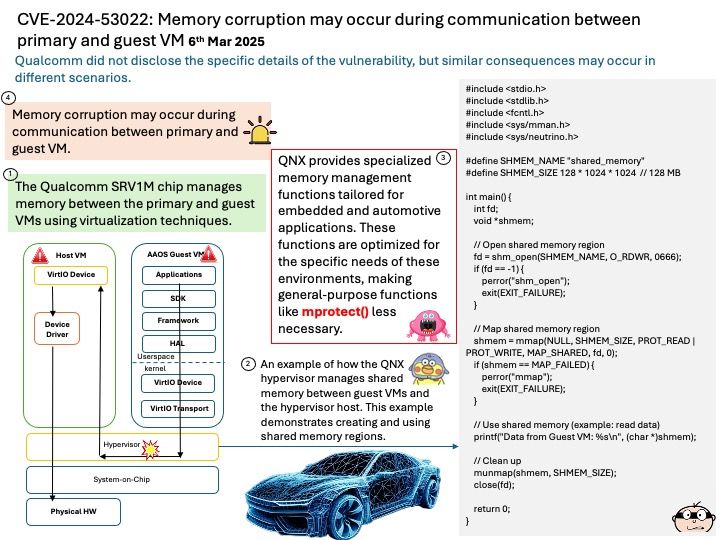
Preface: QNX hypervisors are available in two variants: QNX Hypervisor and QNX Hypervisor for Safety.
The QNX Hypervisor variant (QH), which includes QNX Hypervisor 8.0, is not a safety-certified product. It must not be used in a safety-related production system.
If you are building a safety-related system, you must use the QNX Hypervisor for Safety (QHS) variant that has been built and approved for use in the type of system you are building, and you must use it only as specified in its Safety Manual. The latest QHS release is QNX Hypervisor for Safety 2.2, which is based on QNX SDP 7.1.
Background: Functions like mprotect() are not commonly used in QNX hypervisor memory resource management for reasons:
- Memory Isolation: The hypervisor ensures that each VM (both primary and guest) has its own isolated memory space. This prevents one VM from accessing the memory of another, enhancing security and stability.
- Dynamic Memory Allocation: The hypervisor can dynamically allocate memory to VMs based on their needs. This means that if a guest VM requires more memory, the hypervisor can allocate additional memory from the available pool.
- Memory Ballooning: This technique allows the hypervisor to reclaim unused memory from VMs and reallocate it where needed. The balloon driver within the VM inflates to consume memory, which is then returned to the hypervisor.
- Memory Hotplug: The hypervisor can add or remove memory from a VM while it is running. This allows for flexible memory management without needing to restart the VM.
Vulnerability details: Memory corruption may occur during communication between primary and guest VM.
Official announcement: Please refer to the link for details – https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-53022