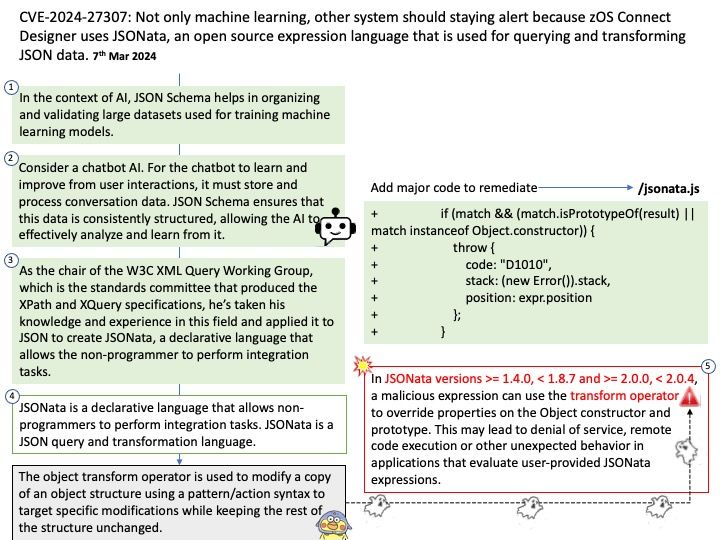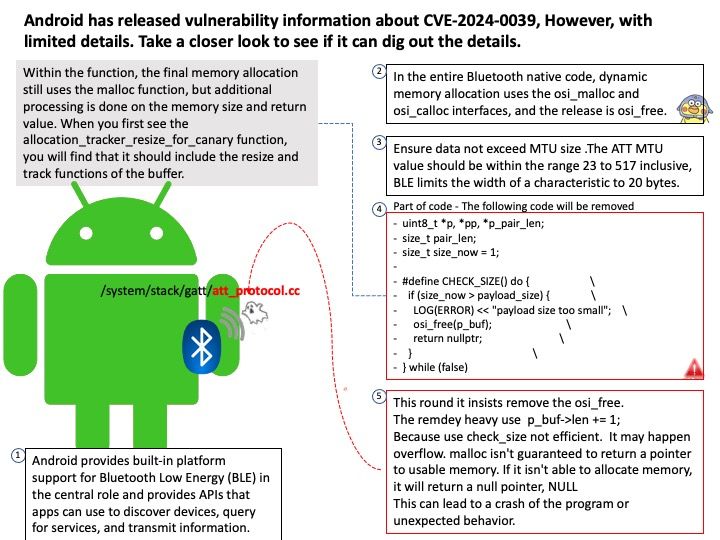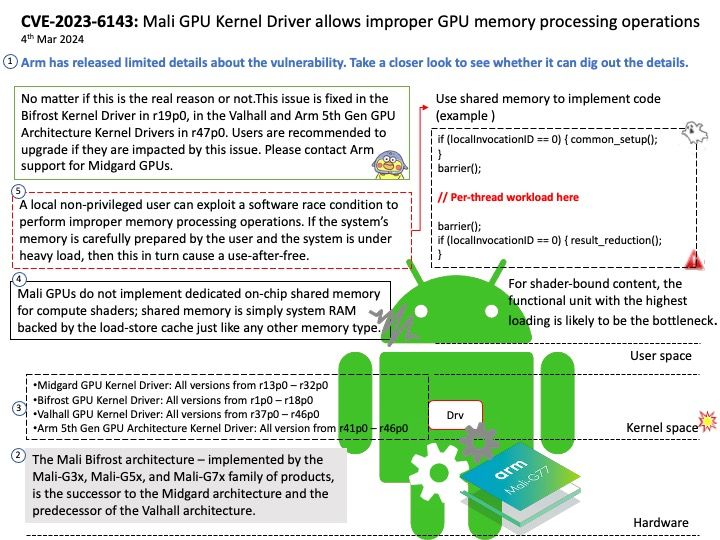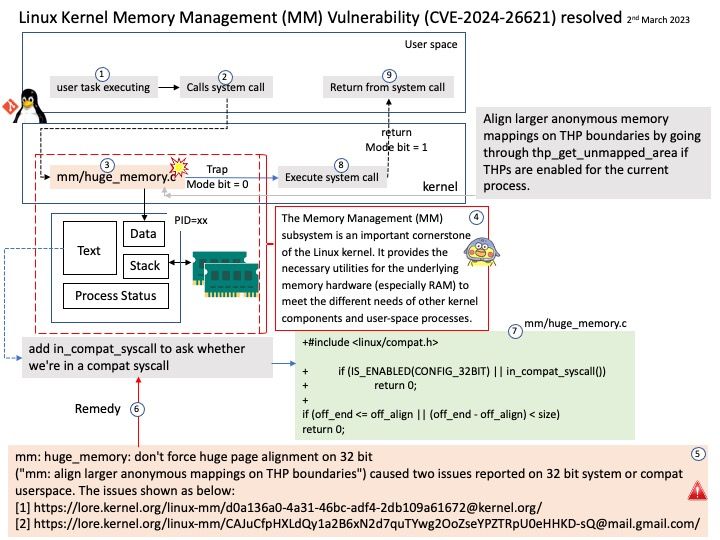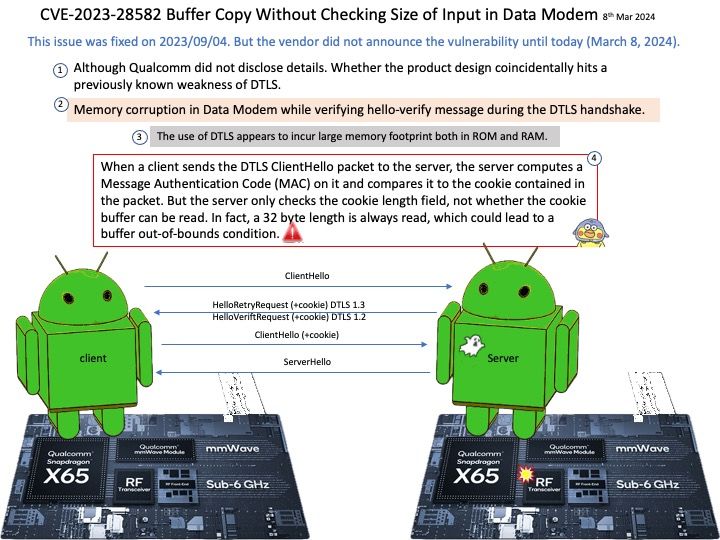
This issue was fixed on 2023/09/04. But the vendor did not announce the vulnerability until today (March 8, 2024).
Preface: Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) is a communications protocol providing security to datagram-based applications by allowing them to communicate in a way designed to prevent eavesdropping, tampering, or message forgery.
Background: 5G security standards bring enhancements to air interface and transport security mechanisms used in 4G.
In terms of transport security, the N2/N3 interfaces connecting the access and core networks and Xn interfaces connecting base stations use IPsec in 4G for transport security. 5G additionally supports Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) over Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) to secure signaling transmission on the control plane, ensuring transport security between RANs and core networks. Operators can select a transport security protection scheme based on security requirements to prevent data breach and attacks on the transport network.
Vulnerability details: Memory corruption in Data Modem while verifying hello-verify message during the DTLS handshake.
Official announcement: https://docs.qualcomm.com/product/publicresources/securitybulletin/march-2024-bulletin.html