Preface: AI deployment is accelerated by hardware advancements (especially GPUs), ML platforms and MLOps for automation, the use of pre-trained models via transfer learning, containerization and orchestration for scalability, cloud infrastructure providing on-demand resources, and industry collaborations and specialized data partners to streamline various stages of the AI lifecycle.
Background: NVIDIA Triton Inference Server is an open-source inference serving platform whose primary goal is to simplify and accelerate the deployment of AI models in production environments. It aims to provide a unified platform capable of serving models from various machine learning frameworks, such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, ONNX Runtime, and custom backends, enabling flexibility and interoperability.
The “model name” parameter in NVIDIA Triton Inference Server is a crucial identifier used to specify which model a client wishes to interact with for inference requests.
Client API Usage: When using Triton client libraries (e.g., tritonclient[.]grpc or tritonclient[.]http), the model_name parameter is typically a required argument in functions used to send inference requests.
Both backends (Python and DALI) are part of Triton’s modular architecture. The Python backend often acts as a wrapper or orchestrator for other backends, including DALI.
Vulnerability details:
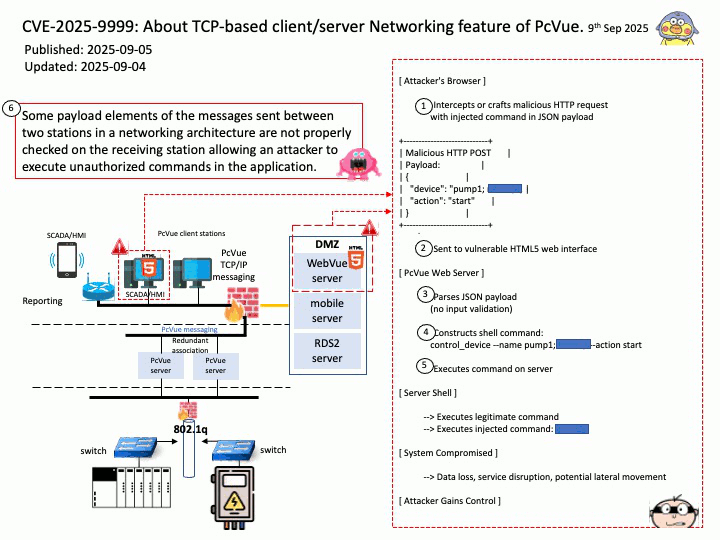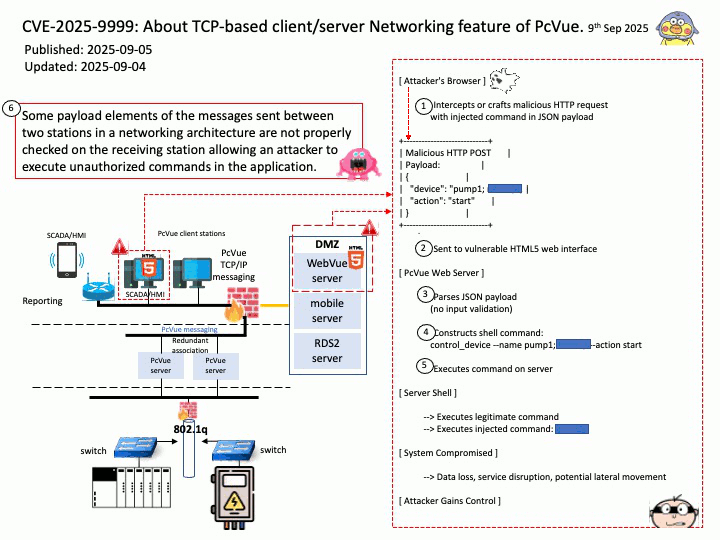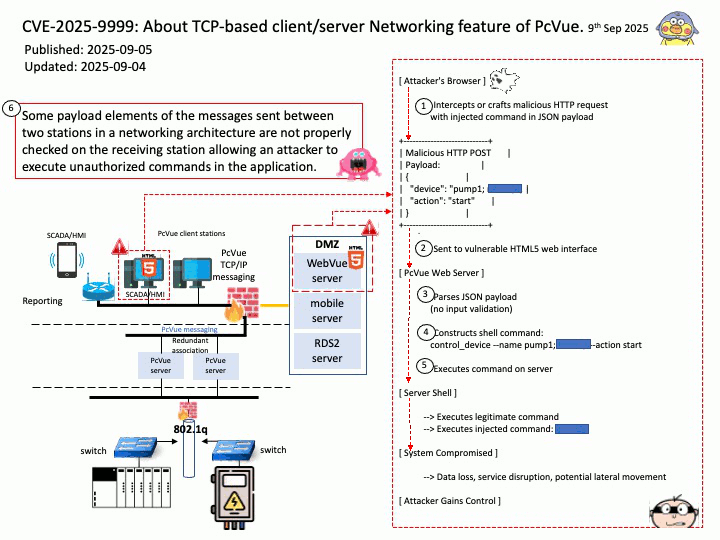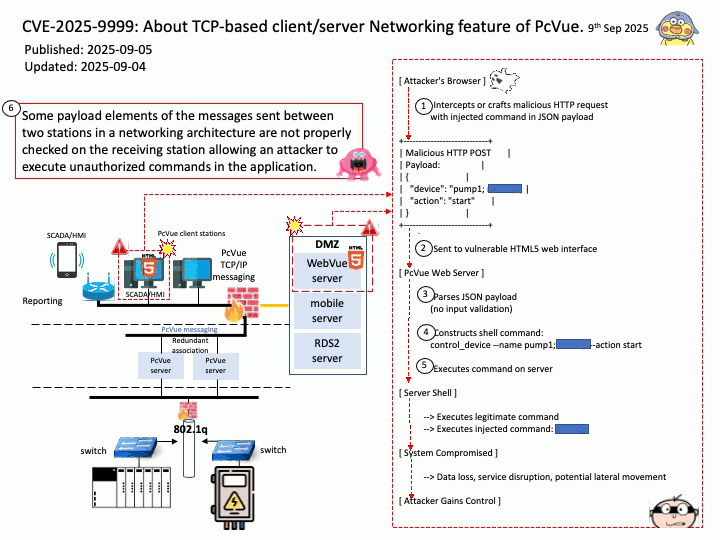
CVE-2025-23316 NVIDIA Triton Inference Server for Windows and Linux contains a vulnerability in the Python backend, where an attacker could cause a remote code execution by manipulating the model name parameter in the model control APIs. A successful exploit of this vulnerability might lead to remote code execution, denial of service, information disclosure, and data tampering.
CVE-2025-23268 VIDIA Triton Inference Server contains a vulnerability in the DALI backend where an attacker may cause an improper input validation issue. A successful exploit of this vulnerability may lead to code execution.
Official announcement: Please see the link for details –