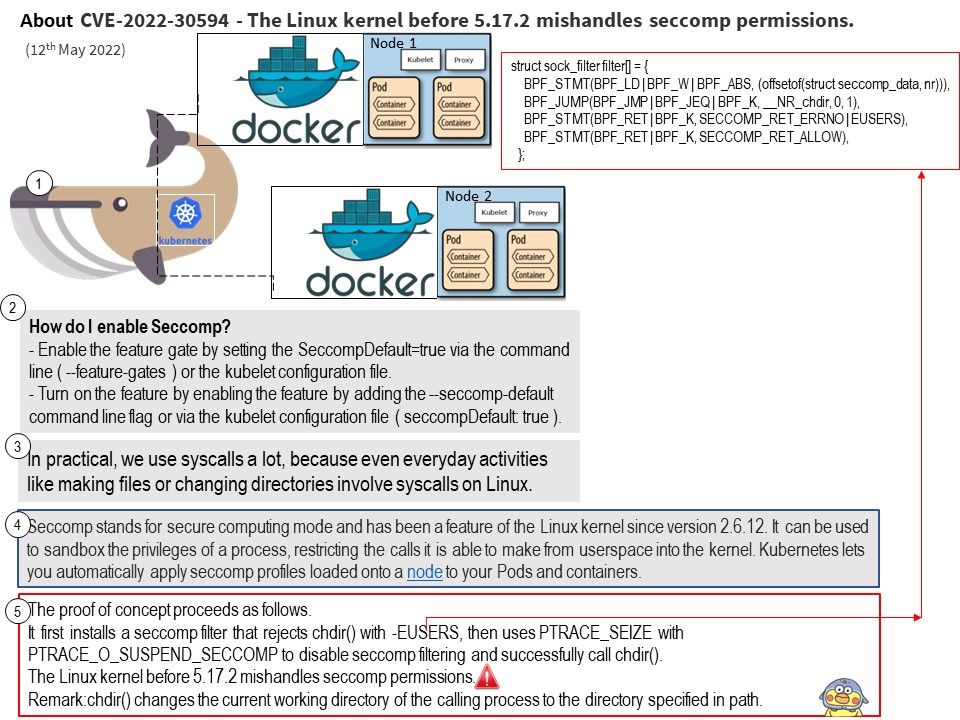
Official Reply from NASA: Not very fast compared to today’s standards. The master clock runs at 4 MHz but the CPU’s clock runs at only 250 KHz. A typical instruction takes 80 microseconds, that is about 8,000 instructions per second. To put this in perspective, a 2013 top-of-the-line smartphone runs at 1.5 GHz with four or more processors yielding over 14 billion instructions per second.
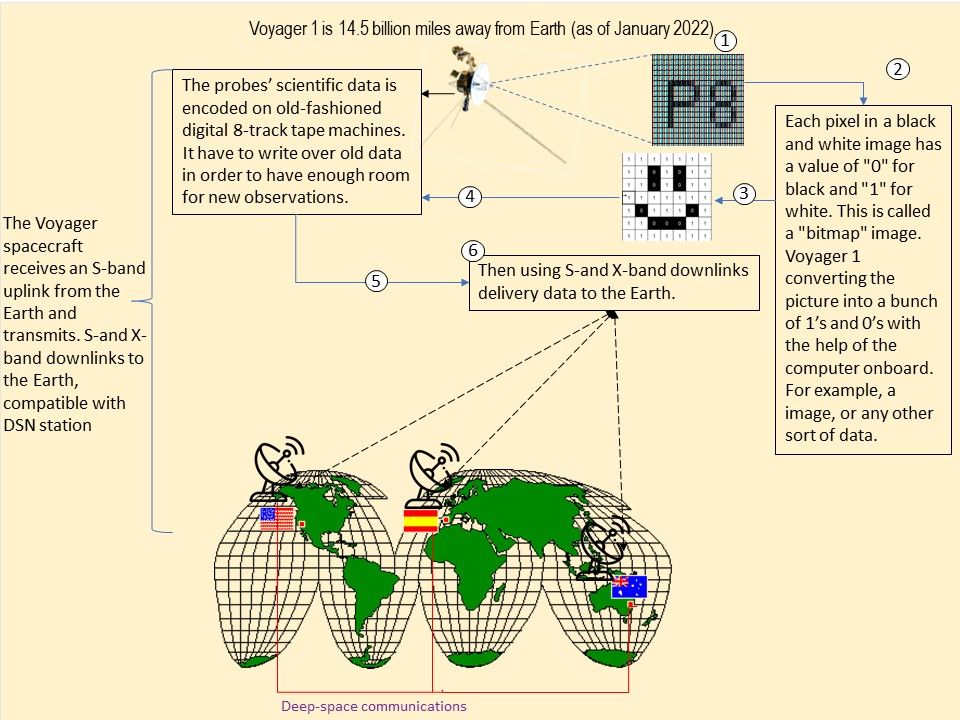
Background: Voyager 1 launched in September 1977 and is now the farthest spacecraft from Earth. The Voyagers transmit data to Earth every day. The spacecraft collect information about their surrounding environment in real time and then send it back through radio signals. Voyager 1 data takes about 19 hours to reach Earth, and signals from Voyager 2 about 16 hours. According to official information, Voyager 1 is 14.5 million miles away from Earth (as of January 2022).
Goal of Voyager Interstellar Mission: NASA’s Deep Space Network (DSN) is an international network of facilities managed and operated by JPL’s Interplanetary Network Directorate. The DSN supports interplanetary spacecraft missions, radio astronomy, radar astronomy and related observations for the exploration of the solar system and the universe.
Voyager 1 is powered by a radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG).
About news related to the topic: NASA is investigating this ‘mystery’ data coming from Voyager 1,…..Everything about the AACS suggests it is functioning normally, yet the telemetry data it’s sending back to Earth is “invalid”, producing what appears to be randomly generated data that doesn’t match any possible state the system could be in.
For details, please refer to the website – https://www.zdnet.com/home-and-office/networking/nasa-is-investigating-this-mystery-data-coming-from-voyager-1/?bhid=%7B%24external_id%7D&cid=%7B%24contact_id%7D&eh=%7B%24CF_emailHash%7D&ftag=TRE6a12a91&mid=%7B%24MESSAGE_ID%7D
Additional comments: Goal of Voyager Interstellar Mission is keen to find out unkown matter of the universe. As of January 2022, Voyager 1 is 14.5 billion miles from Earth. If Deep Space communication center receive randomly generated data.
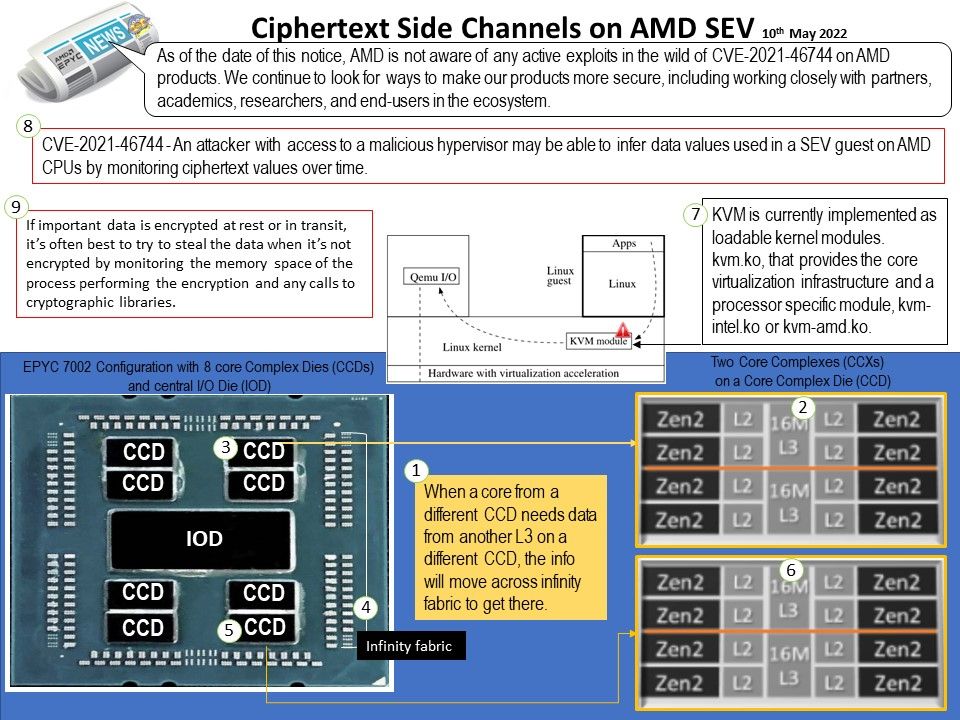
May be it can do a colloboraton with SETI. SETI Research have several observing projects on the Allen Telescope Array. From techincal point of view, randomly generated data do not have reference model is hard to do the interpretation. If there is similar pattern or unknown signal had detected by SETI in past. If it had, perhaps make use of both set of data can do a corellation.Perhaps, it is the advanced civilization that wants to communicate with our earth.
Ref: Random numbers are numbers that occur in a sequence such that two conditions are met: (1) the values are uniformly distributed over a defined interval or set, and (2) it is impossible to predict future values based on past or present ones.
.jpg)

.jpg)