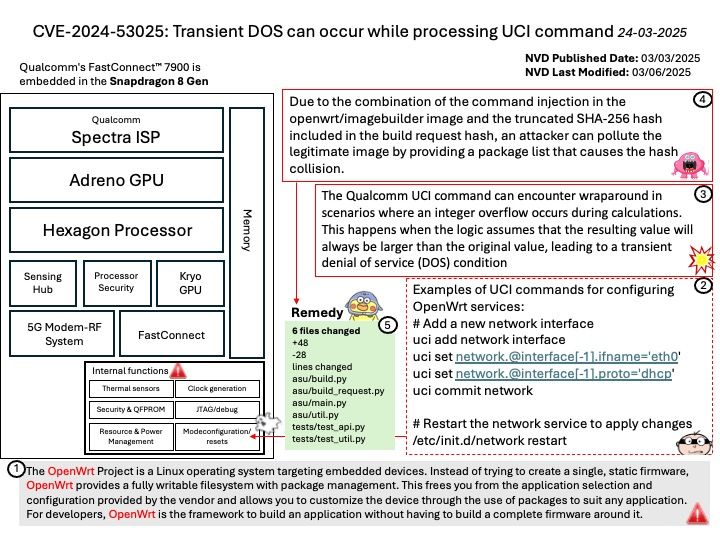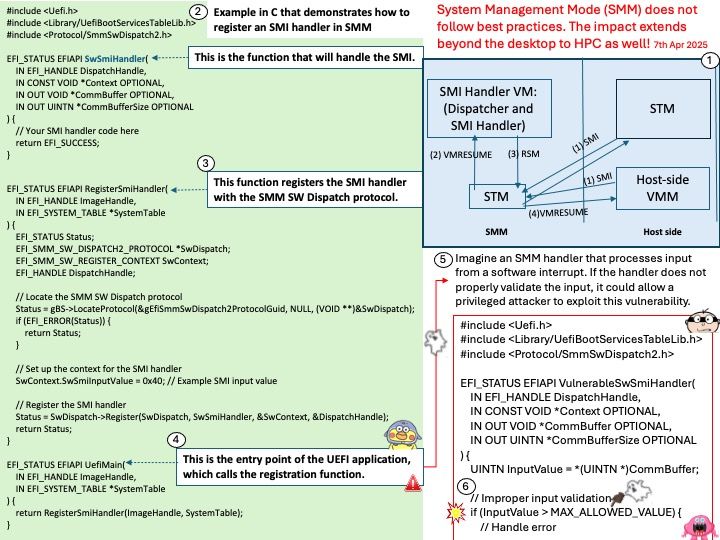
Preface: In the realm of High Performance Computing (HPC), processors that use the x86 architecture typically support System Management Mode (SMM). This includes:
-Intel Xeon Processors: Widely used in HPC systems, Intel Xeon processors support SMM for managing system-wide tasks such as power management and hardware control.
-AMD EPYC Processors: AMD EPYC processors, including the latest generations, also support SMM. These processors are known for their high core counts and robust performance in HPC environments.
Both Intel and AMD continue to leverage SMM in their x86-based processors to ensure efficient and secure system management.
Background: SMM operates transparently to the operating system and applications, allowing it to perform these tasks without interfering with the normal operation of the system.
Under HPC architecture, a cluster of computers essentially operates as a single entity, called a node, that can accept tasks and computations as a collective.
The isolation is particularly beneficial in HPC environments where uninterrupted performance is crucial.
Technical details: System Management Mode (SMM) uses System Management RAM (SMRAM) to store and manage tasks. SMM is triggered through a System Management Interrupt (SMI), a signal sent from the chipset to the CPU. During platform initialization, the firmware configures the chipset to cause a System Management Interrupt for various events that the firmware developer would like the firmware to be made aware of.
- SwSmiHandler: This is the function that will handle the SMI.
- RegisterSmiHandler: This function registers the SMI handler with the SMM SW Dispatch protocol.
- UefiMain: This is the entry point of the UEFI application, which calls the registration function.
The key steps are locating the SMM SW Dispatch protocol, setting up the context for the SMI handler, and registering the handler.
Reference: Design flaw in SMM published by AMD on Feb 2025. Please refer to the link for details – https://www.amd.com/en/resources/product-security/bulletin/amd-sb-4008.html