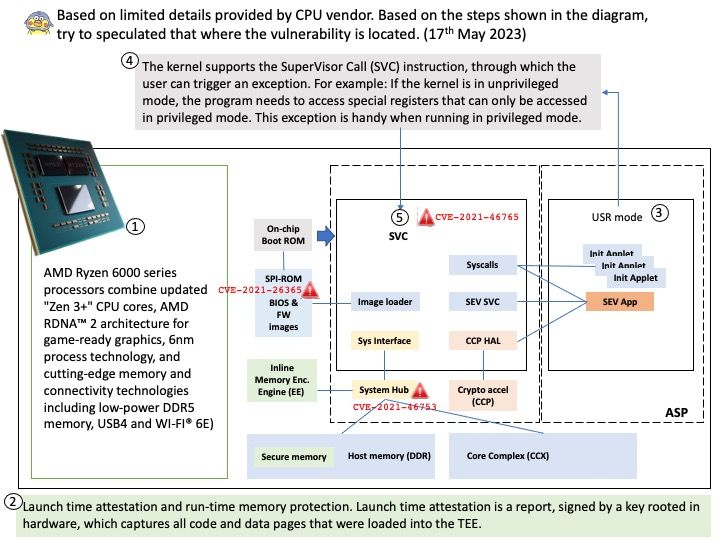
Preface: Based on limited details provided by CPU vendor. Based on the steps shown in the diagram, try to speculated that where the vulnerability is located.
Background: With the introduction of the Ryzen 5000-series Zen 3, AMD leads in gaming performance (especially in single-threaded performance). Announced on January 4, 2022, the Ryzen 6000 mobile-specific series of processors uses TSMC’s modestly altered Zen3+ cores on the 6nm process, claiming up to 15% (typically 10%) performance gains (supposedly from frequency rather than IPC (instructions per clock cycle)).
Ref: Because the IPC varies depending on workload, it’s not a straightforward number.
The clock frequency, on the other hand, generally only varies when there are thermal or power constraints (thermal throttling, TDP limiting).
The AMD secure processor (ASP), also known as platform security processor (PSP), is an isolated ARM processor that runs independently from the main x86 cores of the platform. ASP executes its own firmware, and hosts security sensitive components that can run without being affected by the main system workload.
Remark: The kernel supports the SuperVisor Call (SVC) instruction, through which the user can trigger an exception. For example: If the kernel is in unprivileged mode, the program needs to access special registers that can only be accessed in privileged mode. This exception is handy when running in privileged mode.
Vulnerability details (see below):
CVE-2021-26365 – Certain size values in firmware binary headers could trigger out of bounds reads during signature validation, leading to denial of service or potentially limited leakage of information about out-of-bounds memory contents.
CVE-2021-46753 – Failure to validate the length fields of the ASP (AMD Secure Processor) sensor fusion hub headers may allow an attacker with a malicious Uapp or ABL to map the ASP sensor fusion hub region and overwrite data structures leading to a potential loss of confidentiality and integrity.
CVE-2021-46765 – Insufficient input validation in ASP may allow an attacker with a compromised SMM to induce out-of-bounds memory reads within the ASP, potentially leading to a denial of service.
Official details: For details, please refer to the remedial measures released by AMD – https://www.amd.com/en/resources/product-security/bulletin/amd-sb-4001.html