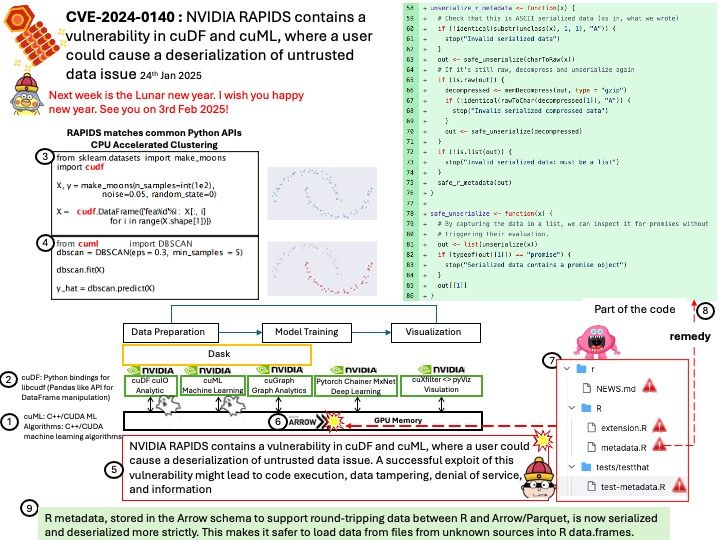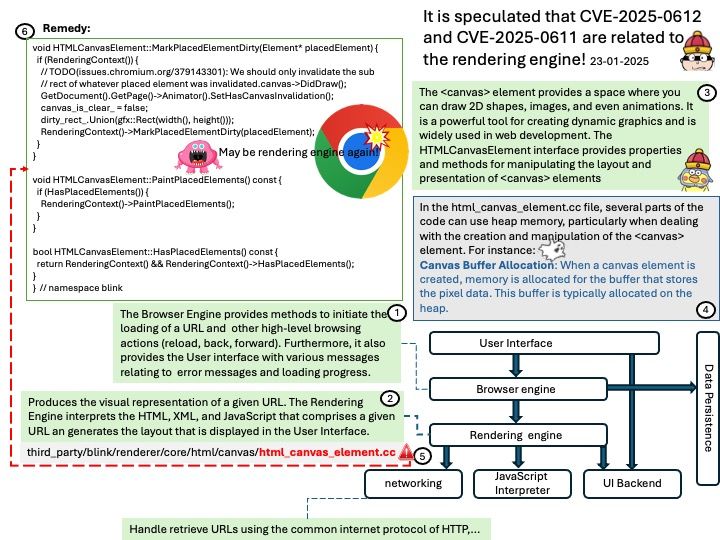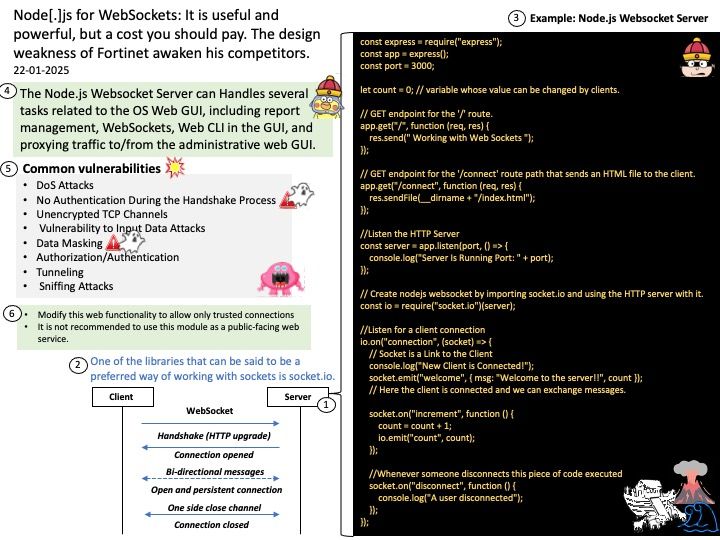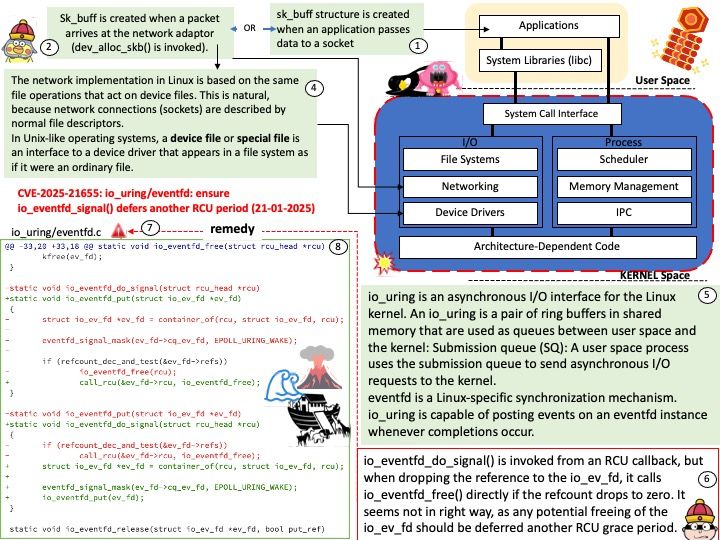
Preface: instruction cache (I-cache) and a data cache (D-cache)
This is the smallest and fastest type of cache memory. It’s embedded directly into the CPU, allowing it to operate at the same speed as the CPU. The L1 cache is typically divided into two parts: one for storing instructions (L1i) and one for storing data (L1d).
Background: Instruction prefetching can boost execution performance by fetching data before it is needed. The Cortex-X4 core supports the AArch64 prefetch memory instructions, PRFM PLI, into the L1 instruction cache or L2 cache. These instructions signal to the memory system that memory accesses from a specified address are likely to occur soon. The memory system takes actions that aim to reduce the latency of memory accesses when they occur. The PRFM PLD and PRFM PST instructions perform preloading in the L1 data cache, L2 cache, or L3 cache. PRFM PLD and PRFM PST instructions translate through the Data TLB. The PRFM PLI instruction performs preloading to the L1 instruction cache and L2 cache. Instruction preloading is performed in the background. PRFM PLI instructions translate through the Instruction TLB.
Vulnerability details: An issue has been identified in some Arm-based CPUs that may allow an unprivileged context to trigger a data memory-dependent prefetch engine to fetch the contents of a privileged location (for which it does not have read permission) and consume those contents as an address that is also dereferenced.
Note that this issue does not affect guest-to-guest and guest-to-hypervisor isolation guarantees. Likewise, in configurations with RME enabled, Granule Protection Checks (GPC) are honoured by the prefetcher.
Official details: Please refer to the link for details –
https://developer.arm.com/Arm%20Security%20Center/Arm%20CPU%20Vulnerability%20CVE-2024-7881