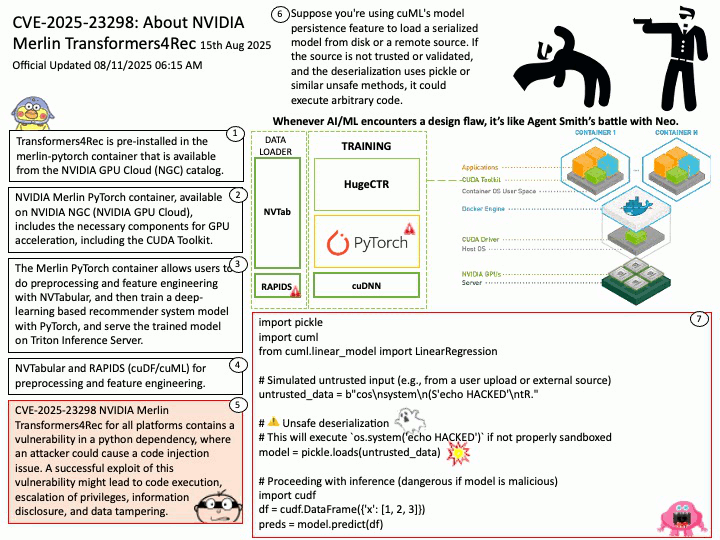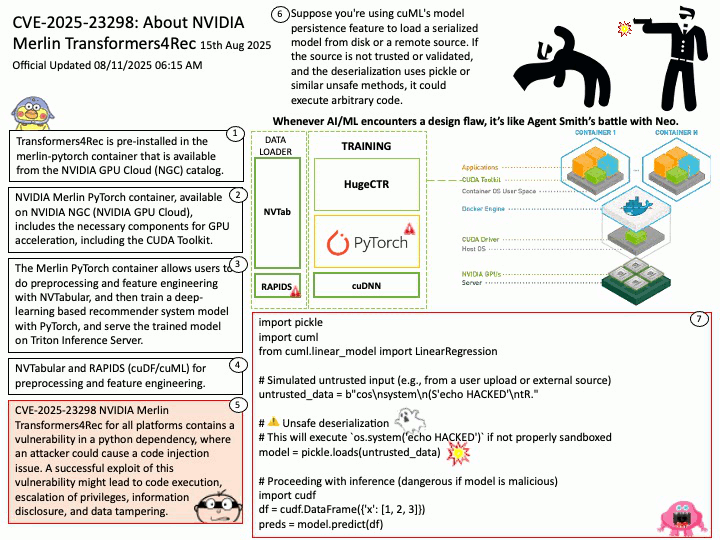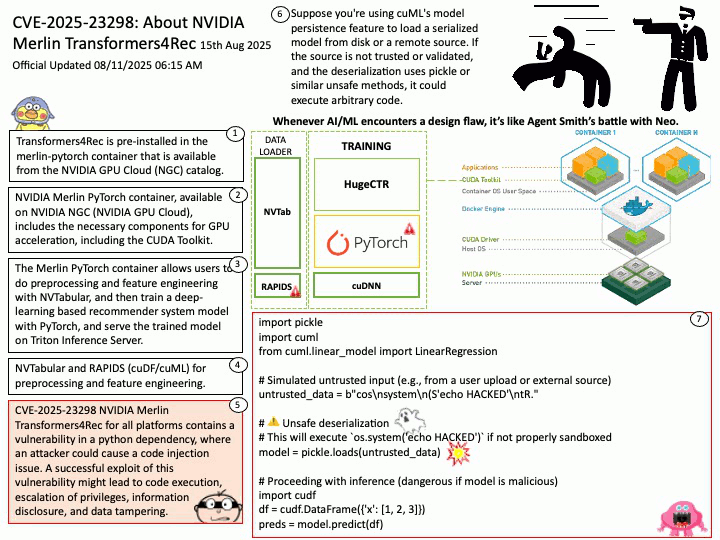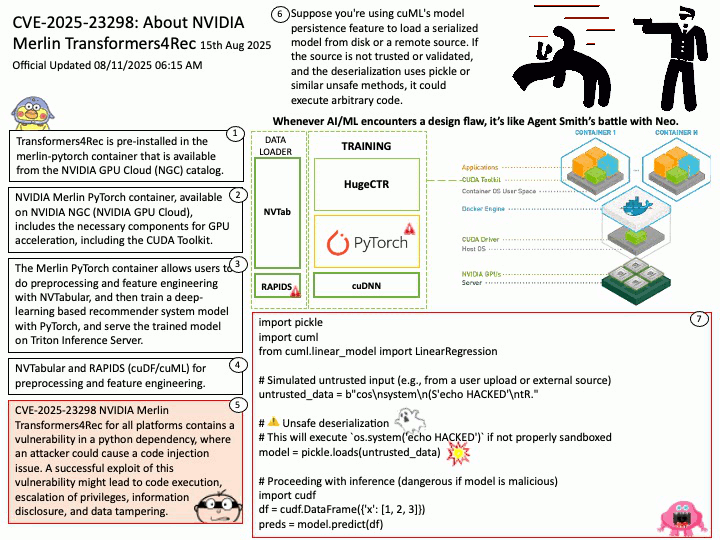
Official Updated 08/11/2025 06:16 AM
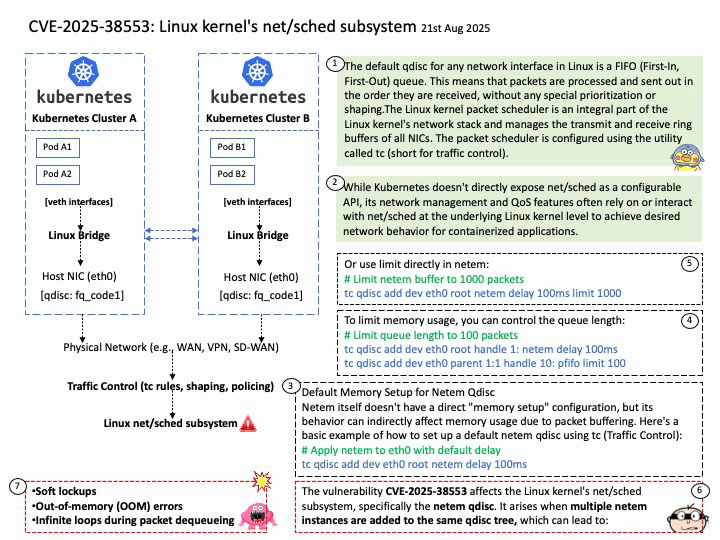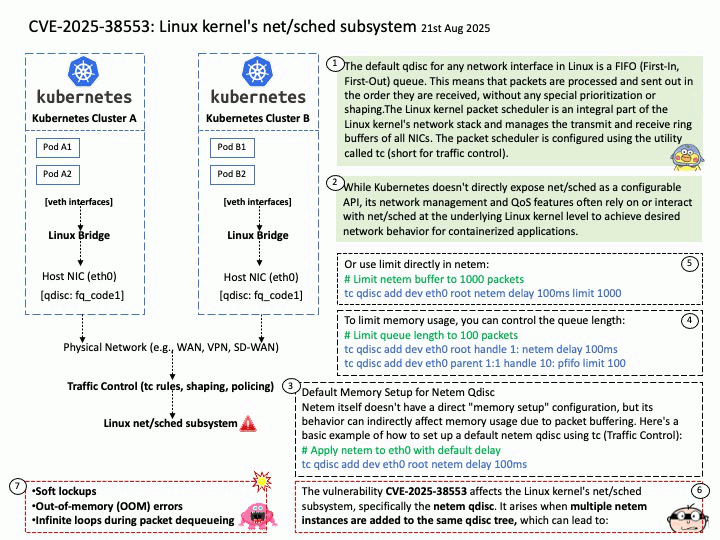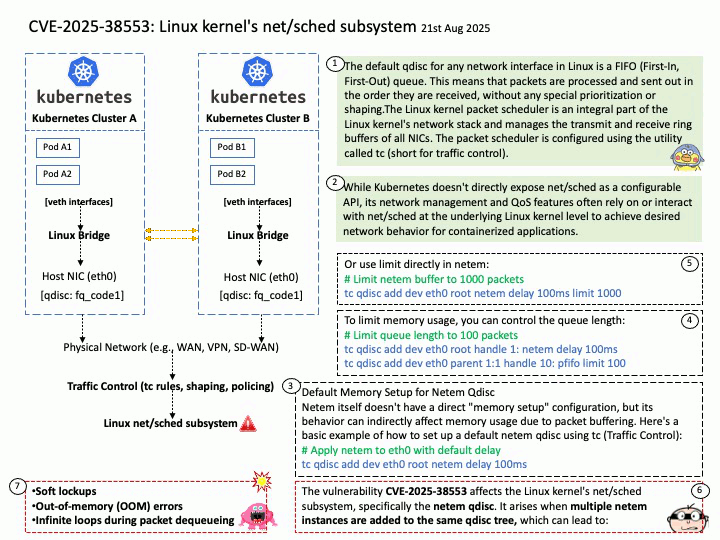
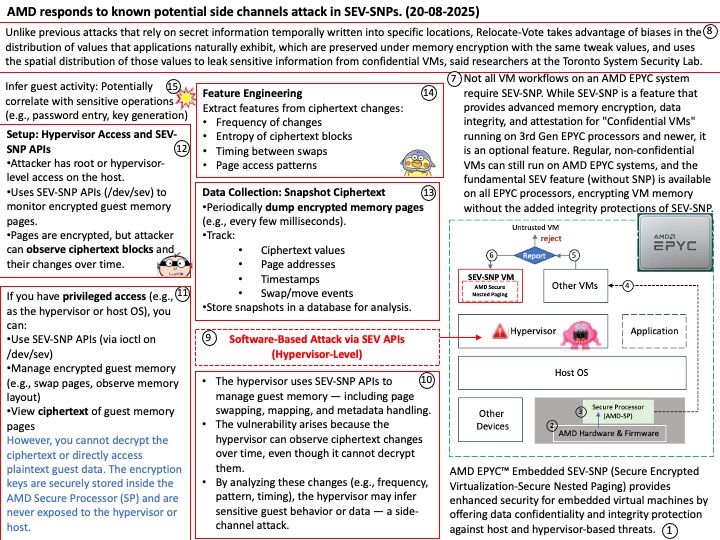
Preface: GPT-4 offers several key benefits, including improved accuracy, longer context handling, and the ability to process both text and image inputs. It also exhibits stronger guardrails, leading to more reliable and ethical outputs. Additionally, GPT-4 excels in various tasks like professional and academic benchmarks, creative writing, and adapting to user needs.
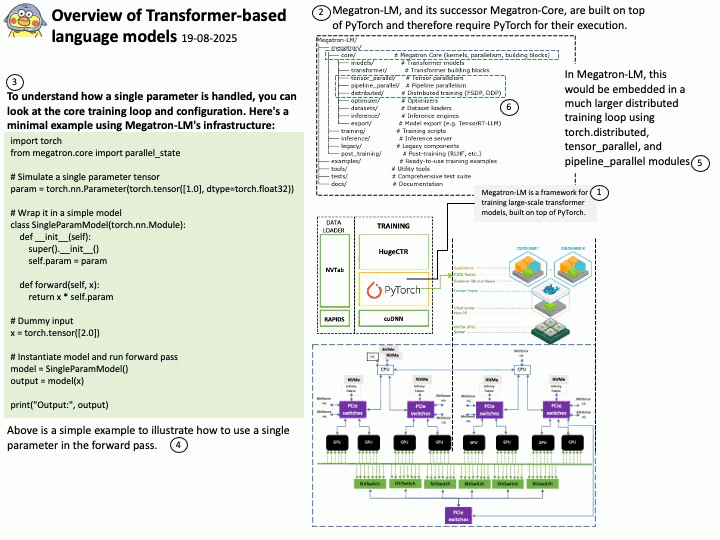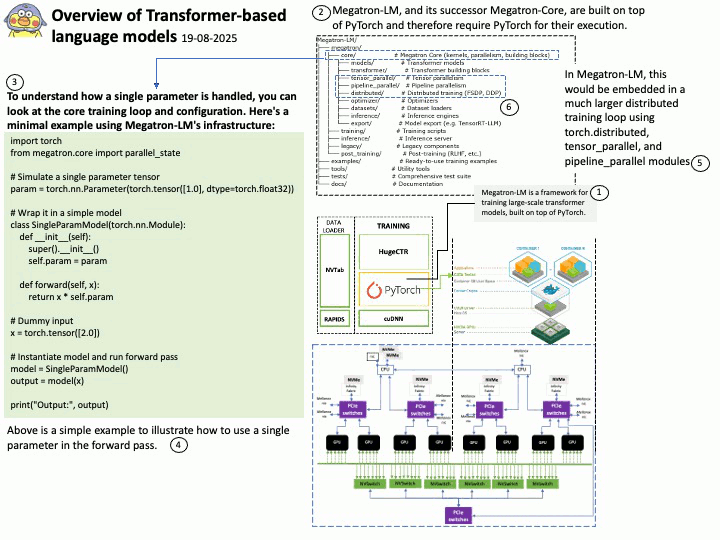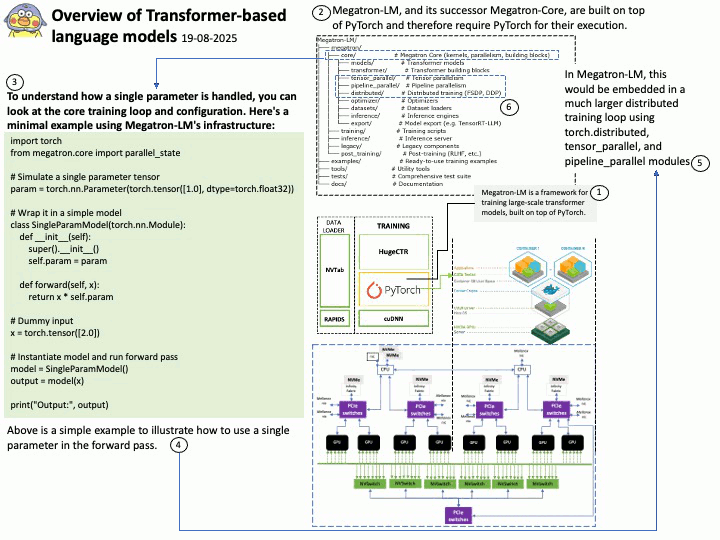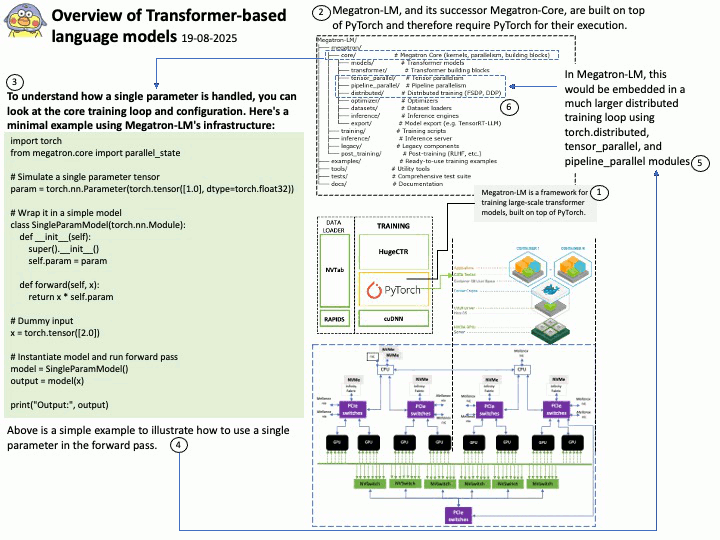
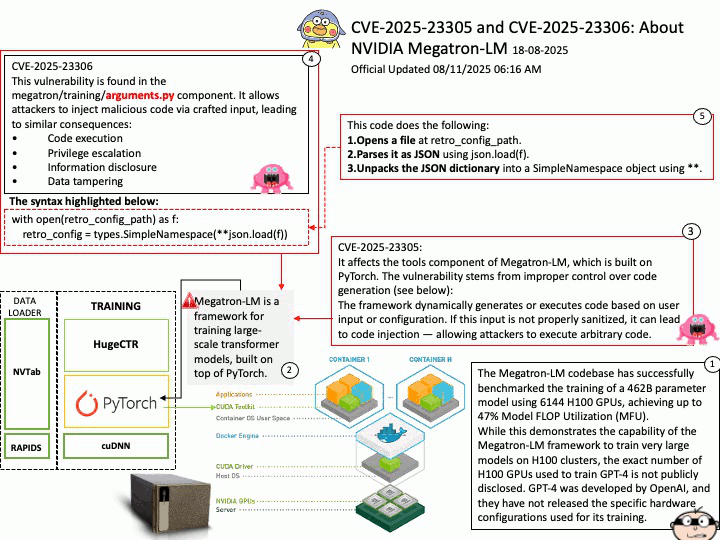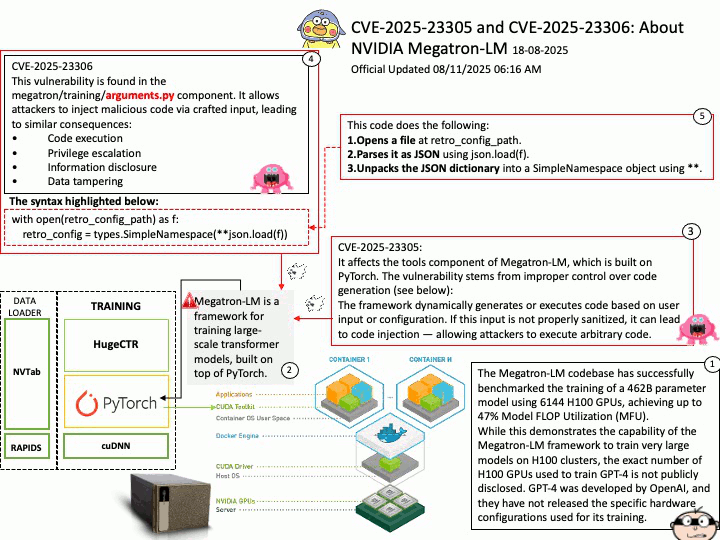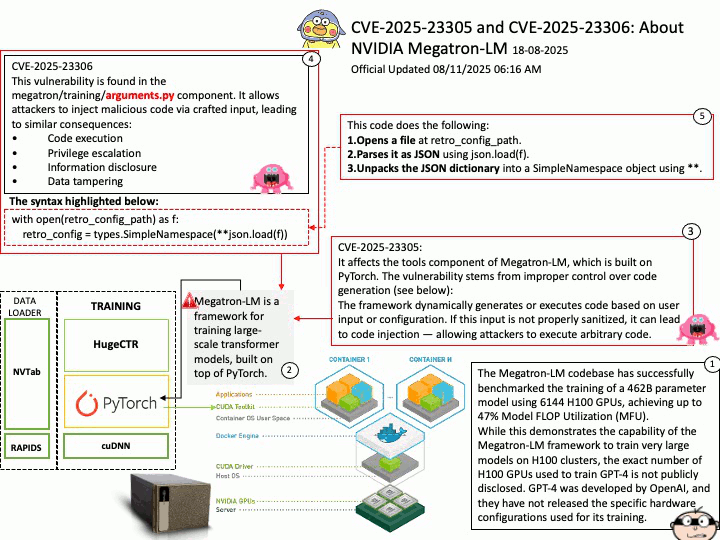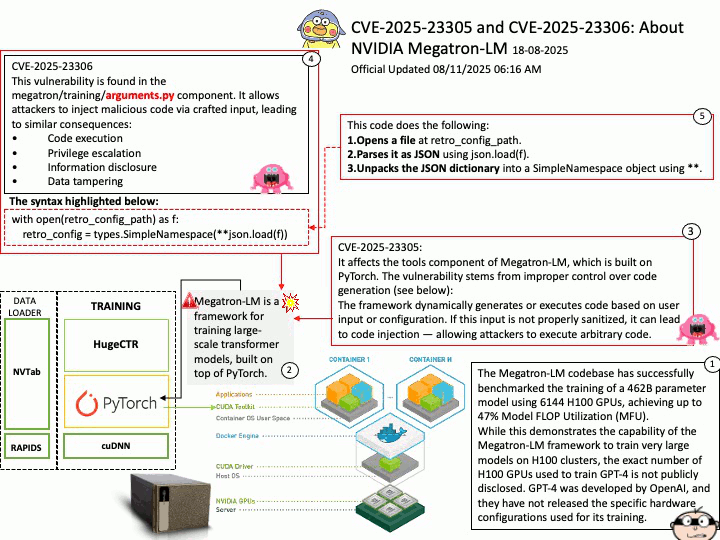
Background: The Megatron-LM codebase is a framework for training large, powerful transformer language models at scale, developed by NVIDIA. It focuses on efficient, model-parallel (tensor and pipeline) and multi-node pre-training of transformer-based models like GPT, BERT, and T5 using mixed precision
Megatron-LM codebase efficiently trains models from 2B to 462B parameters across thousands of GPUs, achieving up to 47% Model FLOP Utilization (MFU) on H100 clusters.
GPT-4, the latest iteration in OpenAI’s Generative Pre-trained Transformer series, significantly scales up the parameter count compared to its predecessors. While GPT-2 had 1.5 billion parameters and GPT-3 boasted 175 billion, GPT-4 is estimated to have a staggering 1.76 trillion parameters.
The Megatron-LM codebase has successfully benchmarked the training of a 462B parameter model using 6144 H100 GPUs, achieving up to 47% Model FLOP Utilization (MFU).
While this demonstrates the capability of the Megatron-LM framework to train very large models on H100 clusters, the exact number of H100 GPUs used to train GPT-4 is not publicly disclosed. GPT-4 was developed by OpenAI, and they have not released the specific hardware configurations used for its training.
Vulnerability details:
CVE-2025-23305 NVIDIA Megatron-LM for all platforms contains a vulnerability in the tools component, where an attacker may exploit a code injection issue. A successful exploit of this vulnerability may lead to code execution, escalation of privileges, information disclosure, and data tampering.
CVE-2025-23306 NVIDIA Megatron-LM for all platforms contains a vulnerability in the megatron/training/
arguments.py component where an attacker could cause a code injection issue by providing a malicious input. A successful exploit of this vulnerability may lead to code execution, escalation of privileges, information disclosure, and data tampering.
Official announcement: For more information, please refer to the link
https://nvidia.custhelp.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/5685