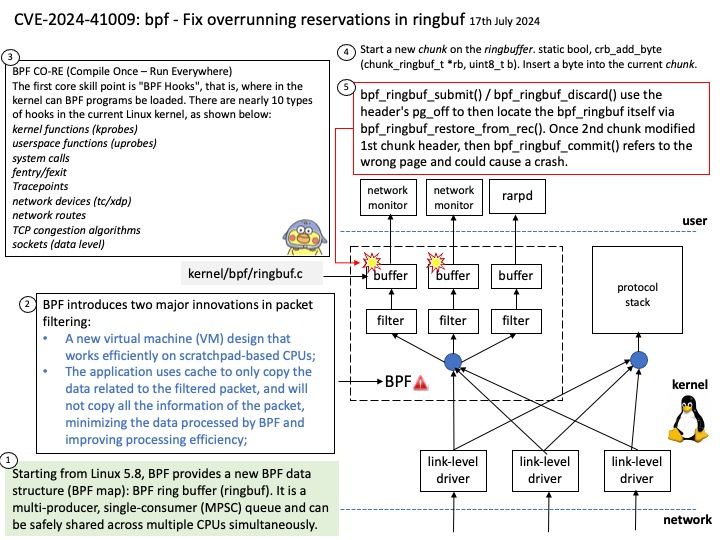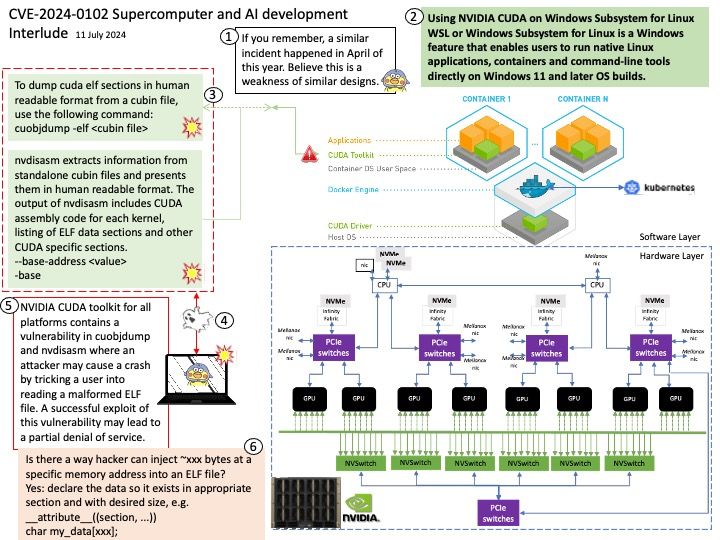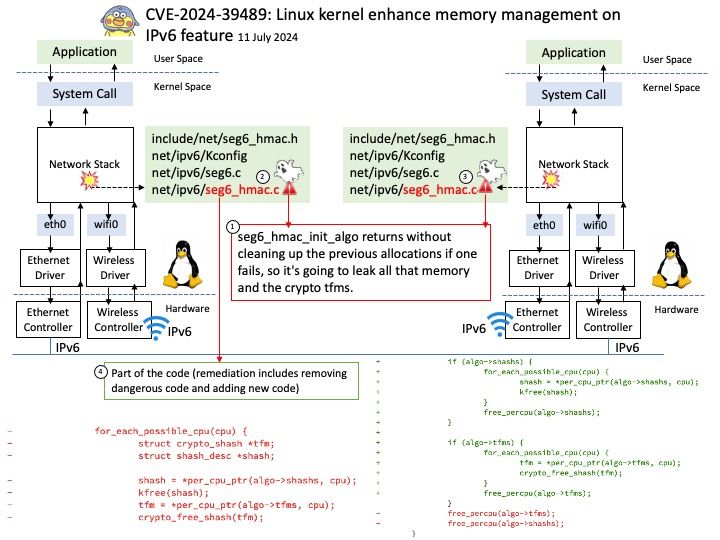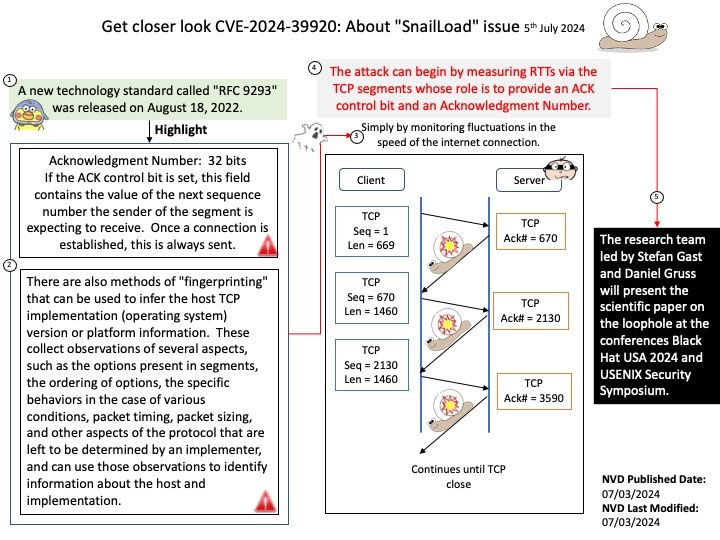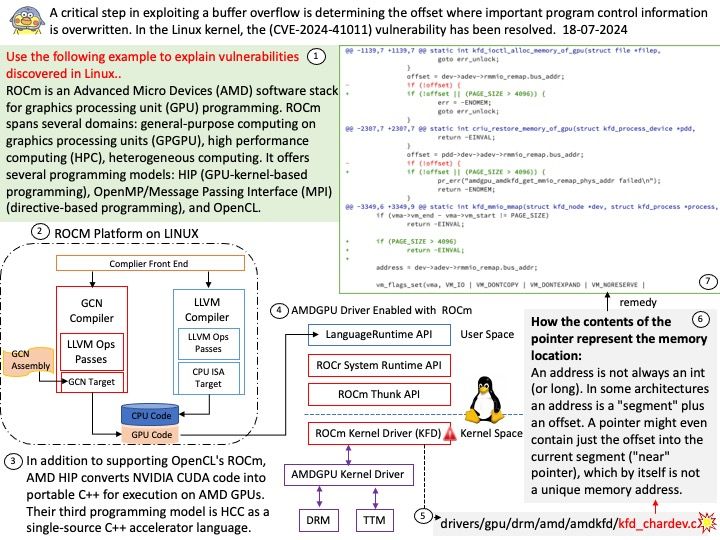
Preface: The PAGE_SIZE macro defined in the Linux kernel source determines the page size. Its definition is in the kernel header file /usr/src/kernels/5.14[.] 0-22. el9[.] x86_64/include/asm-generic/page.
Background: MMIO stands for Memory-Mapped Input/Output. In Linux, MMIO is a mechanism used by devices to interface with the CPU that involves mapping their control registers and buffers directly into the processor’s memory address space.
This enables the CPU to access device registers and exchange data with devices using load and store instructions, just as if they were conventional memory locations. Graphics cards, network interfaces, and storage controllers all employ MMIO to effectively conduct input and output tasks.
Vulnerability details: drm/amdkfd: don’t allow mapping the MMIO HDP page with large pages We don’t get the right offset in that case. The GPU has an unused 4K area of the register BAR space into which you can remap registers. We remap the HDP flush registers into this space to allow userspace (CPU or GPU) to flush the HDP when it updates VRAM. However, on systems with >4K pages, we end up exposing PAGE_SIZE of MMIO space.
Official announcement: Please refer to the official announcement for details – https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-41011