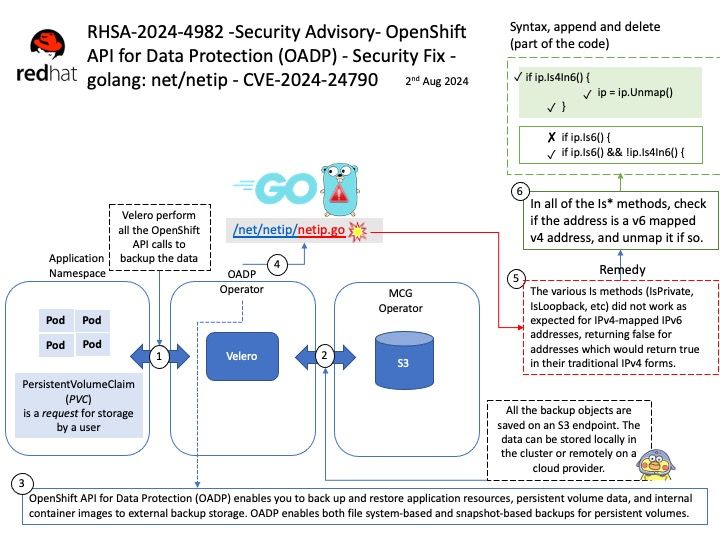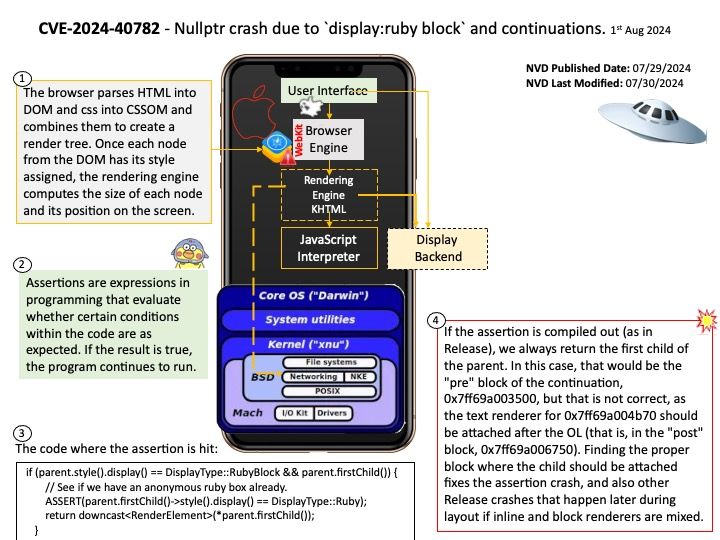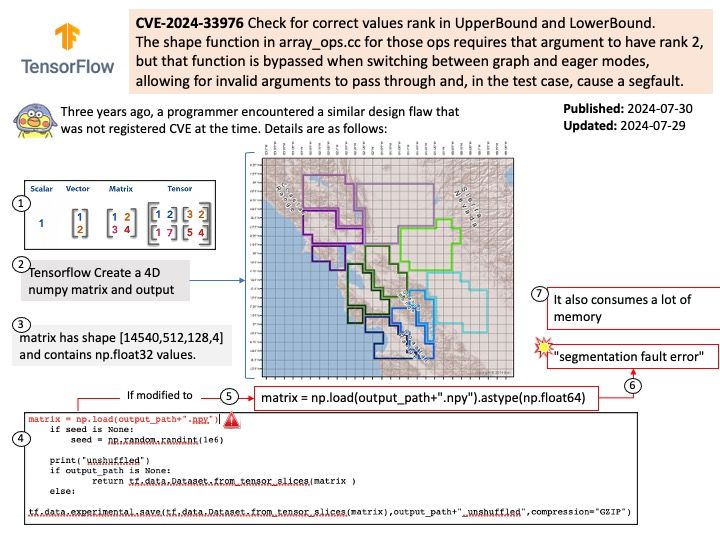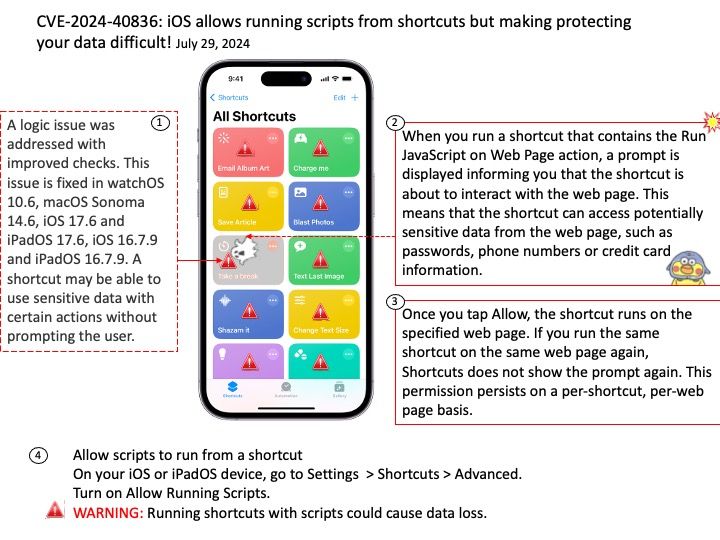
Preface: Size of /dev/shm. A unit can be b (bytes), k (kibibytes), m (mebibytes), or g (gibibytes). If the unit is omitted, the system uses bytes. If the size is omitted, the default is 64m. When size is 0, there is no limit on the amount of memory used for IPC by the container. This option conflicts with –ipc=host.
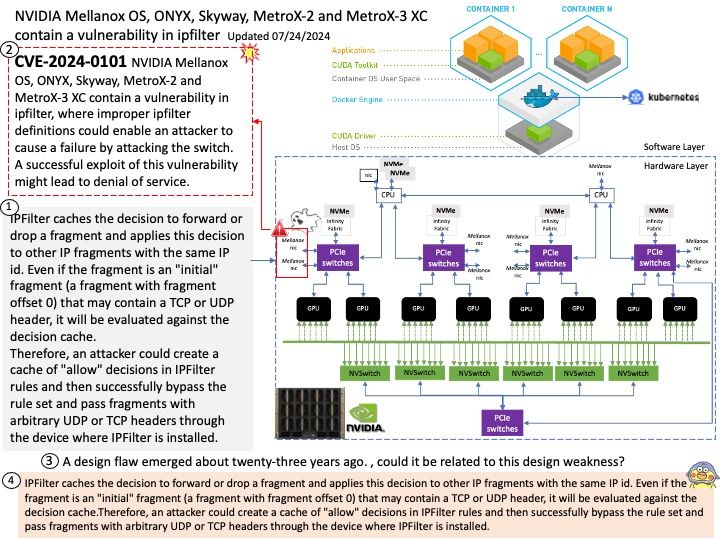
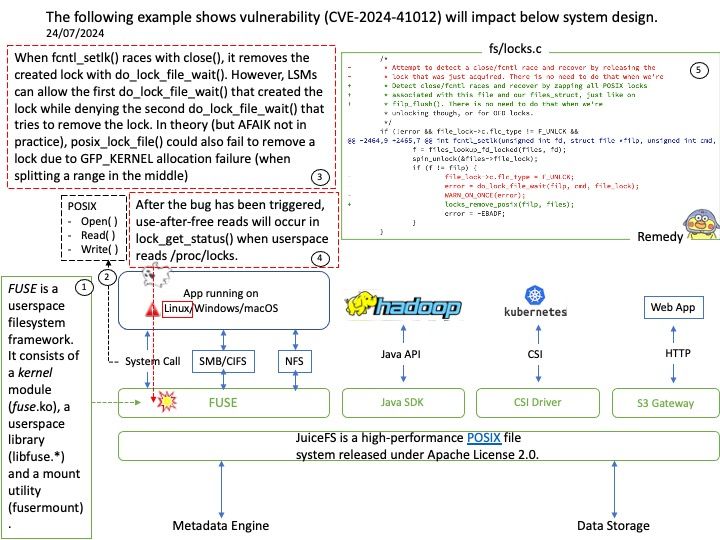
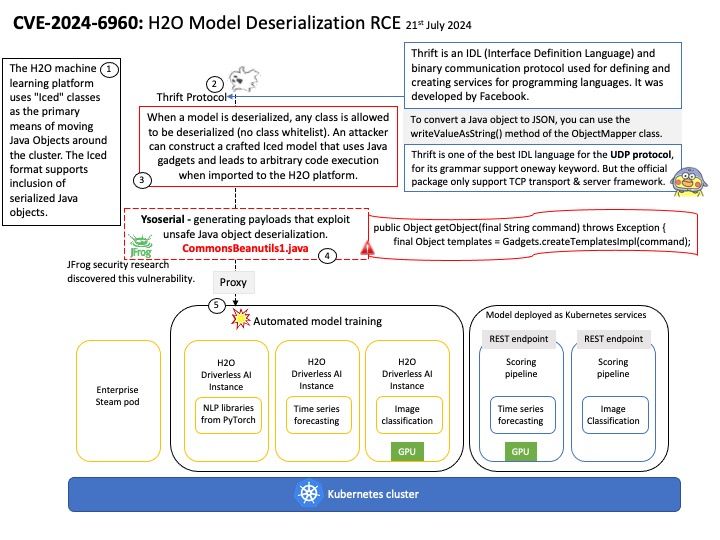
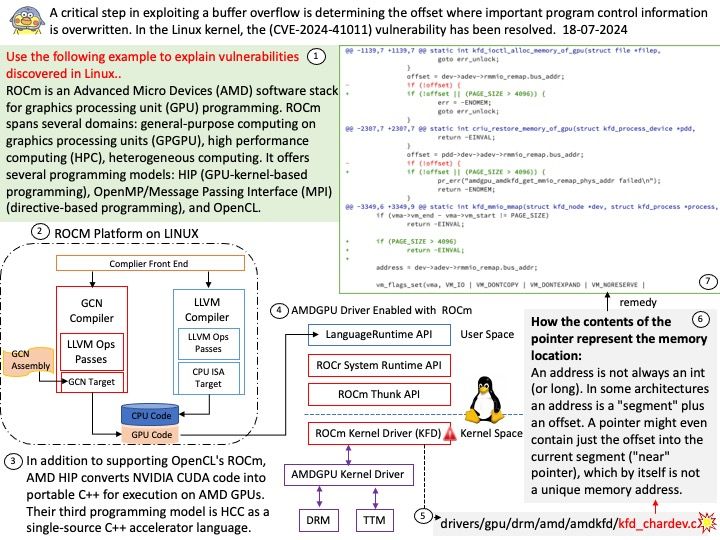
IPC:Shared Memory
Two processes comunicating via shared memory.
shm_server[.]c — simply creates the string and shared memory portion.
shm_client[.]c — attaches itself to the created shared memory portion and uses the string (printf.
Background: Podman, Podman Desktop, and other open standards-based container tools make Red Hat Enterprise Linux a powerful container host that delivers production-grade support, stability, and security features as well as a path forward to Kubernetes and Red Hat OpenShift.
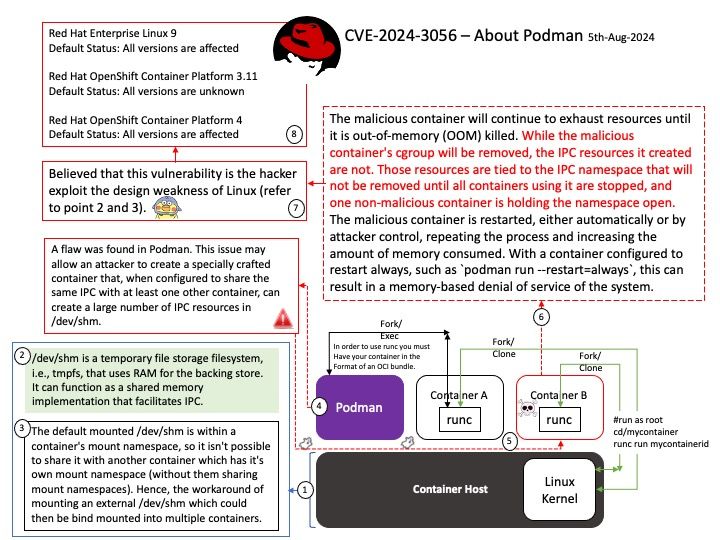
Vulnerability details: A flaw was found in Podman. This issue may allow an attacker to create a specially crafted container that, when configured to share the same IPC with at least one other container, can create a large number of IPC resources in /dev/shm. The malicious container will continue to exhaust resources until it is out-of-memory (OOM) killed. While the malicious container’s cgroup will be removed, the IPC resources it created are not. Those resources are tied to the IPC namespace that will not be removed until all containers using it are stopped, and one non-malicious container is holding the namespace open. The malicious container is restarted, either automatically or by attacker control, repeating the process and increasing the amount of memory consumed. With a container configured to restart always, such as `podman run –restart=always`, this can result in a memory-based denial of service of the system.
Official announcement: Please refer to the link for details – https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-3056