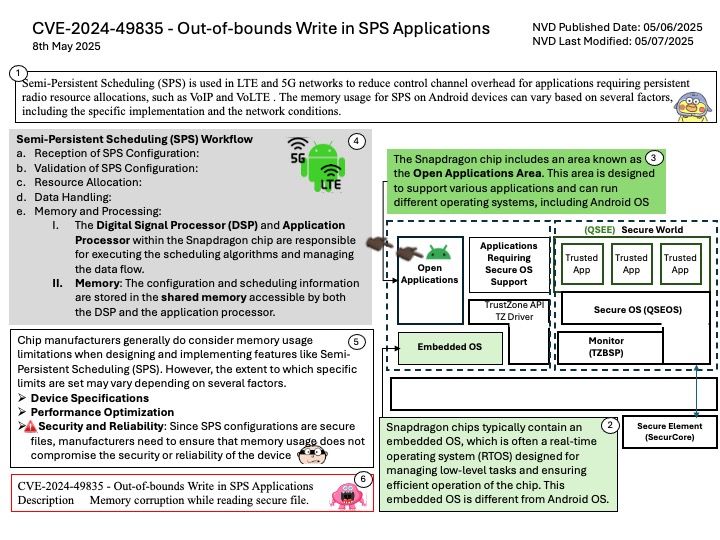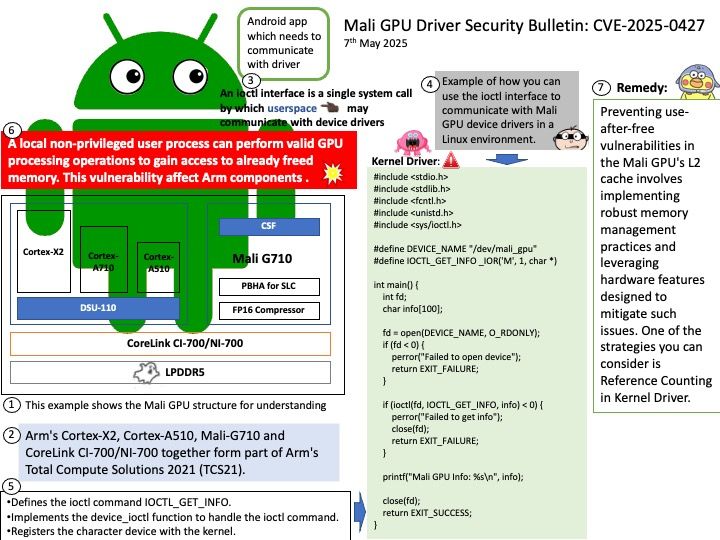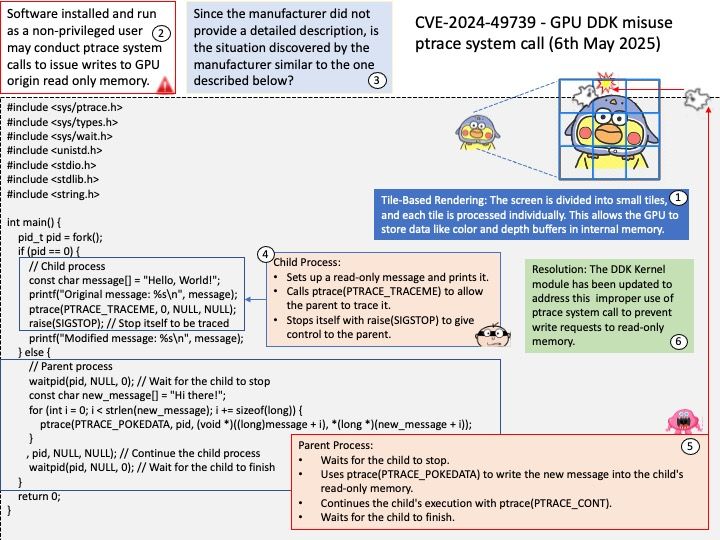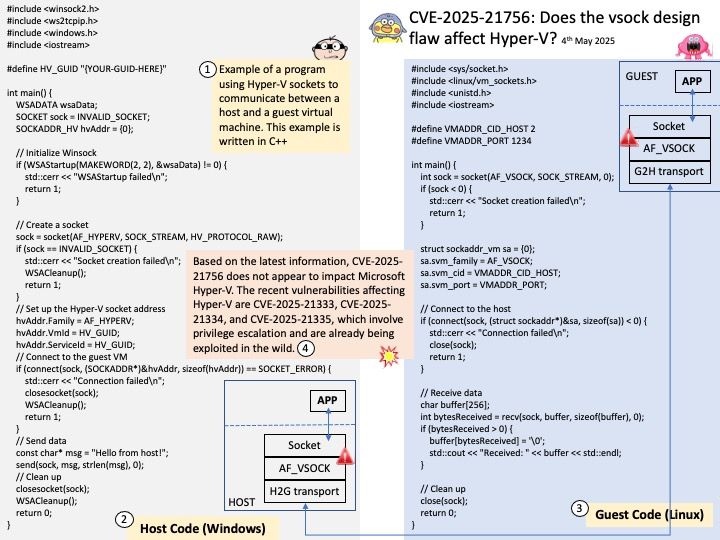
Preface: All systems based on the Linux kernel utilize the vmscan[.]c file for memory management. This file is integral to the kernel’s memory reclamation process, ensuring efficient use of system memory across various Linux distributions.
Background: The vmscan[.]c file in the Linux kernel is responsible for managing memory reclamation. It contains functions that help the system reclaim memory by scanning and freeing up pages that are no longer in use. This process is crucial for maintaining system performance and preventing memory shortages.
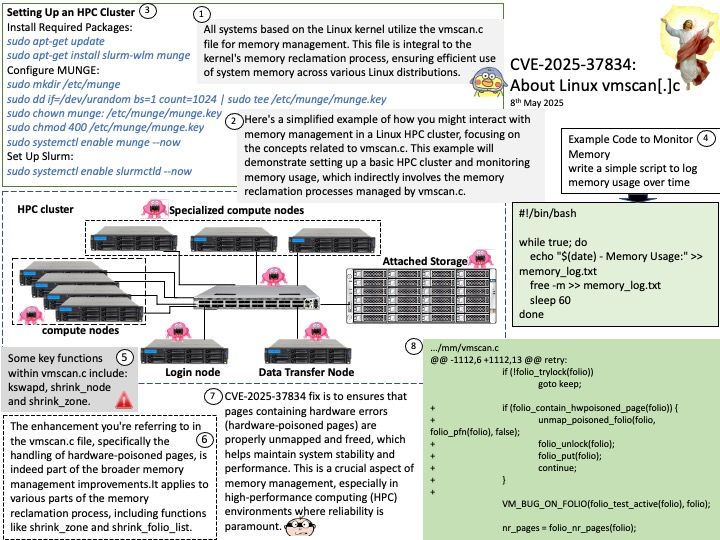
Some key functions within vmscan.c include:
kswapd: A kernel thread that periodically scans and frees up memory pages.
shrink_node: This function attempts to reclaim memory from a specific node.
shrink_zone: It works on reclaiming memory from a specific zone within a node.
These functions work together to ensure that the system has enough free memory to operate efficiently.
Vulnerability details: mm/vmscan: don’t try to reclaim hwpoison folio. The vulnerability has been resolved.
The enhancement in the vmscan[.]c file, specifically the handling of hardware-poisoned pages, is indeed part of the broader memory management improvements. This enhancement is not limited to the shrink_node function alone. It applies to various parts of the memory reclamation process, including functions like shrink_zone and shrink_folio_list.
Official announcement: Please see the link for details – https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2025-37834