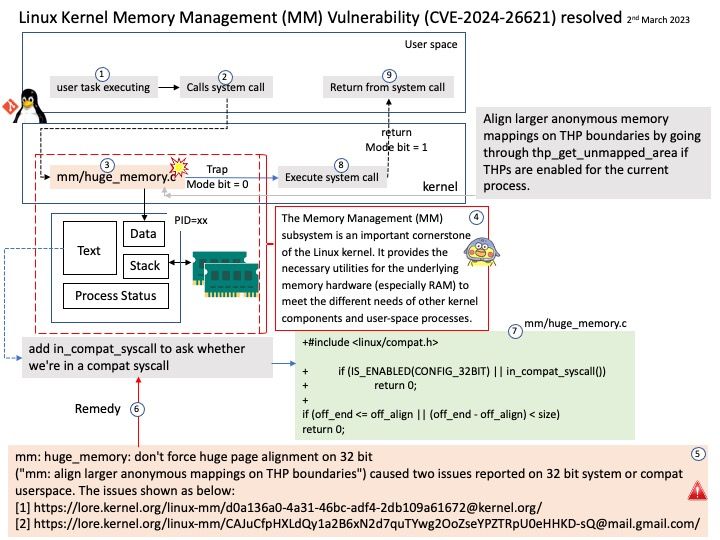
Preface: The Memory Management (MM) subsystem is an important cornerstone of the Linux kernel. It provides the necessary utilities for the underlying memory hardware (especially RAM) to meet the different needs of other kernel components and user-space processes.
Background: About two months ago, larger anonymous mappings are now THP aligned. When a malloc library allocates a 2MB or larger arena, that arena can now be mapped with THPs right from the start, which can result in better TLB hit rates and execution time.
Ref: Align larger anonymous memory mappings on THP boundaries by going through thp_get_unmapped_area if THPs are enabled for the current process.
Vulnerability details: mm: huge_memory: don’t force huge page alignment on 32 bit.
mm: huge_memory: don’t force huge page alignment on 32 bit
(“mm: align larger anonymous mappings on THP boundaries”) caused two issues reported on 32 bit system or compat userspace. The issues shown as below:
[1] https://lore.kernel.org/linux-mm/d0a136a0-4a31-46bc-adf4-2db109a61672@kernel.org/
[2] https://lore.kernel.org/linux-mm/CAJuCfpHXLdQy1a2B6xN2d7quTYwg2OoZseYPZTRpU0eHHKD-sQ@mail.gmail.com/
Official announcement: Please refer to the official announcement for details –