Preface: Gartner Reports give people direction, but sometime as a customer, you can select your appropriate product on your decision. For instance cyber security product
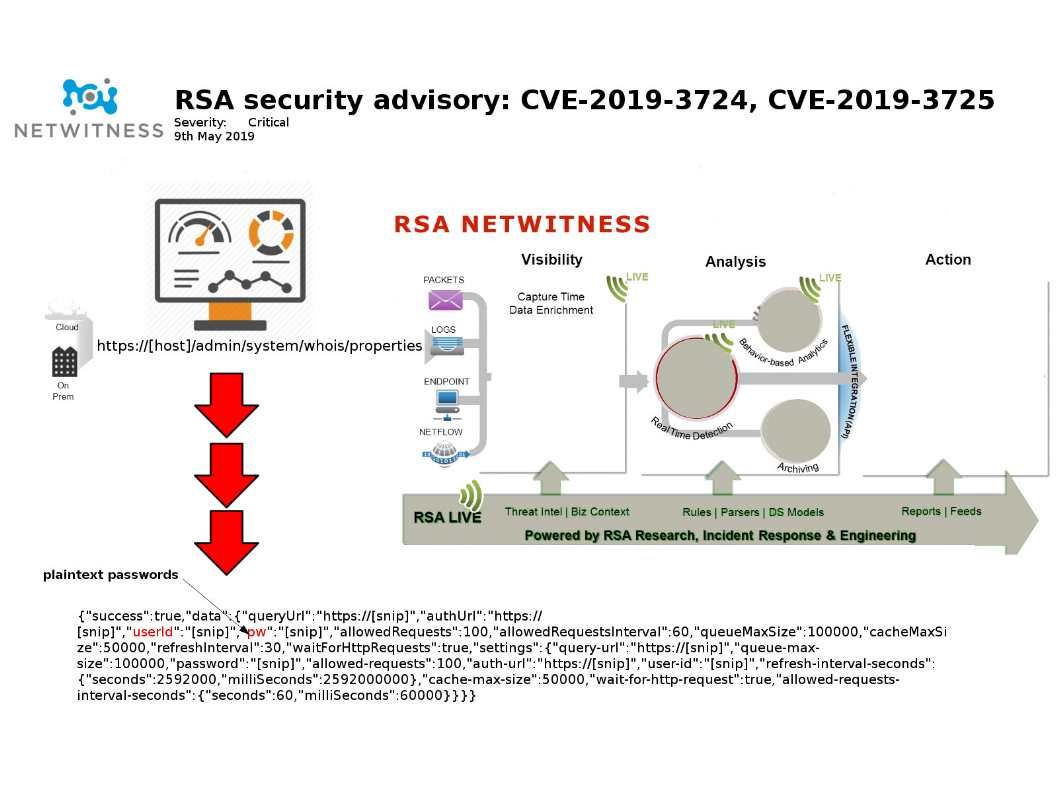
Technical background: SIEM software products provides real-time analysis of security alerts generated by applications and network hardware. Netwitness can investigate data capture and display the real scenario on screen.It is very important in IT world nowadays.
Synopsis: RSA security product pioneer go to the market more than decade. From 2011 acquire Netwitness and conduct a product integration. It was today naming convention security analytic. It contains SIEM, real time network activities data capture (Big data) and malware analysis (ECAT). From technical point of view, the GUI (Dashboard) and web access technology looks did not have any security enhancement.
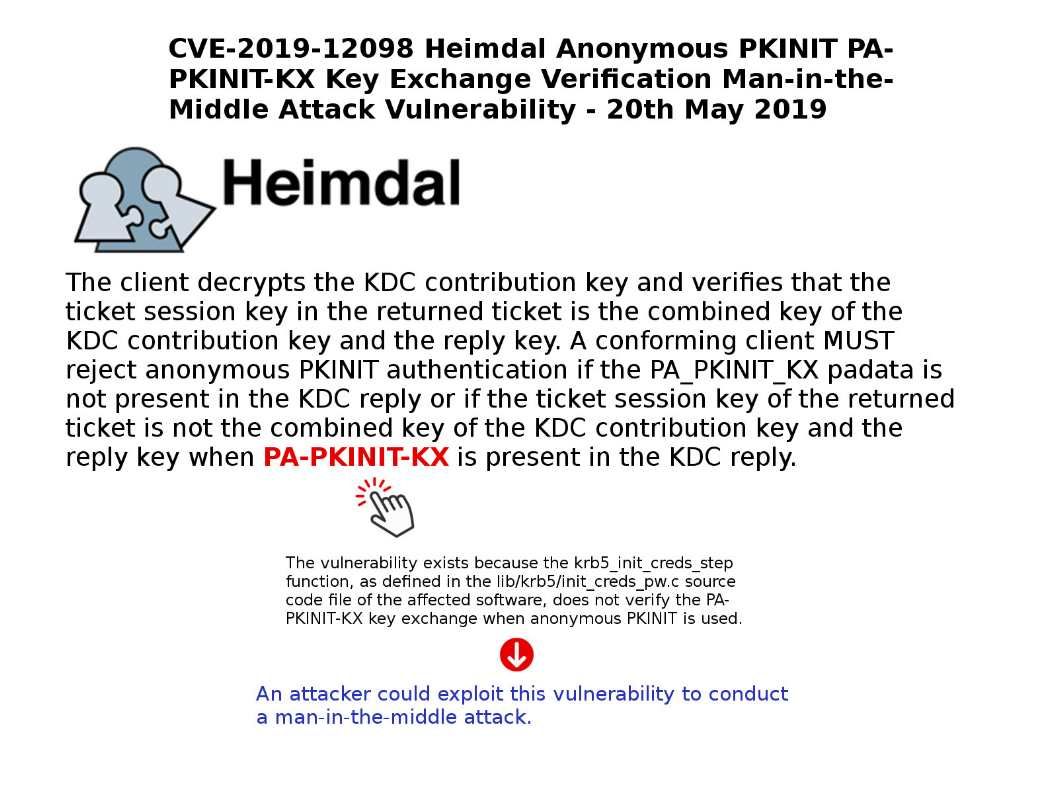
Vulnerability details: Netwitness Platform versions prior to 11.2.1.1 and RSA Security Analytics versions prior to 10.6.6.1 are vulnerable to an Authorization Bypass vulnerability and command injection vulnerability. For more details please refer to the link below: