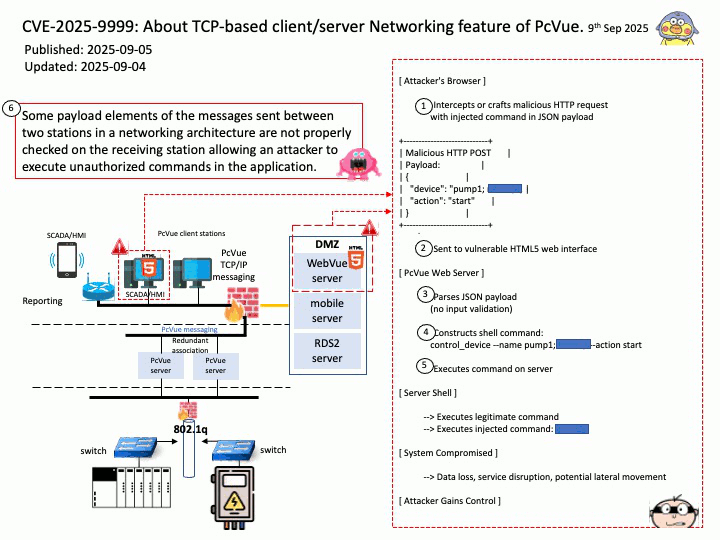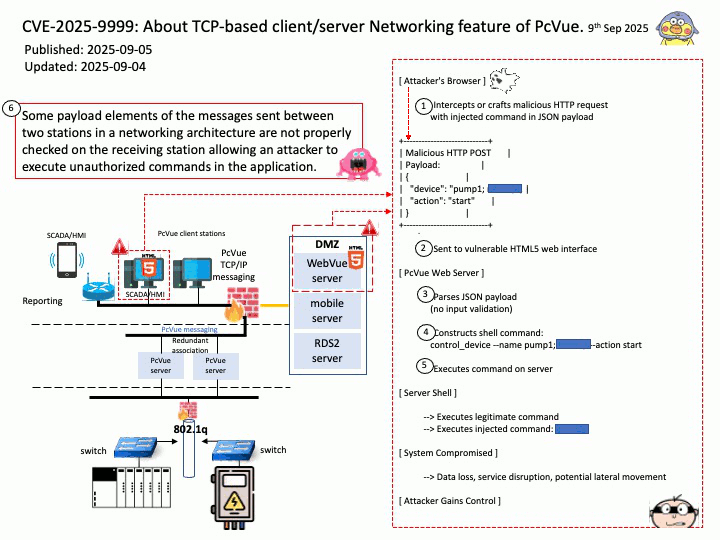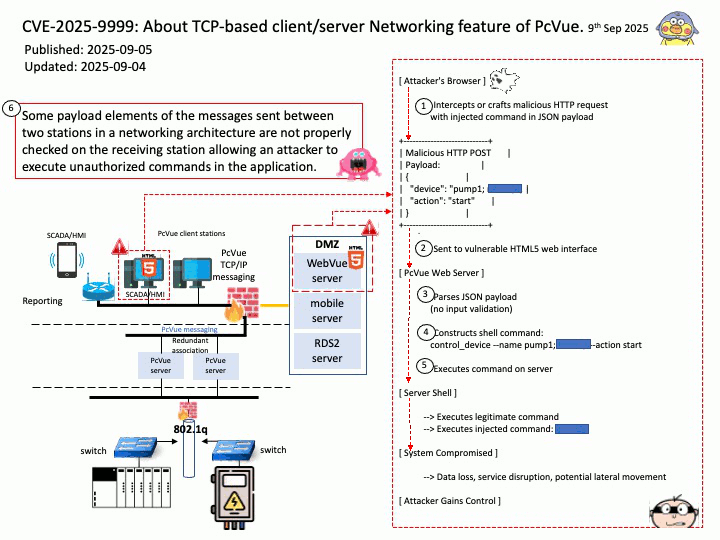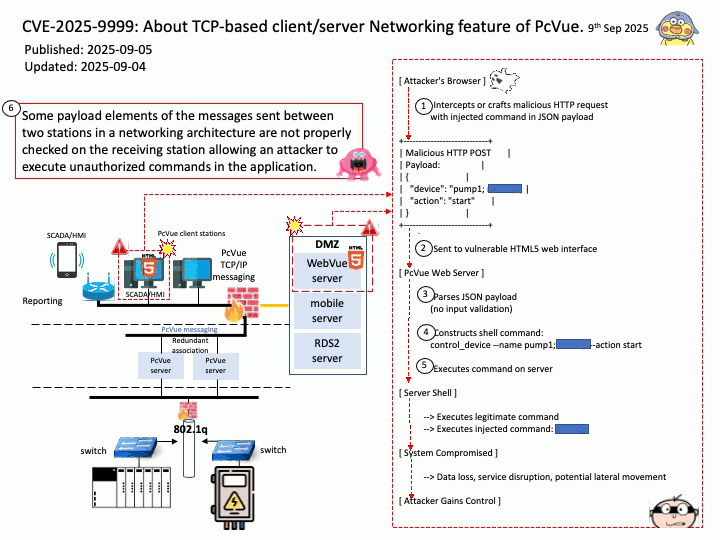
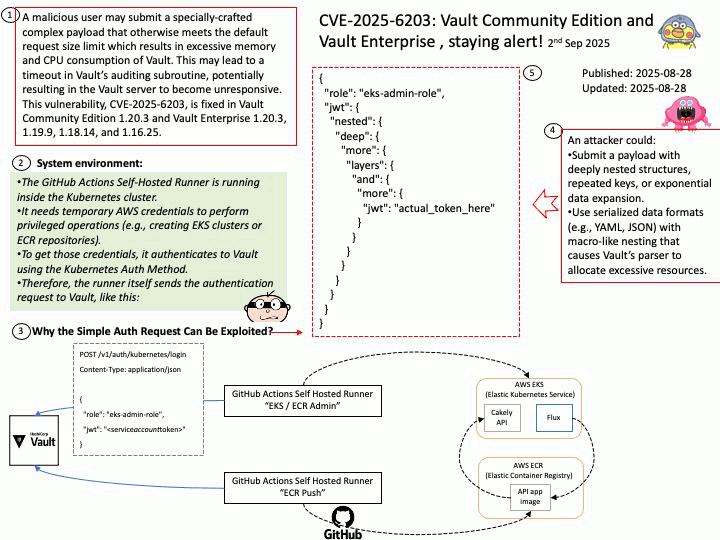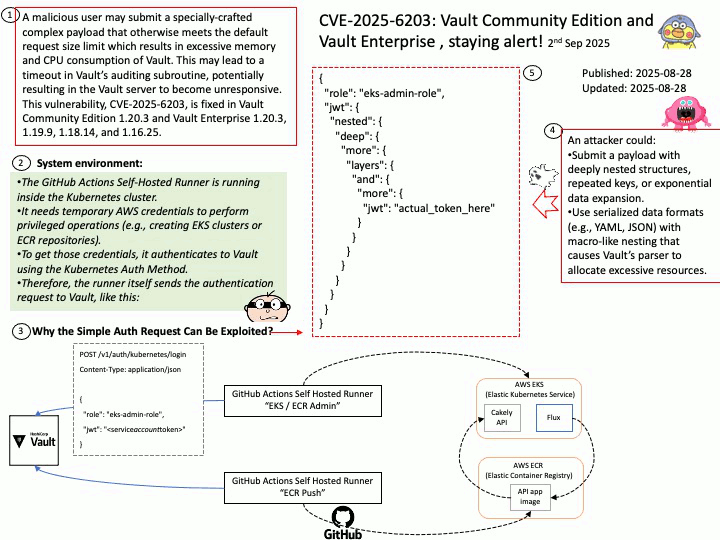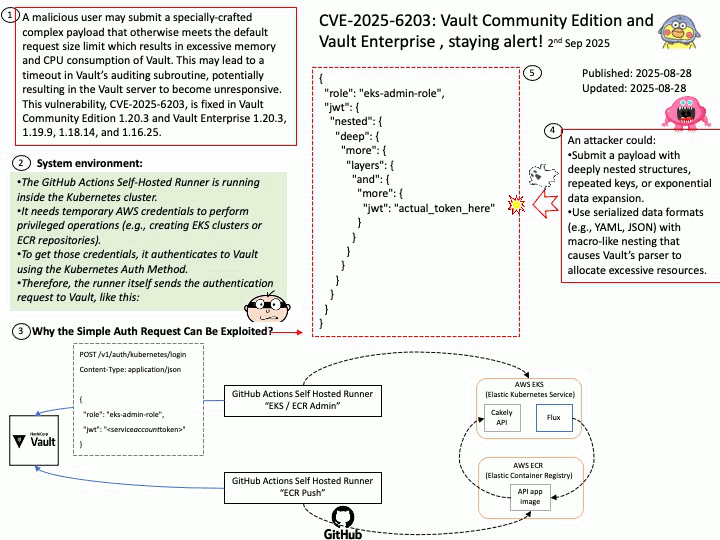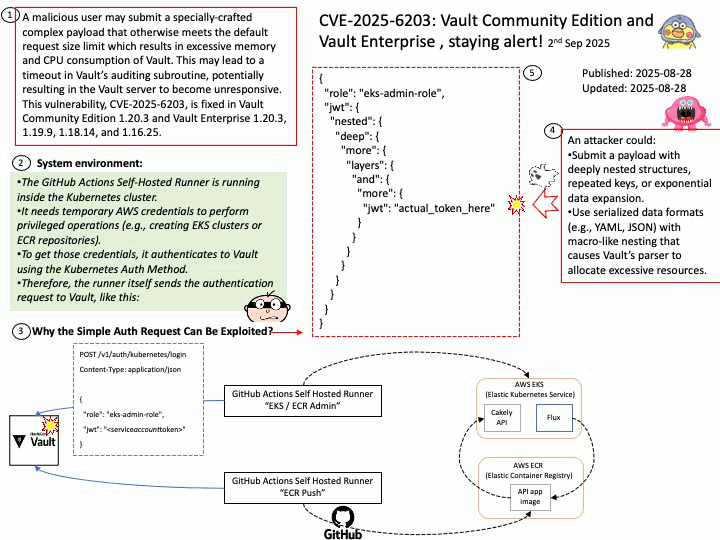
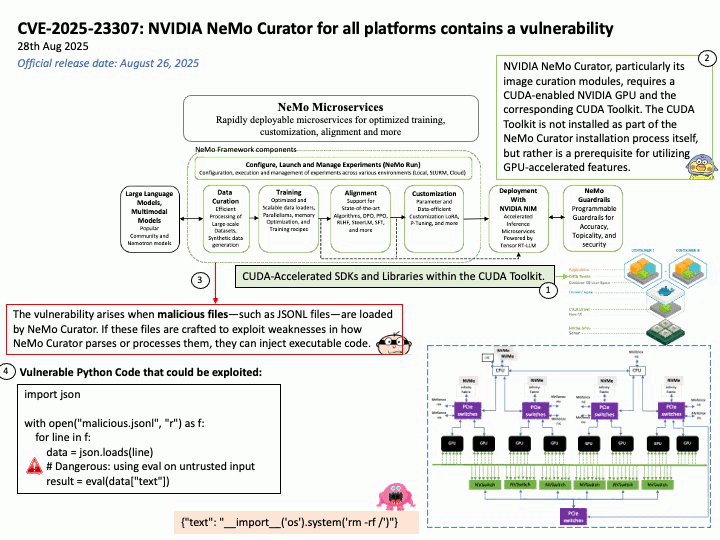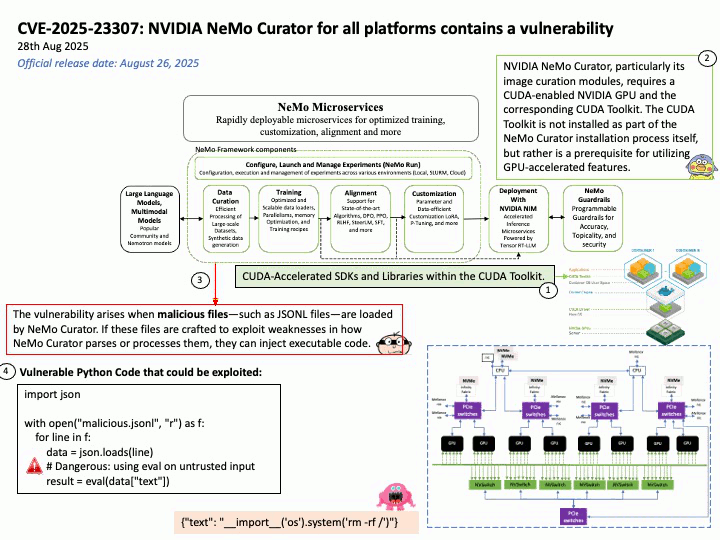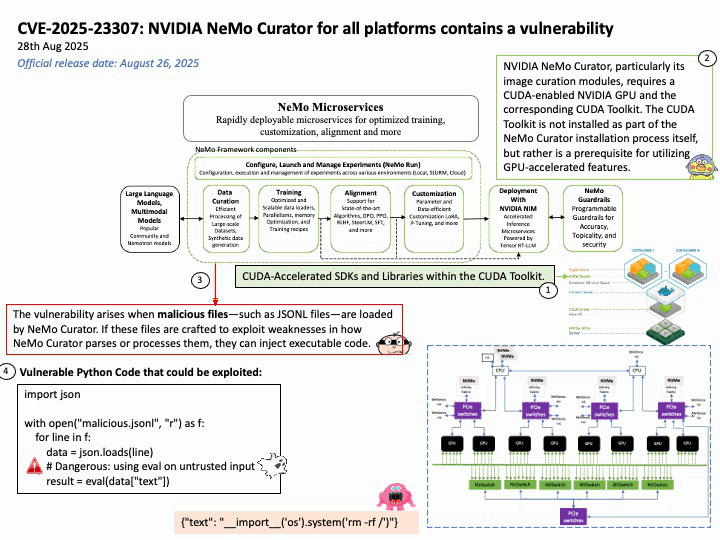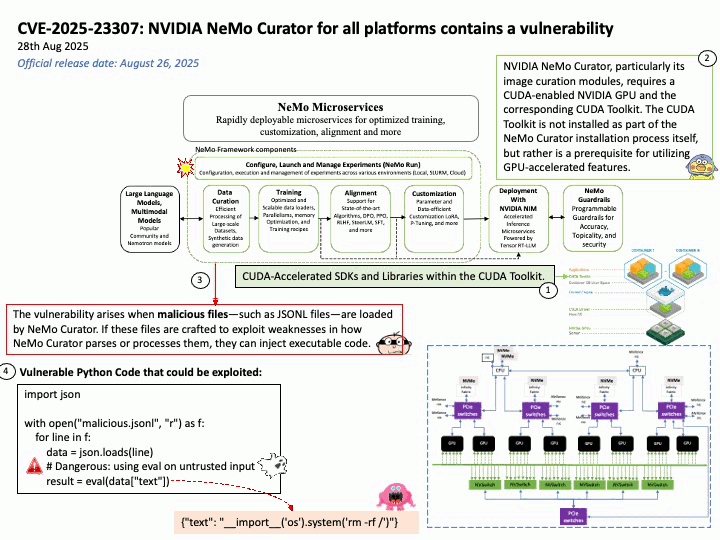
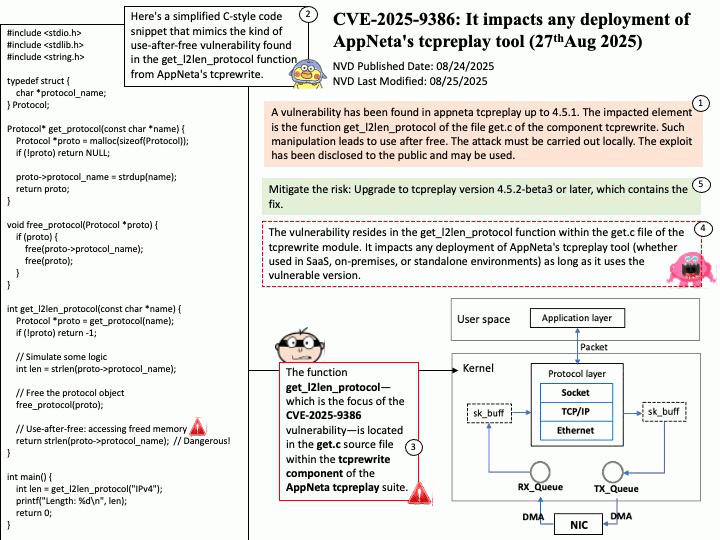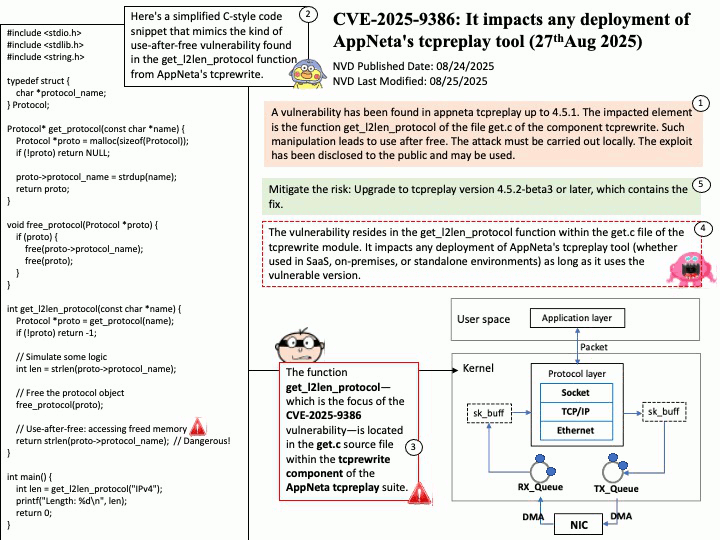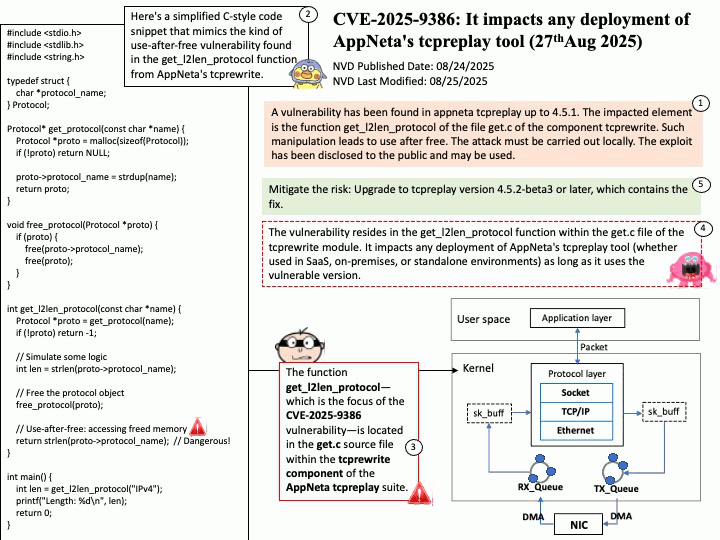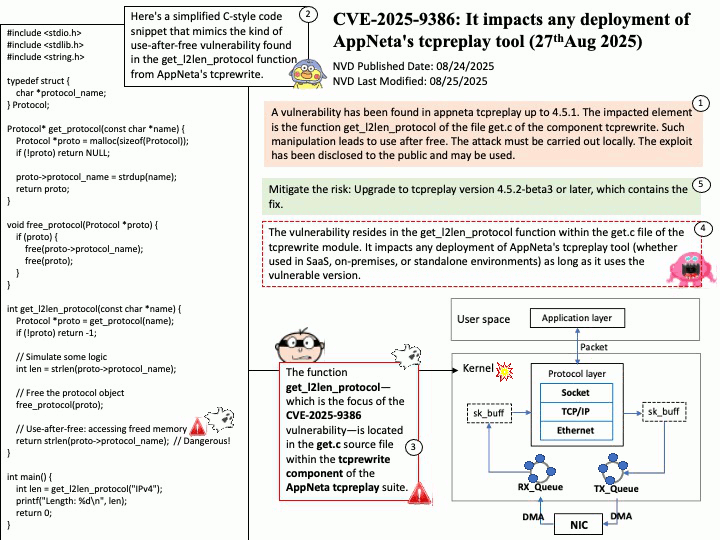
Preface:
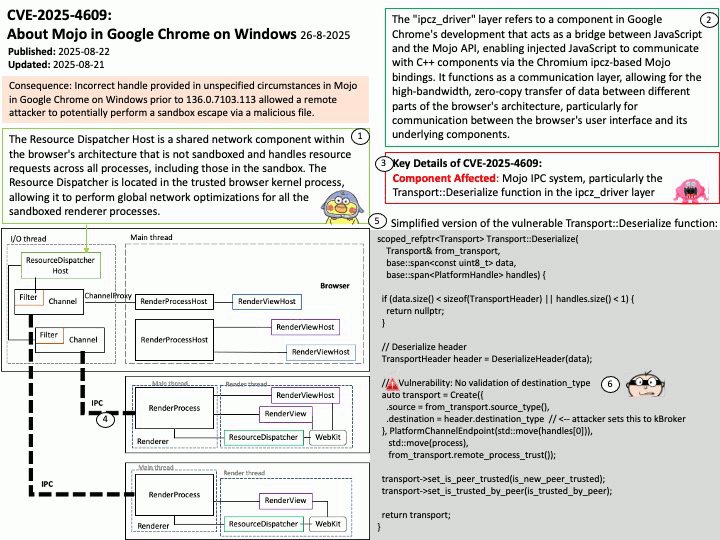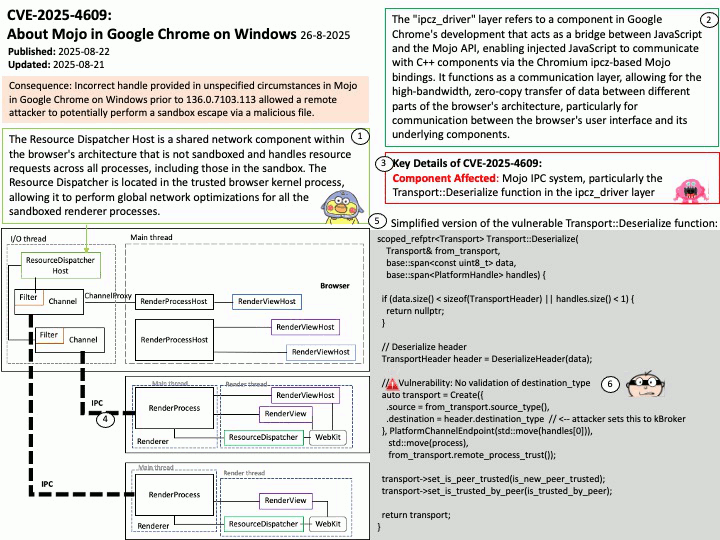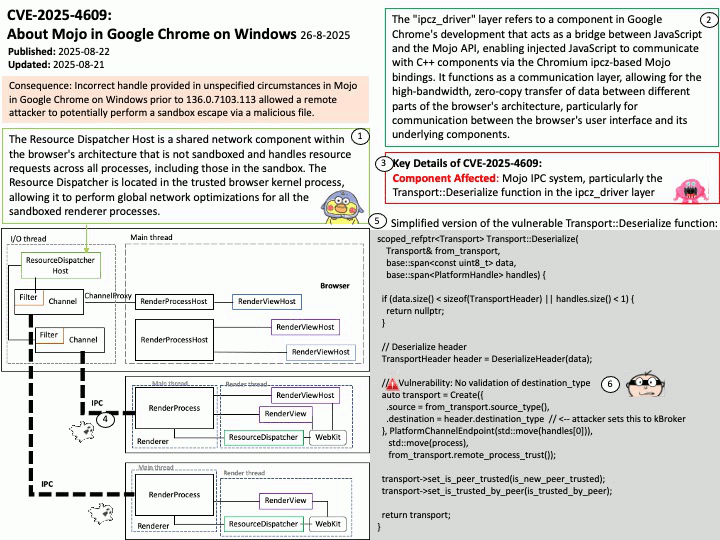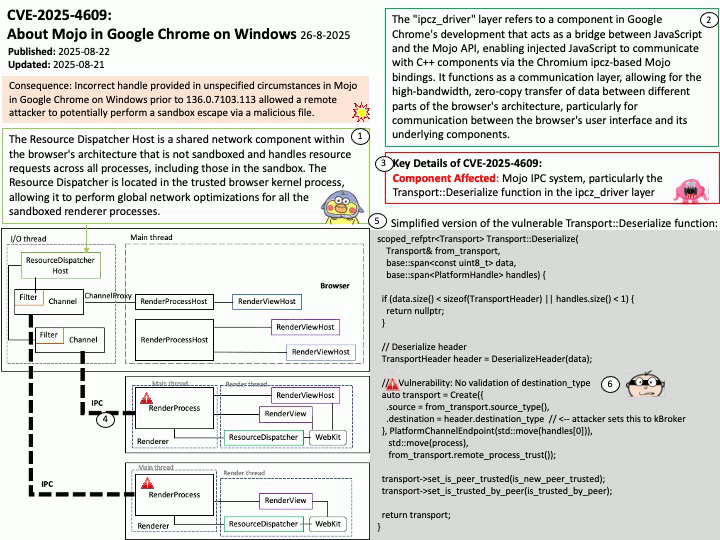
- IPMI is a standardized interface for hardware management, operating via the Baseboard Management Controller (BMC).
- It supports both in-band (local) and out-of-band (remote) access.
- BlueField’s reliance on OpenIPMI and IPMItool makes it susceptible to kernel-level vulnerabilities.
Background: The Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) is a standard interface for hardware management used by system administrators to control the devices and monitor the sensors. For these, it is necessary the IPMI Controller called Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) and a manager software (for example, IPMItool). It provides an interface to manage IPMI functions in a local (in-band) or remote (out-of-band) system.
Vulnerability details:
This advisory explores a potential causal relationship between two recent vulnerabilities:
- CVE-2025-23256 – A high-severity vulnerability in the NVIDIA BlueField DPU management interface, allowing local attackers to bypass authorization and modify configurations.
https://nvidia.custhelp.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/5655
- CVE-2025-38456 – A moderate-severity vulnerability in the Linux IPMI subsystem, involving memory corruption due to mishandled pointers in ipmi_create_user().
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2025-38456
Recommendations
- Patch Kernel IPMI Subsystem: Ensure CVE-2025-38456 is mitigated in all systems running BlueField.
- Update BlueField Firmware: Apply NVIDIA’s latest firmware updates addressing CVE-2025-23256.
- Audit IPMI Access Controls: Review and restrict local access to /dev/ipmi0 and IPMItool.