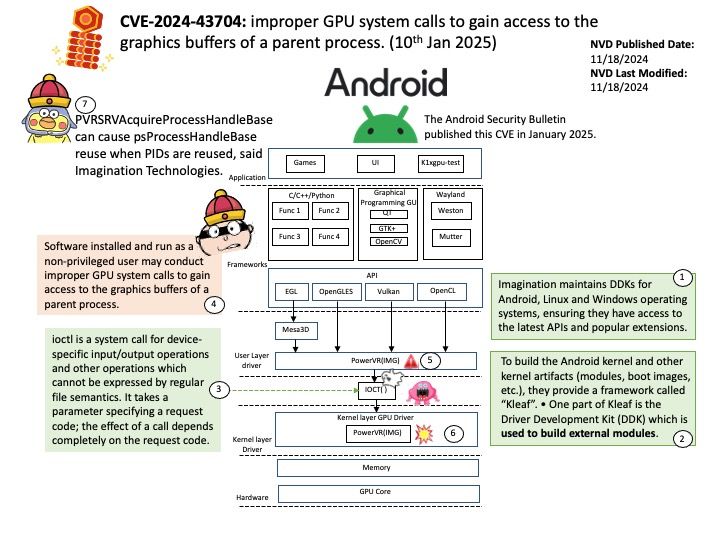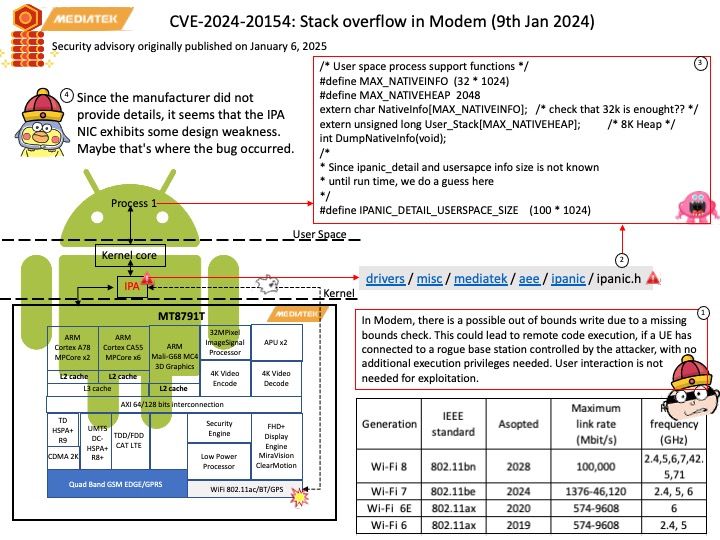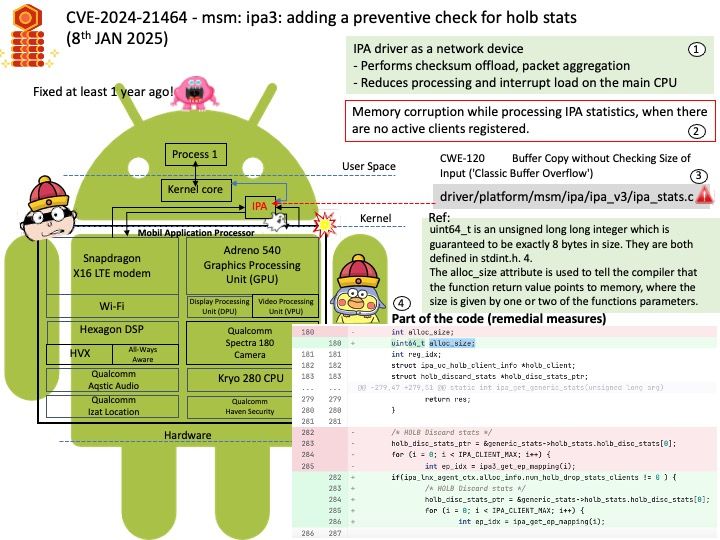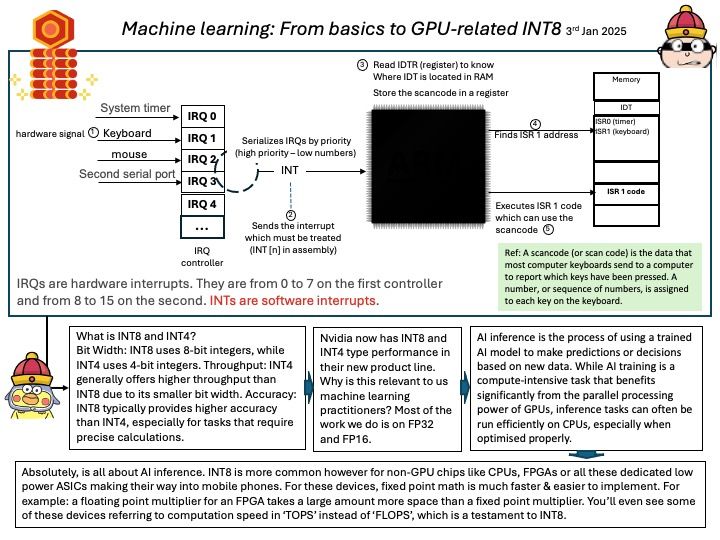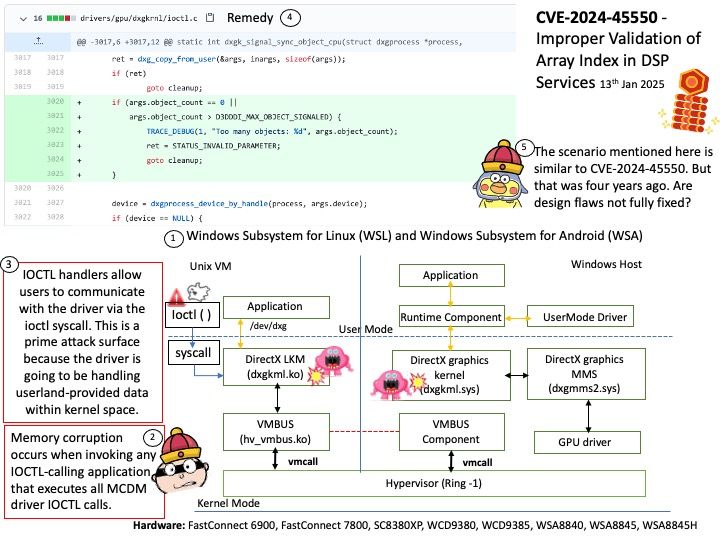
Preface: IOCTL handlers allow users to communicate with the driver via the ioctl syscall. This is a prime attack surface because the driver is going to be handling userland-provided data within kernel space.
Background: dxgkrnl is a driver for Hyper-V virtual compute devices, such as vGPU devices, which are projected to a Linux virtual machine (VM) by a Windows host. dxgkrnl works in context of WDDM (Windows Display Driver Model)for GPU or MCDM (Microsoft Compute Driver Model) for non-GPU devices.
WDDM/MCDM consists of the following components:
Graphics or Compute applications
A graphics or compute user mode API (for example OpenGL, Vulkan, OpenCL, OpenVINO, OneAPI, CUDA, DX12, …)
User Mode Driver (UMD), written by a hardware vendor
optional libdxg library helping UMD portability across Windows and Linux
dxgkrnl Linux kernel driver (this driver)
Kernel mode port driver on the Windows host (dxgkrnl.sys / dxgmms*.sys)
Kernel Mode miniport driver (KMD) on the Windows host, written by a hardware vendor running on the Windows host and interfacing with the hardware device.
Vulnerability details: Memory corruption occurs when invoking any IOCTL-calling application that executes all MCDM driver IOCTL calls.
Official announcement: Please refer to the link for details –