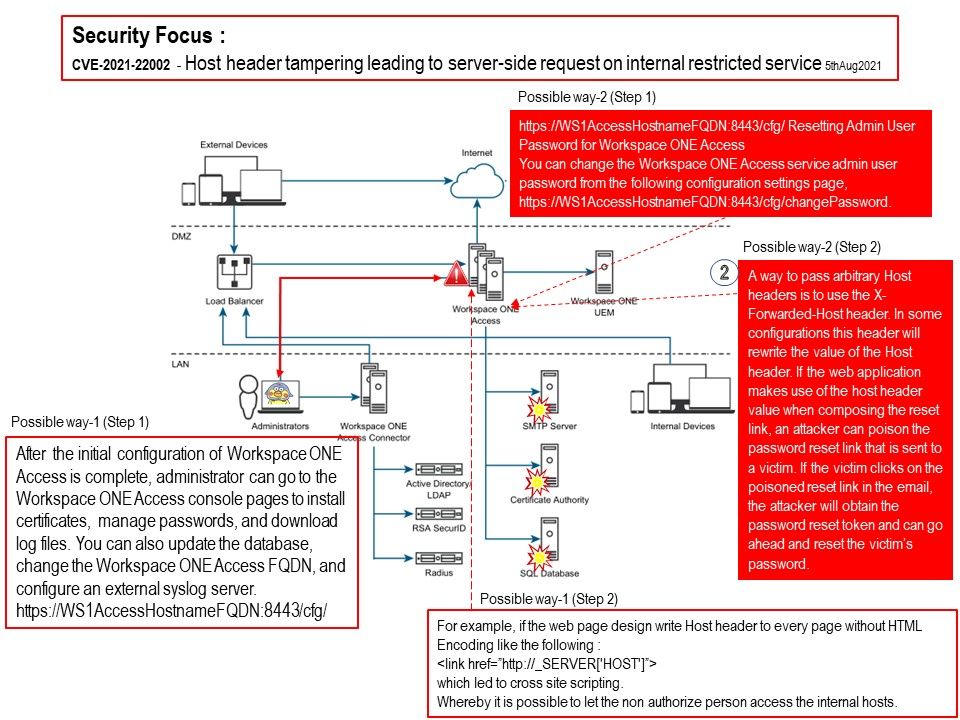
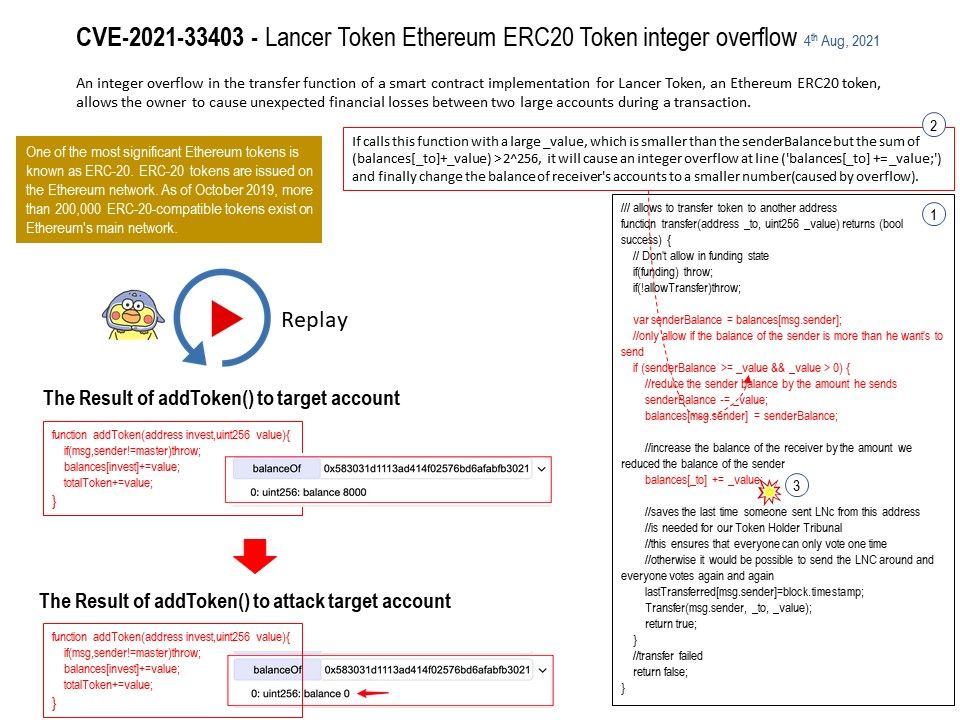
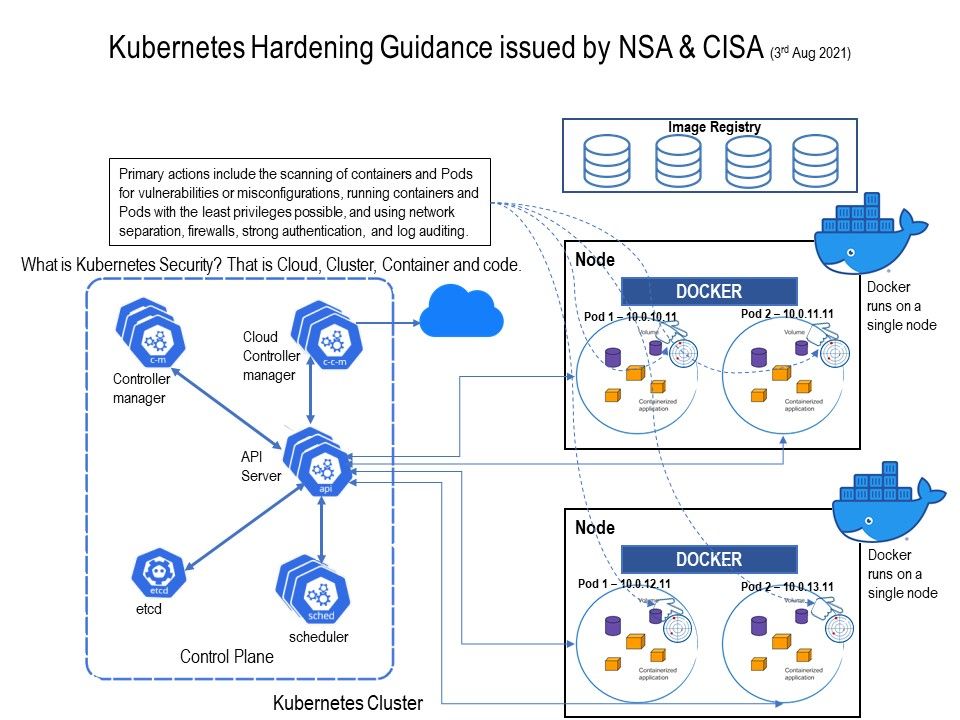
.jpg?width=1920&height=1080&fit=bounds)
Preface: Since xml data is irregular and verbose, it can impact both query processing and data exchange.
Background: XMill is a tool for compressing XML data efficiently. It is based on a regrouping strategy that leverages the effect of highly-efficient compression techniques in compressors such as gzip (Please refer to attached diagram for details).
The architecture od XMill is based on the 3 principles:
– The XML file is parsed by a SAX parser that sends tokens to the path processor.
– Every XML token (tag, attribute, or data value) is assigned to a container.
– Tags and attributes forming the XML structure, are senf to the structure container. Data values are send to various data containers.
Vulnerability details: Xmill contains four heap-based buffer overflow vulnerabilities: TALOS-2021-1290 (CVE-2021-21825), TALOS-2021-1291 (CVE-2021-21826 – CVE-2021-21828), TALOS-2021-1292 (CVE-2021-21829) and TALOS-2021-1293 (CVE-2021-21830). These could all be exploited by an adversary to gain the ability to execute code on the victim machine. Since XMill tool contains multiple vulnerabilities. Please refer to Cisco Talos official link for details – https://blog.talosintelligence.com/2021/08/vuln-spotlight-att.html
Additional details: Only a subset of these Xmill vulnerabilities directly affects Schenider’s Control Expert software:
TALOS-2021-1290, TALOS-2021-1291, TALOS-2021-1292 and TALOS-2021-1293, which all directly affect Control Expert and are based around XML decompression within the software.
Reference: EcoStruxure Control Expert is a unique software platform to increase design productivity and performance of your Modicon M340, M580 and M580 Safety, Momentum, Premium, Quantum applications.