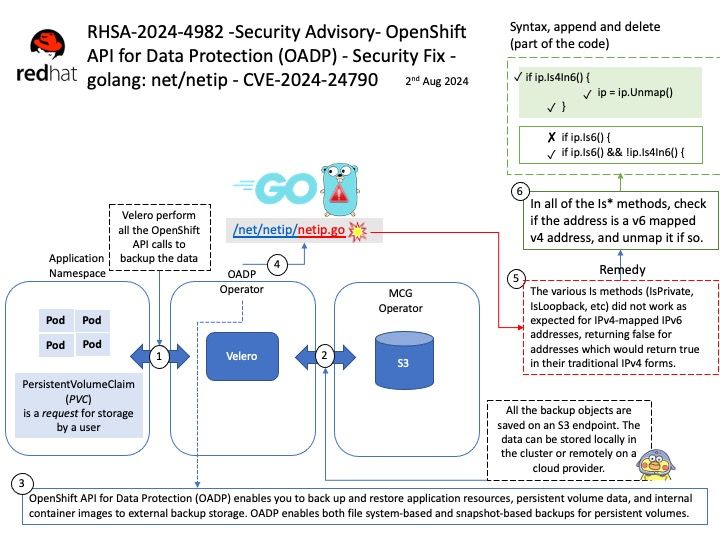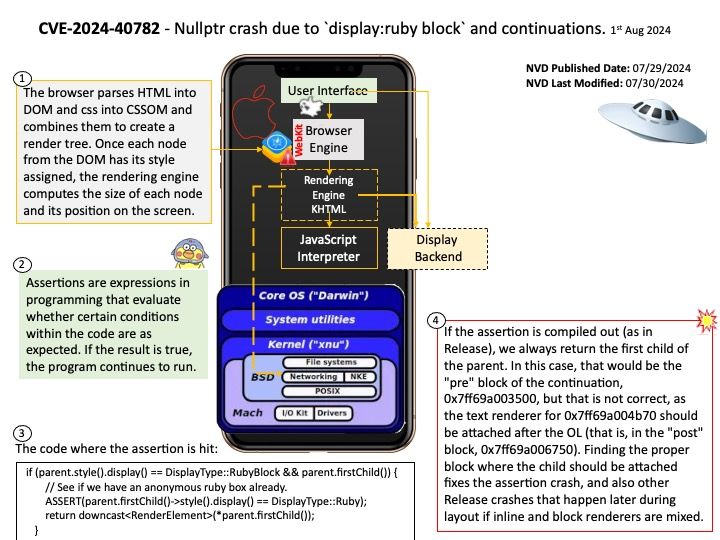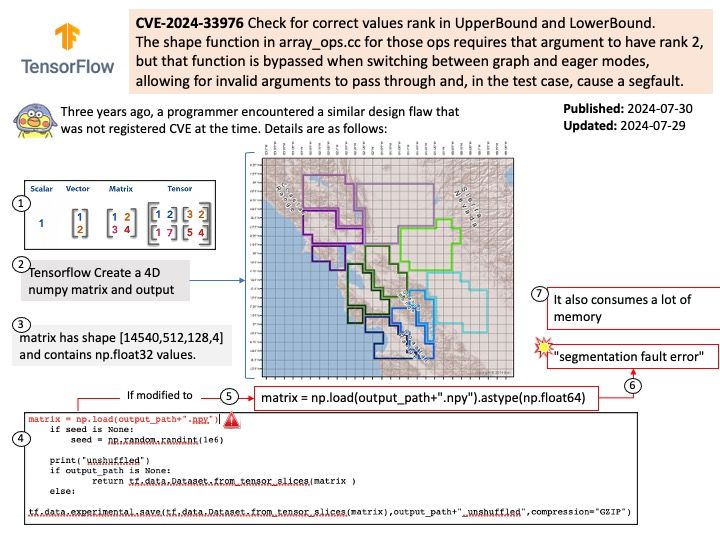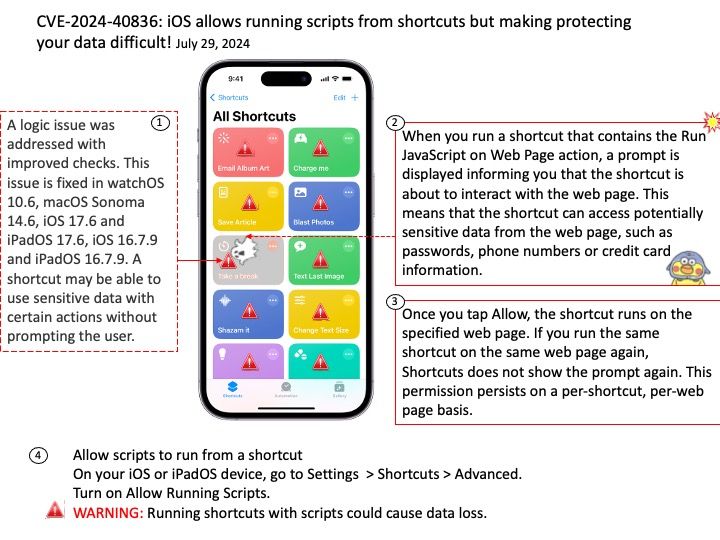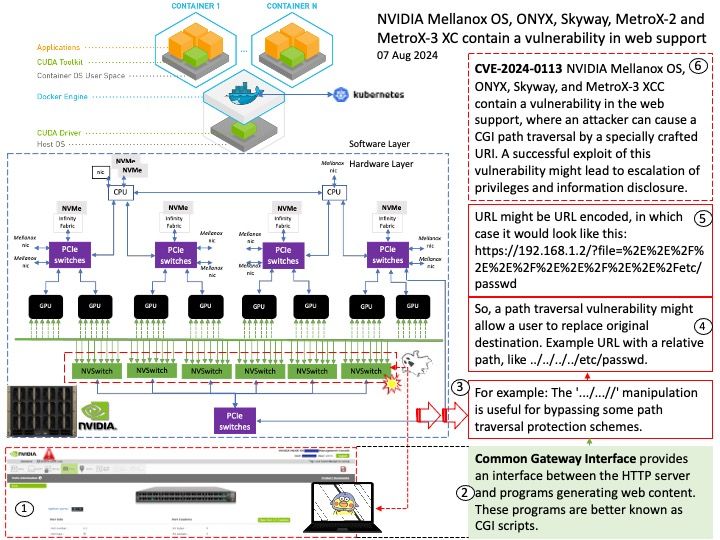
Preface: CGI is a standard protocol that allows web servers to execute external programs or scripts, typically written in languages like Perl or Python, in response to client requests.
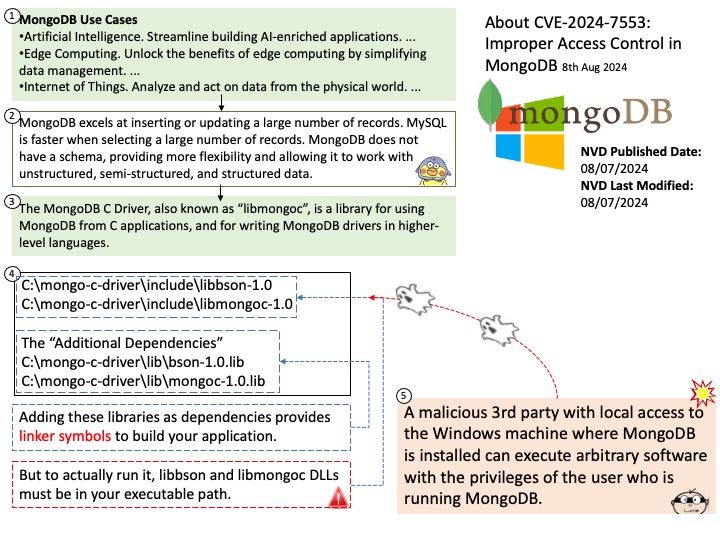
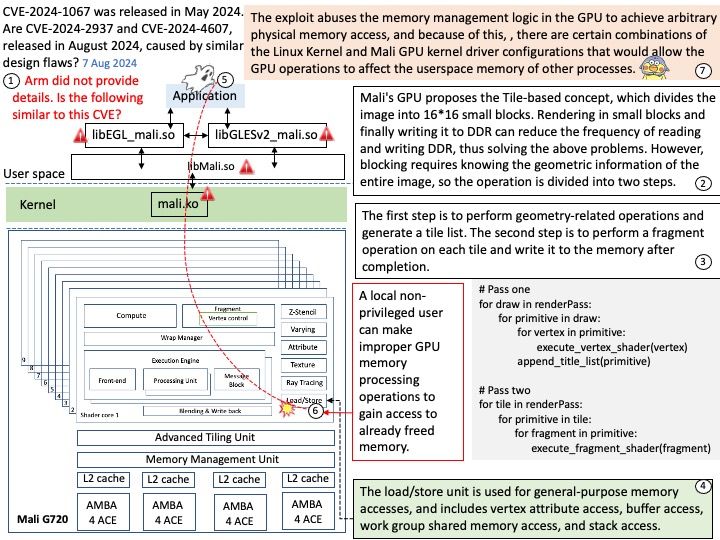
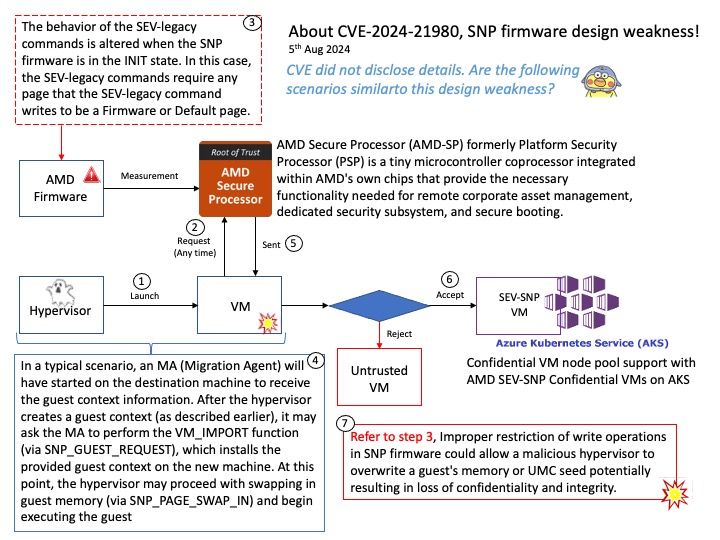
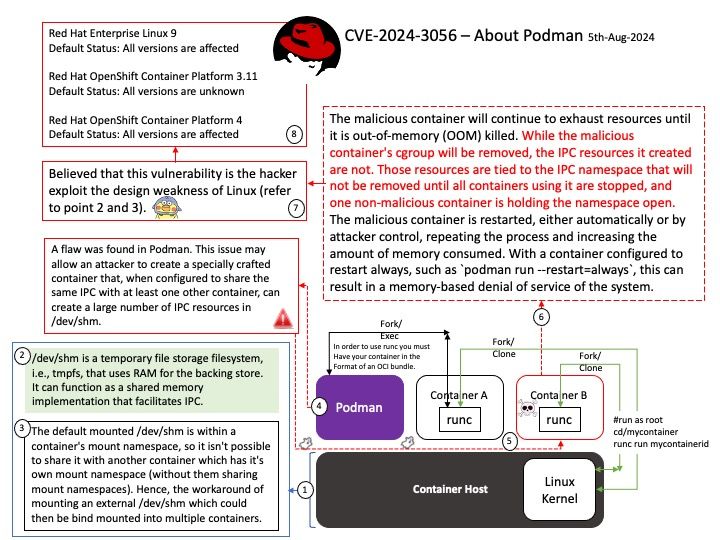
Path Traversal: Exploiting lax file path validation, attackers navigate outside the intended directory, accessing restricted files or directories.
Background: MLNX-OSis a next-generation switch operating system for data centers with storage, enterprise, high-performance computing and cloud fabrics. Building networks with MLNX-OS enables scaling to thousands of compute and storage nodes with monitoring and provisioning capabilities, whether they are InfiniBand or Virtual Protocol Interconnect (VPI).
NVIDIA Onyx, with its robust layer-3 protocol stack, built-in monitoring and visibility tools, and high-availability mechanisms, Onyx is an ideal network operating system for enterprise and cloud data centers.
The NVIDIASkyway gateway appliance provides 1.6Tb/s throughput, enabling scalable and efficient connectivity from InfiniBand data centers to external Ethernet-based infrastructures and storage.
The NVIDIAMetroX-3 XC long-haul system seamlessly and securely extends the reach of the NVIDIA Quantum InfiniBand networking platform, providing high data throughput, In-Network Computing, and native remote direct-memory access (RDMA) communications. Enhancing data security, MetroX-3 XC provides encrypted connectivity over long distances and dense wavelength-division multiplexing (DWDM) infrastructures.
Extending InfiniBand connectivity to 10 or 40 kilometers,. MetroX–2 systems enable high data throughput, native remote direct memory access (RDMA).
Vulnerability details: NVIDIA Mellanox OS, ONYX, Skyway, and MetroX-3 XCC contain a vulnerability in the web support, where an attacker can cause a CGI path traversal by a specially crafted URI. A successful exploit of this vulnerability might lead to escalation of privileges and information disclosure.
Official announcement: Please refer to the link for details – https://nvidia.custhelp.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/5563