Preface: “Logic 0” and “logic 1” represent binary digits (0 and 1) or Boolean logic conditions (true and false). A vulnerability in the cryptography of Microsoft’s Netlogon process that allows an attack against Microsoft Active Directory domain controllers.
Background: The algorithm originally used to encrypt the logon process in Windows NT was 2DES. Thus design weakness found in this place. MS-NRPC uses an obscure setting known as AES-CFB8 (Advanced Encryption Standard – Cipher Feed Back 8 bit). However use of AES-CFB8 within MS-NRPC has an issue with the Initialisation Vector (IV) which should be a random number, but MS-NRPC has it fixed at a value of 16 bytes of zeros.
Impact: Tom Tervoort from Secura, he discovered there is a likelihood of one of every 256 keys used will create cipher text that has a value of all zeros. Whereby, a high possibility way to root AD server. To change the password, attackers use the message NetServerPasswordSet2 in MS-NRPC. It is possible to change a password by simply sending the frame with the preferred new password. The easiest approach is to remove the password or set it to a blank value – the hacker can now log in through a normal process.
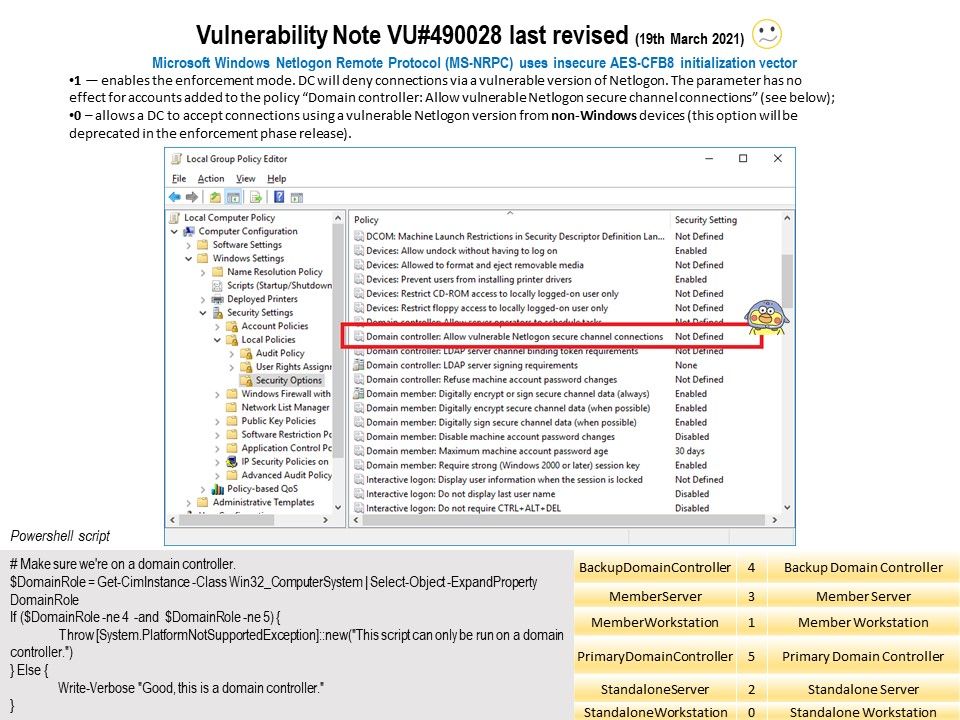
Since February 9, 2021 is the enforcement phase. And therefore, vendor will be enforce the following setttings.
- Enforces secure RPC usage for machine accounts on non-Windows based devices unless allowed by “Domain controller: Allow vulnerable Netlogon secure channel connections” group policy.
- Logging of Event ID 5829 will be removed. Since all vulnerable connections are denied, you will now only see event IDs 5827 and 5828 in the System event log.
Official announcement: https://kb.cert.org/vuls/id/490028