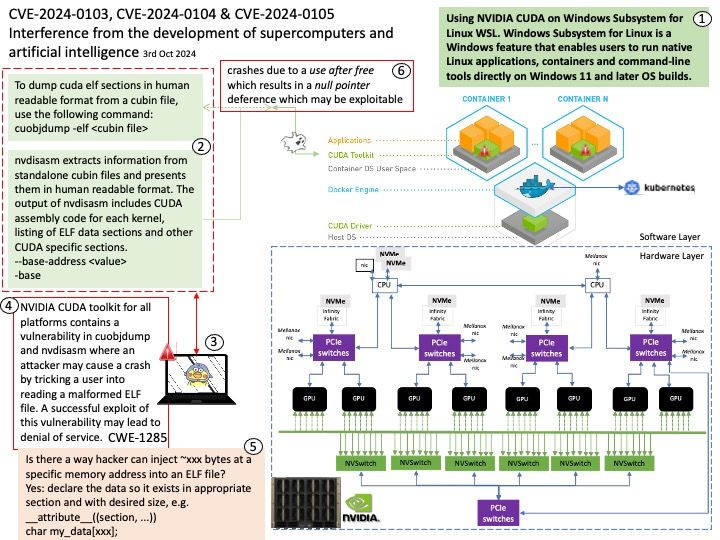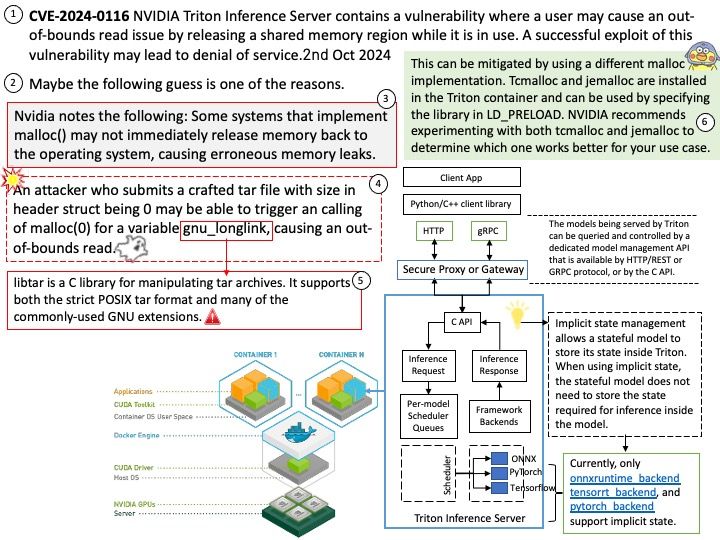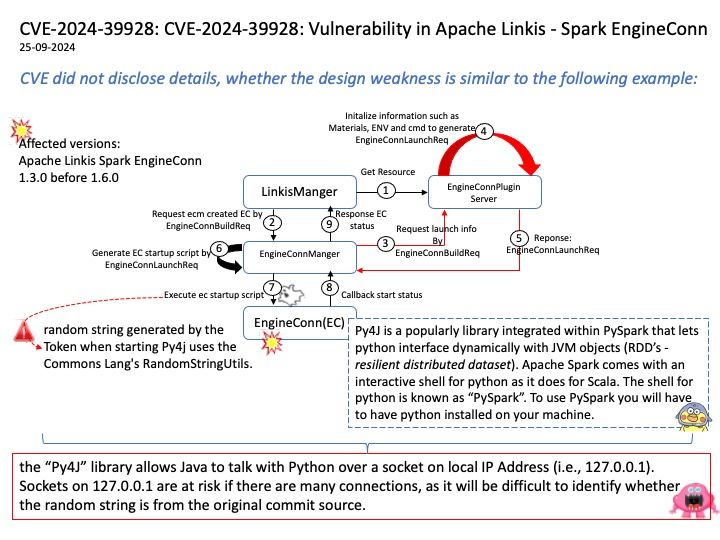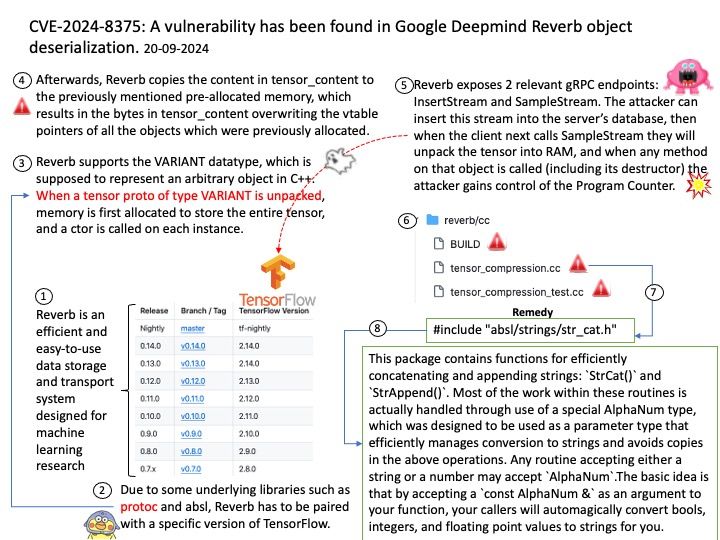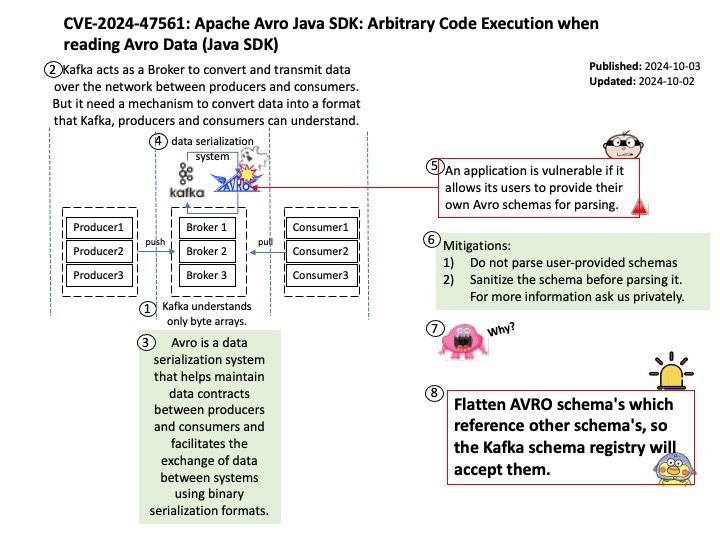
Preface: Kafka understands only byte arrays. Kafka acts as a Broker to convert and transmit data over the network between producers and consumers. But it need a mechanism to convert data into a format that Kafka, producers and consumers can understand.
Background: Apache Avro is a powerful data serialization framework that provides many useful features. It uses the AVRO file format, which is a compact binary format suitable for evolving data schemas. For example, it supports schema enforcement and schema transformations, which are essential for data integrity and compatibility.
Vulnerability details: Schema parsing in the Java SDK of Apache Avro 1.11.3 and previous versions allows bad actors to execute arbitrary code. Users are recommended to upgrade to version 1.11.4 or 1.12.0, which fix this issue.
Official announcement: Please refer to the link for details – https://lists.apache.org/thread/c2v7mhqnmq0jmbwxqq3r5jbj1xg43h5x