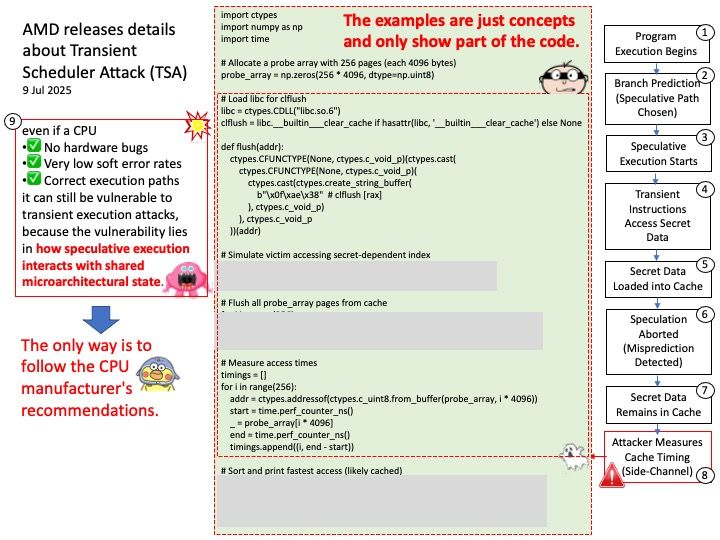
Preface: CPU transient instructions refer to instructions that are speculatively executed by a processor’s out-of-order execution engine, but which may ultimately be discarded and not reflected in the processor’s architectural state. These instructions are executed based on predictions about control flow or data dependencies, and if the prediction is incorrect, the results of these transient instructions are discarded.
Background: Transient Scheduler Attacks (TSA) are new speculative side channel attacks related to the execution timing of instructions under specific microarchitectural conditions. In some cases, an attacker may be able to use this timing information to infer data from other contexts, resulting in information leakage.
Vulnerability details:
CVE-2024-36350 – A transient execution vulnerability in some AMD processors may allow an attacker to infer data from previous stores, potentially resulting in the leakage of privileged information.
CVE-2024-36357 – A transient execution vulnerability in some AMD processors may allow an attacker to infer data in the L1D cache, potentially resulting in the leakage of sensitive information across privileged boundaries.
CVE-2024-36348 – A transient execution vulnerability in some AMD processors may allow a user process to infer the control registers speculatively even if UMIP[3] feature is enabled, potentially resulting in information leakage.
CVE-2024-36349 – A transient execution vulnerability in some AMD processors may allow a user process to infer TSC_AUX even when such a read is disabled, potentially resulting in information leakage.
Official announcement: Please see the link for details –
https://www.amd.com/en/resources/product-security/bulletin/amd-sb-7029.html