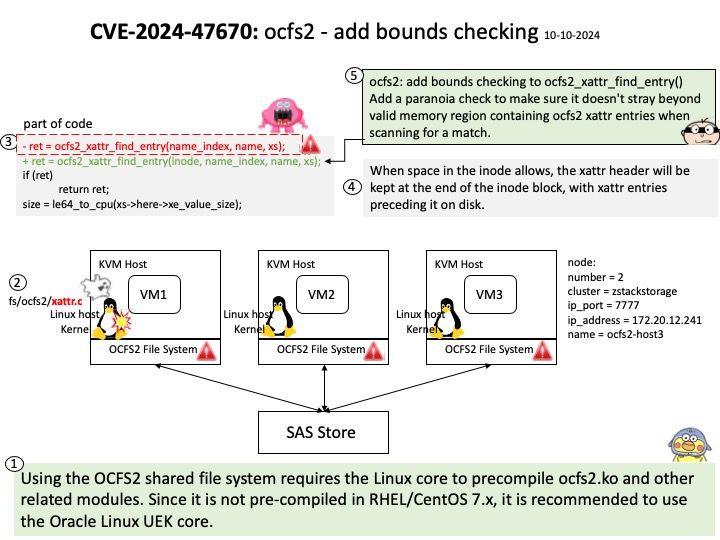
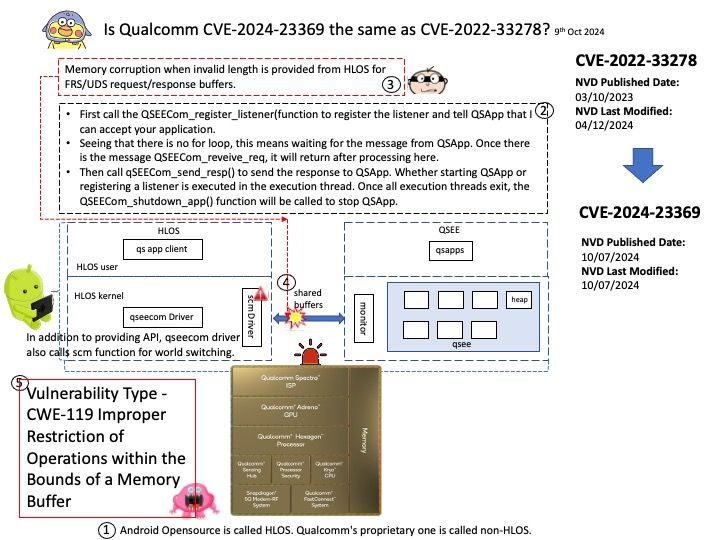
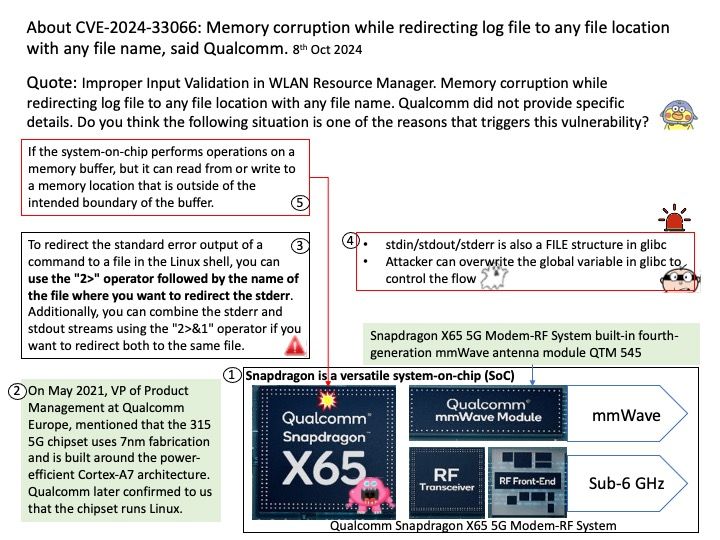
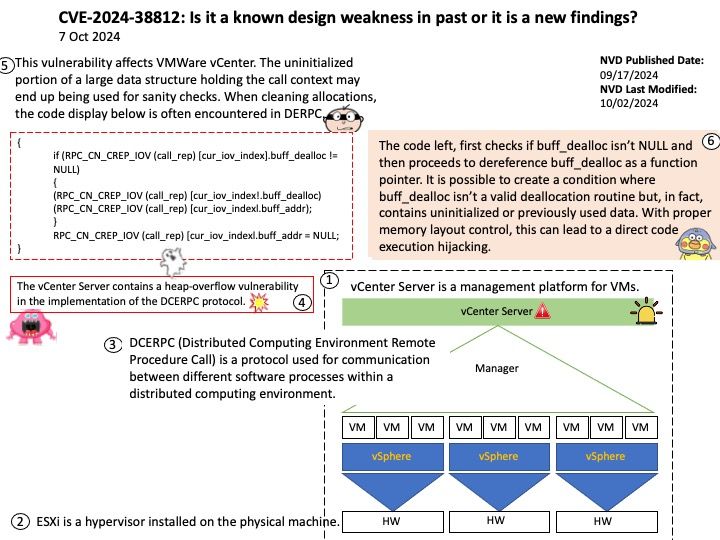
Preface: A hardware prefetcher is a data prefetching technique implemented as a hardware component in a processor, aimed at improving performance by fetching data before it is actually needed. Let’s take a closer look at prefetching. And speculate what kind of prefetching will approach this discussion.
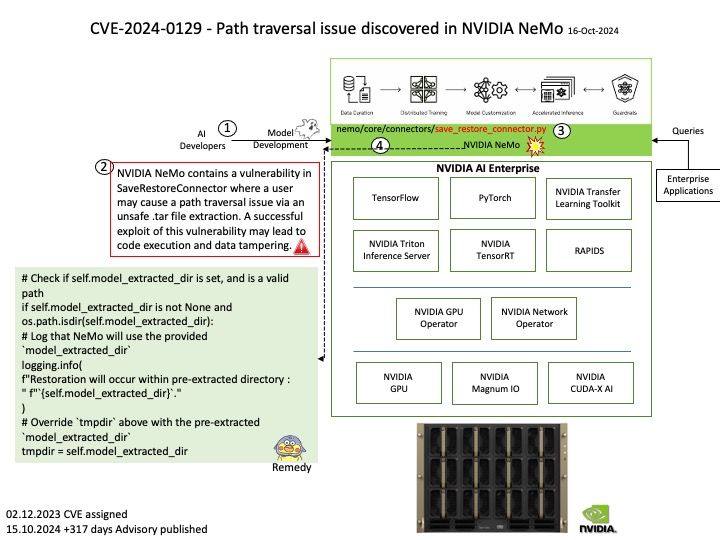
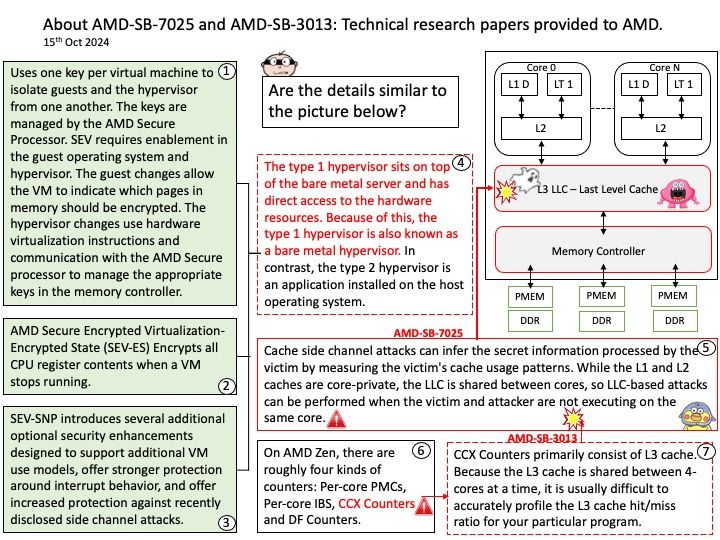
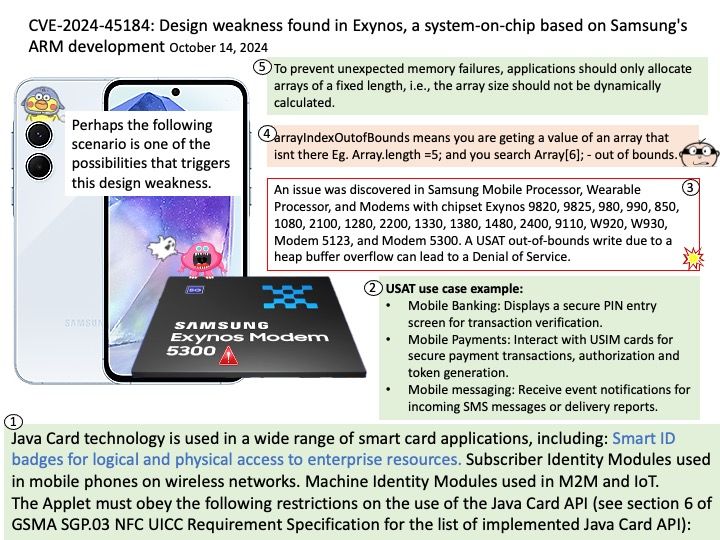
Background: A research paper titled ‘ShadowLoad: Injecting State into Hardware Prefetchers’ was provided to AMD in February 2024.
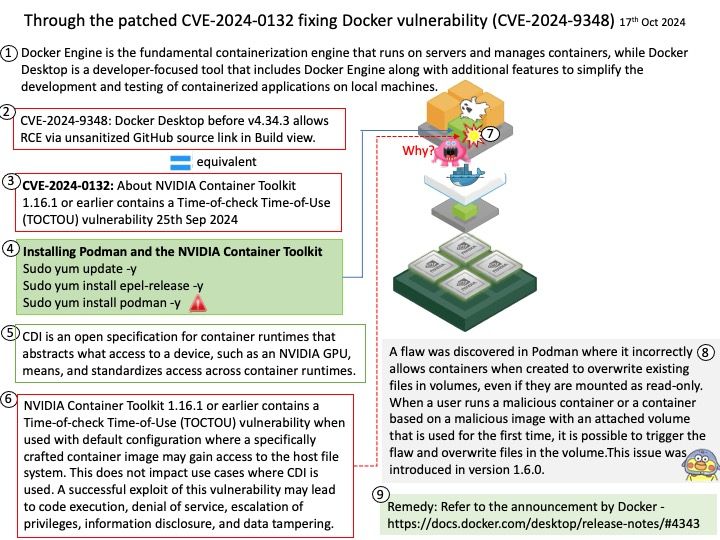
The paper discusses the possibility for prefetchers to be used to inject cache loads using a technique referred to as ”ShadowLoad”. The technique can potentially expand the attack surface of existing attacks.
Using a framework referred to as ”StrideRE” the researchers automatically reverse engineer parameters required for hardware stride-prefetch attacks. The paper describes how this stride prefetcher can be used to leak offsets for stride patterns across contexts, possibly creating a covert channel.
Official announcement: AMD has evaluated the paper and has determined that the researchers did not identify any AMD prefetchers that have not already been publicly disclosed in the referenced Software Optimization Guide and did not identify any new security implications with AMD prefetchers.
Official details: Please refer to the link for details – https://www.amd.com/en/resources/product-security/bulletin/amd-sb-7023.html