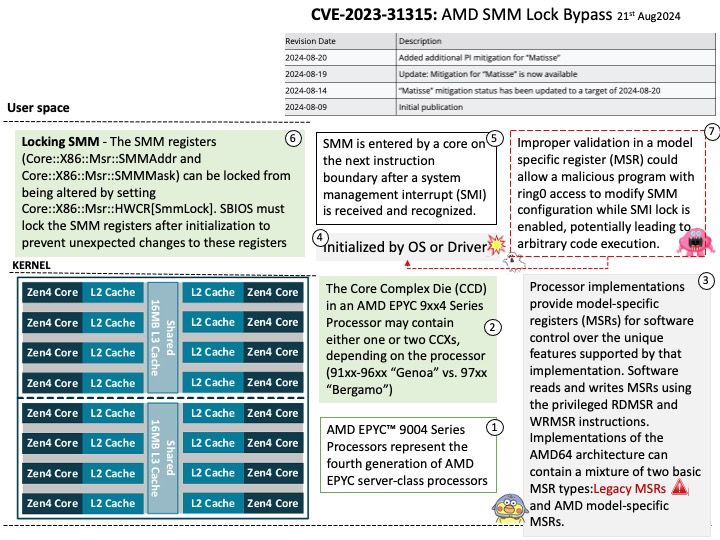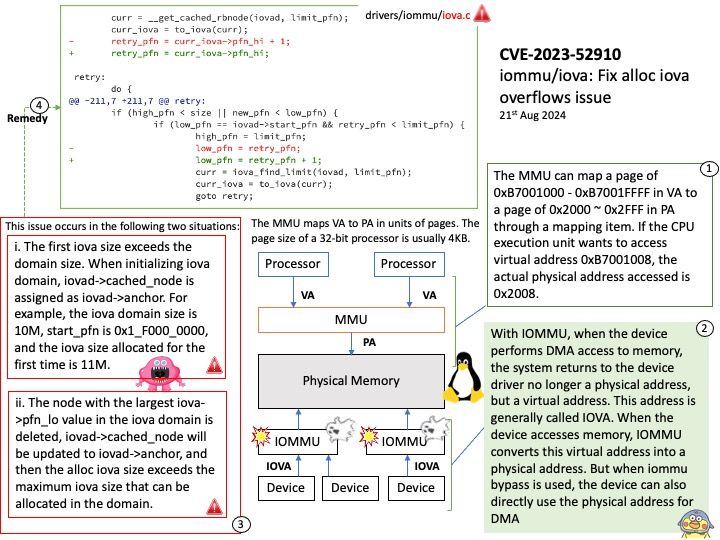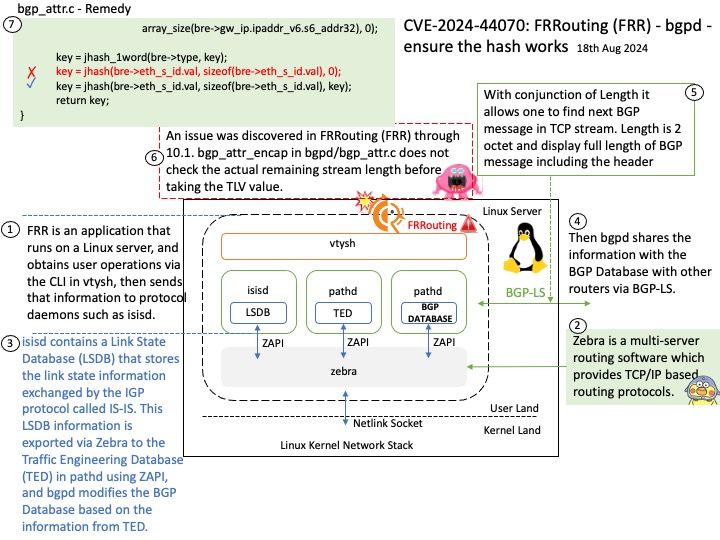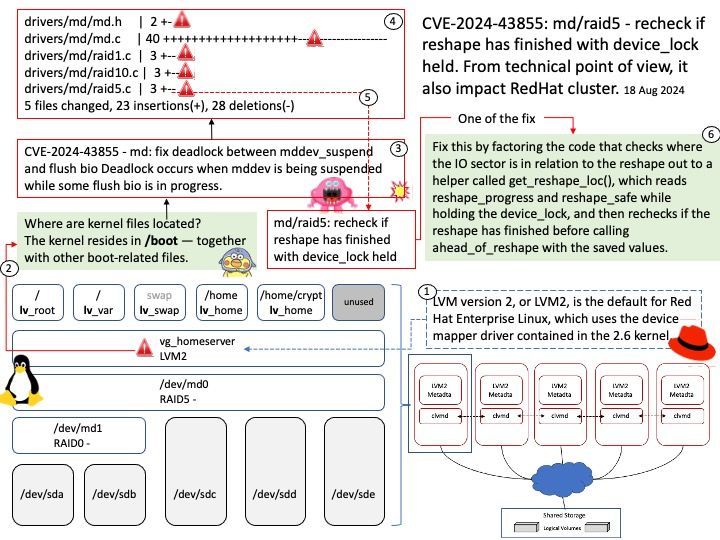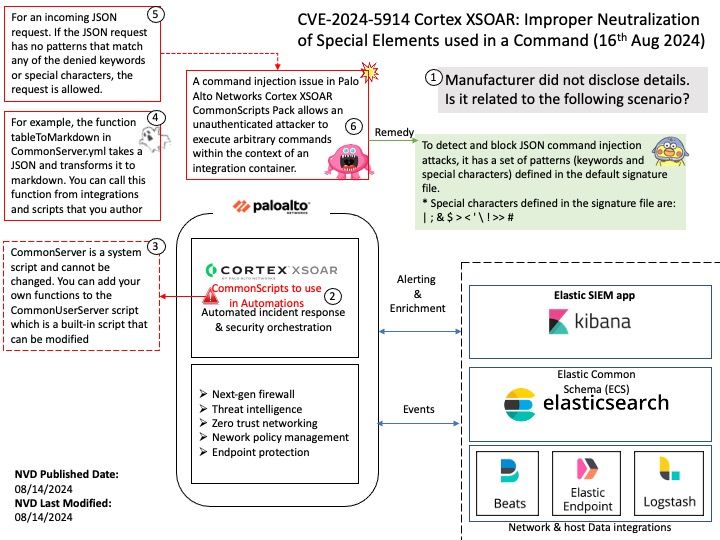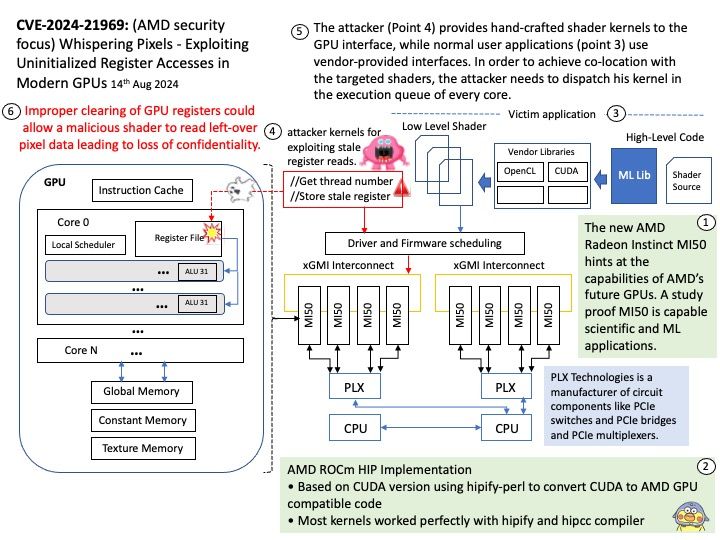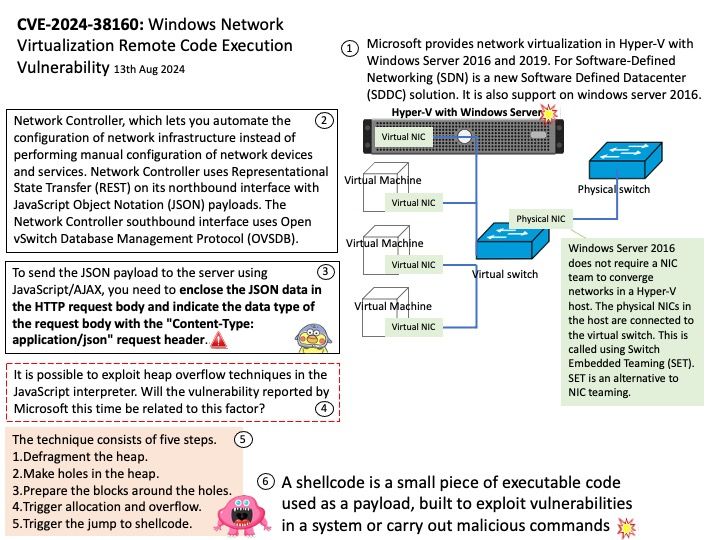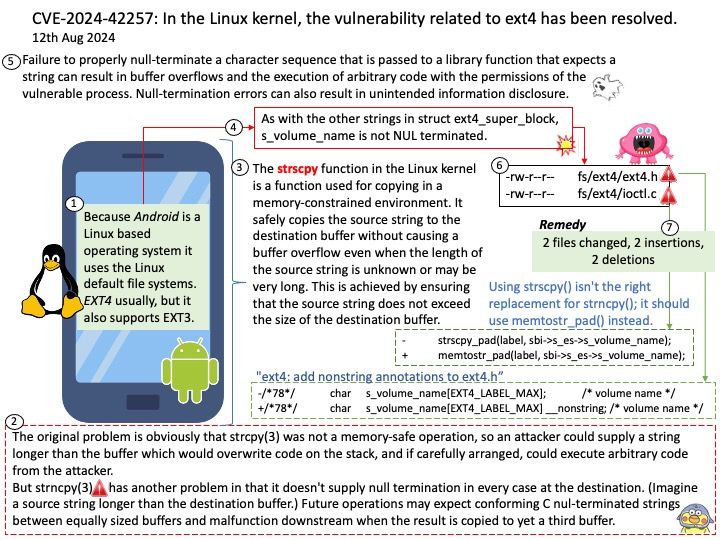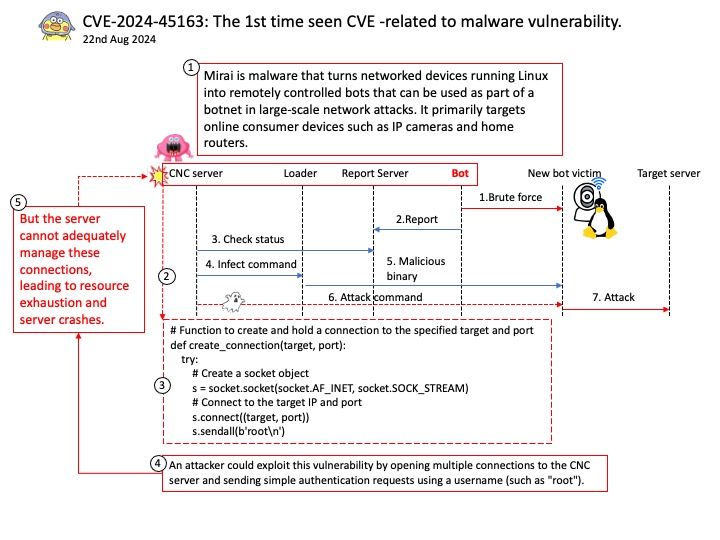
Preface: Mirai is malware that turns networked devices running Linux into remotely controlled bots that can be used as part of a botnet in large-scale network attacks. It primarily targets online consumer devices such as IP cameras and home routers.
Background: The Mirai botnet connects to the CNC (command and control) server via simultaneous TCP. An unauthenticated session remains open, allowing an attacker, for example, to send a recognizable username (such as root), or to send arbitrary data.
Vulnerability details: The Mirai botnet through 2024-08-19 mishandles simultaneous TCP connections to the CNC (command and control) server. Unauthenticated sessions remain open, causing resource consumption. But the CNC server cannot adequately manage these connections, leading to resource exhaustion and server crashes.
Official announcement: Please refer to the link for details – https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-45163