Preface: The traditional content distribution network (CDN) can no longer meet the specifications of 5G networks because it requires high bandwidth, low latency and on demand massive connections. The bottlenecks of traditional CDN cannot been resolved the rapidly growth in video traffic, rate, and cost.
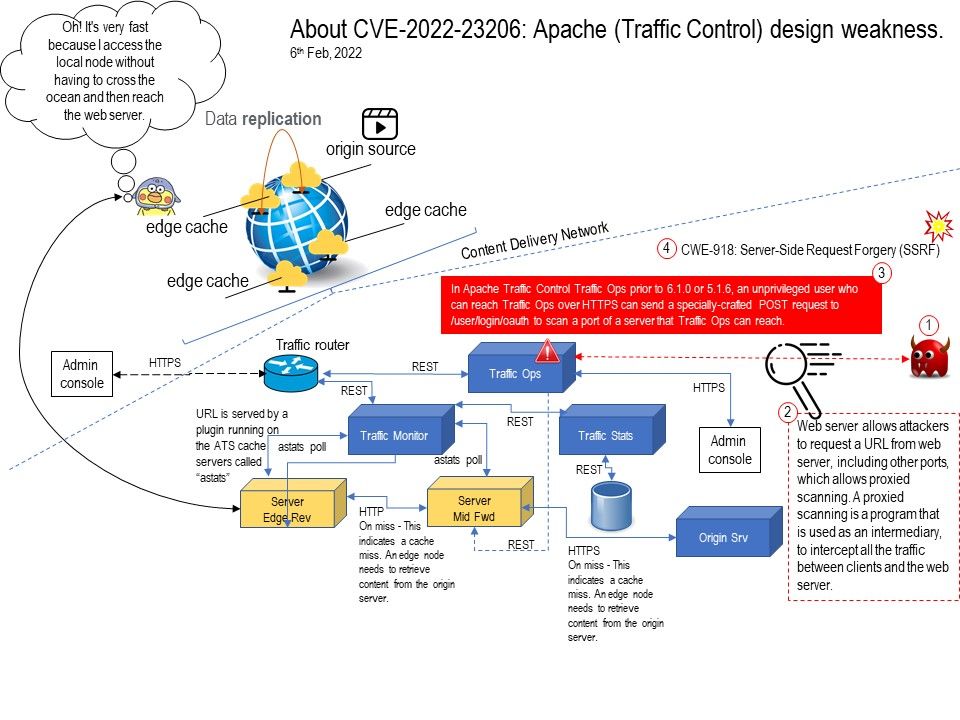
Background: Apache Traffic Server™ software is a fast, scalable and extensible HTTP/1.1 and HTTP/2 compliant caching proxy server. Traffic Control is a control plane for a CDN (Content Delivery Network).
In addition to being an HTTP proxy, Apache Traffic Server™ is also an HTTP cache. Traffic Server can cache any octet stream, although it currently supports only those octet streams delivered by the HTTP protocol. When such a stream is cached (along with the HTTP protocol headers) it is termed an object in the cache. Each object is identified by a globally unique value called a cache key.
Traffic Ops is the tool for administration (configuration and monitoring) of all components in a Traffic Control CDN. Traffic Portal uses the Traffic Ops API to manage servers, Cache Groups, Delivery Services, etc.
Vulnerability details: In Apache Traffic Control Traffic Ops prior to 6.1.0 or 5.1.6, an unprivileged user who can reach Traffic Ops over HTTPS can send a specially-crafted POST request to /user/login/oauth to scan a port of a server that Traffic Ops can reach.
Weakness Enumeration: CWE-918: Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF). For possible ways to trigger the specified vulnerability, please refer to the attached image.
Official announcement: https://lists.apache.org/thread/lsrd2mqj29vrvwsh8g0d560vvz8n126f