Preface: What is the difference between FreeRTOS and Cmsis-RTOS?
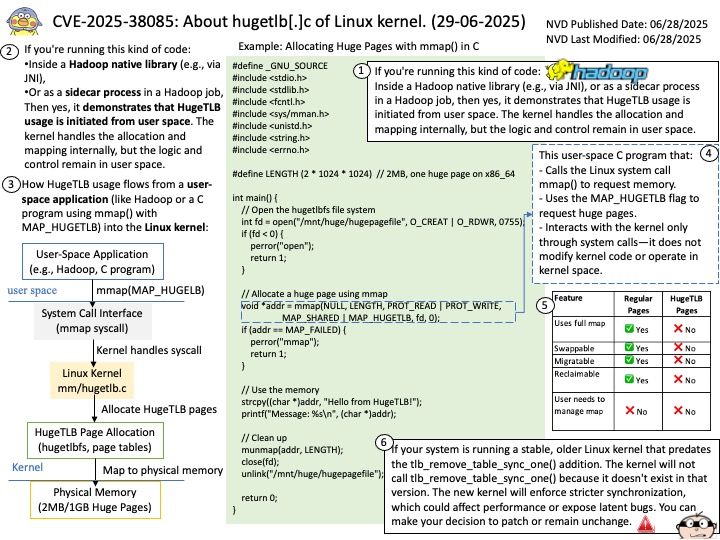
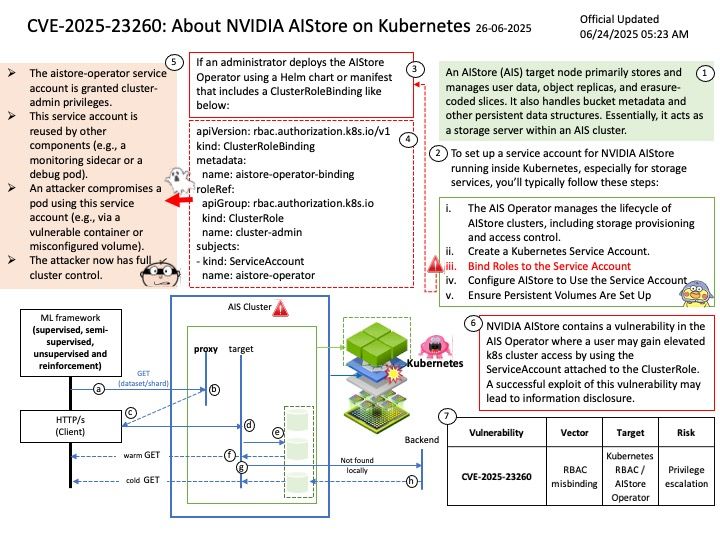
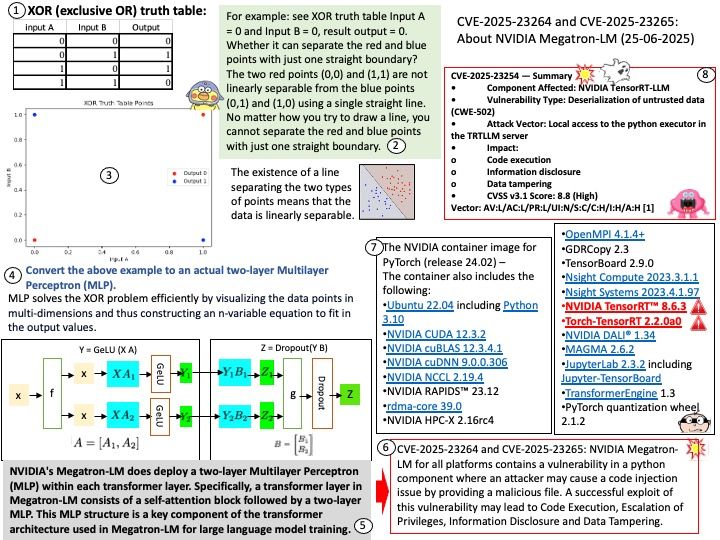
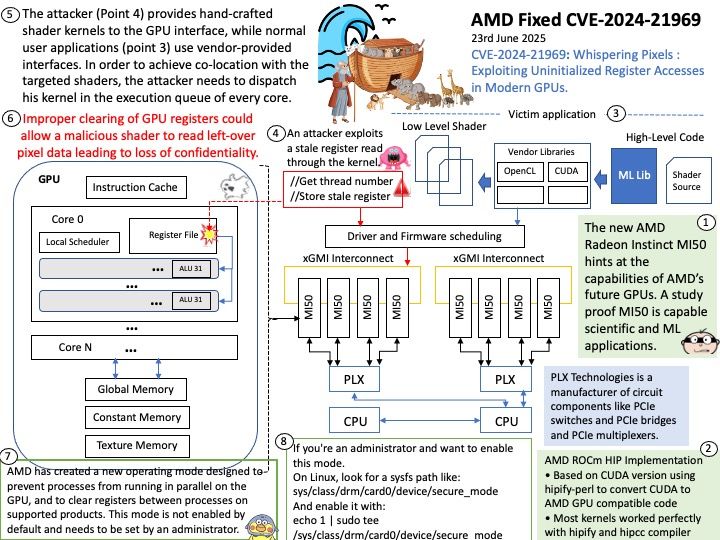
Basically FreeRTOS is a RTOS, while CMSIS-RTOS is only a wrapper for any RTOS (like FreeRTOS, CMSIS-RTOS RTX or anything you want). CMSIS-RTOS is an API that enables consistent software layers with middleware and library components. Mbed TLS aims to provide a set of powerful and flexible cryptographic and security building blocks, mainly for embedded systems, focusing on ease of integration and security. The design objective strives to be lean, prioritizing readability, documentation and testability, while minimizing dependencies and providing a loosely coupled architecture. This allows developers to integrate only the necessary components without the overhead of the entire library.
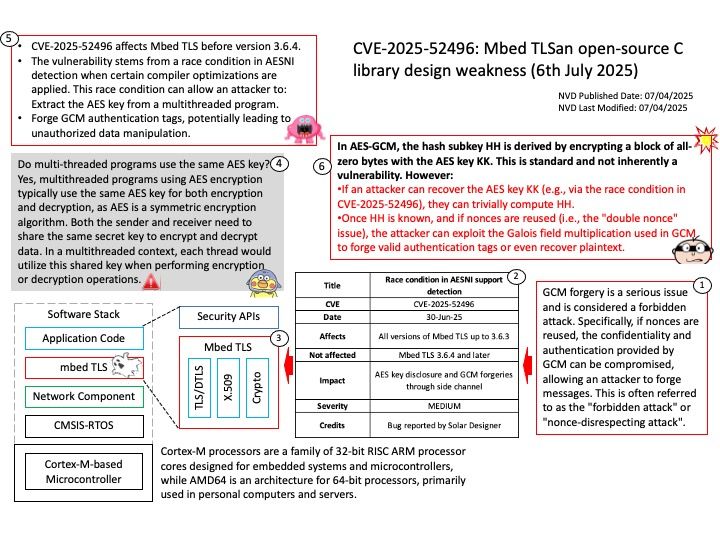
Background: Do multi-threaded programs use the same AES key?
Yes, multithreaded programs using AES encryption typically use the same AES key for both encryption and decryption, as AES is a symmetric encryption algorithm. Both the sender and receiver need to share the same secret key to encrypt and decrypt data. In a multithreaded context, each thread would utilize this shared key when performing encryption or decryption operations.
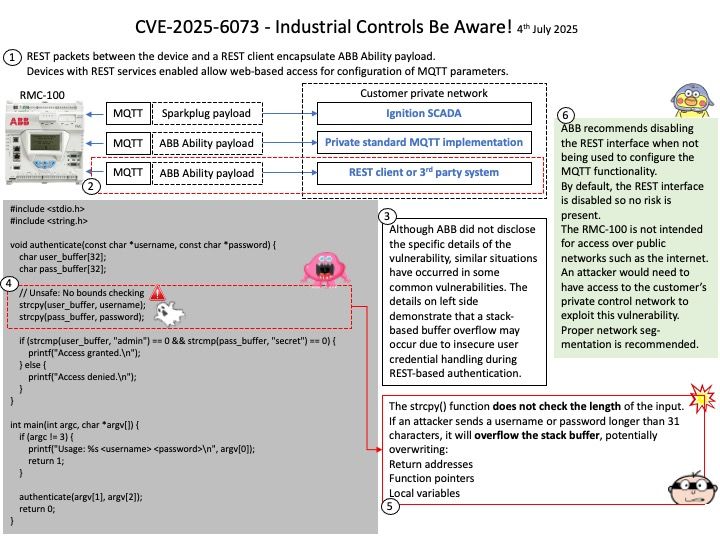
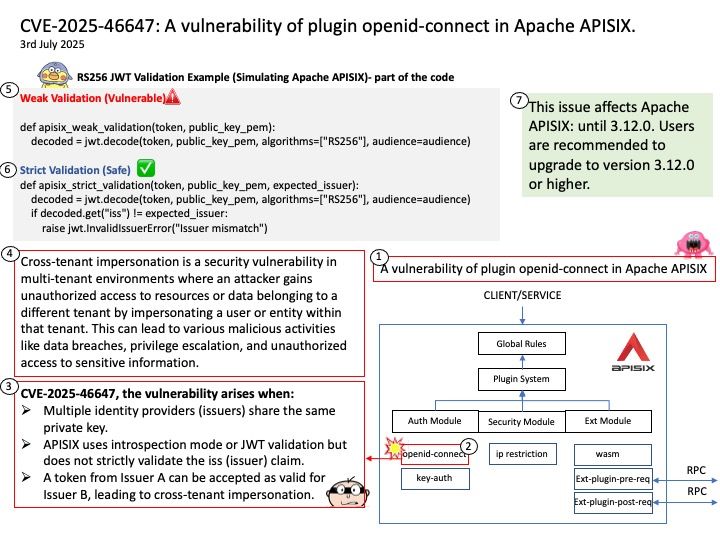
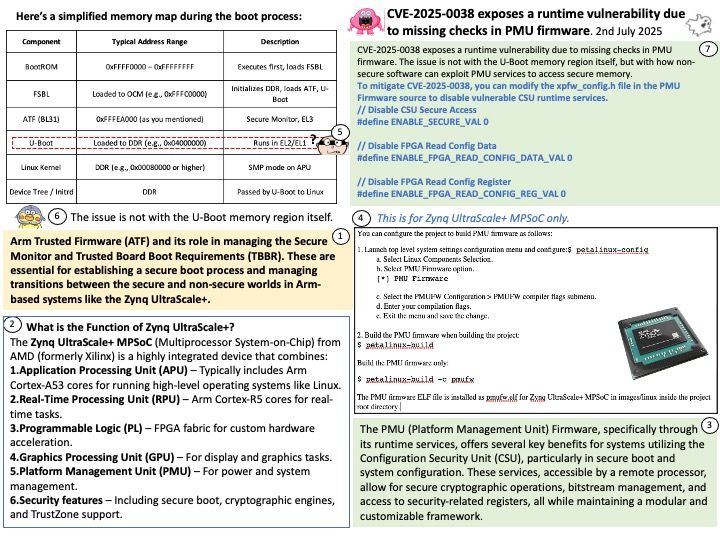
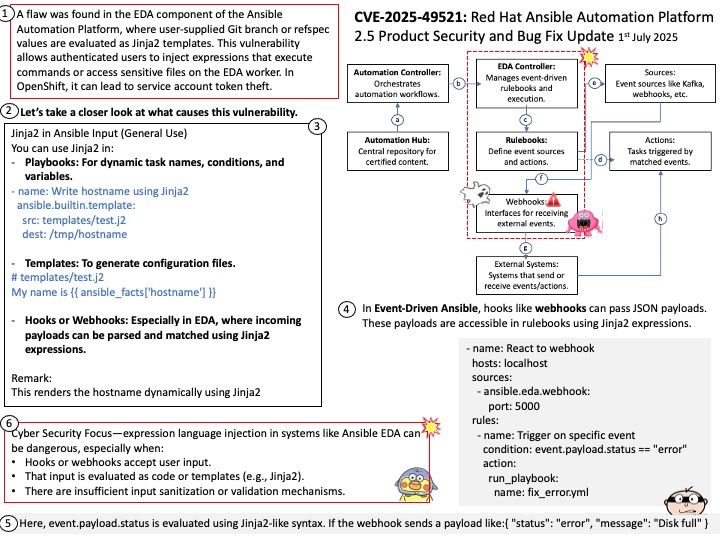
Vulnerability details: Mbed TLS before 3.6.4 has a race condition in AESNI detection if certain compiler optimizations occur. An attacker may be able to extract an AES key from a multithreaded program, or perform a GCM forgery.
Official announcement: Please refer to the link for details – https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2025-52496