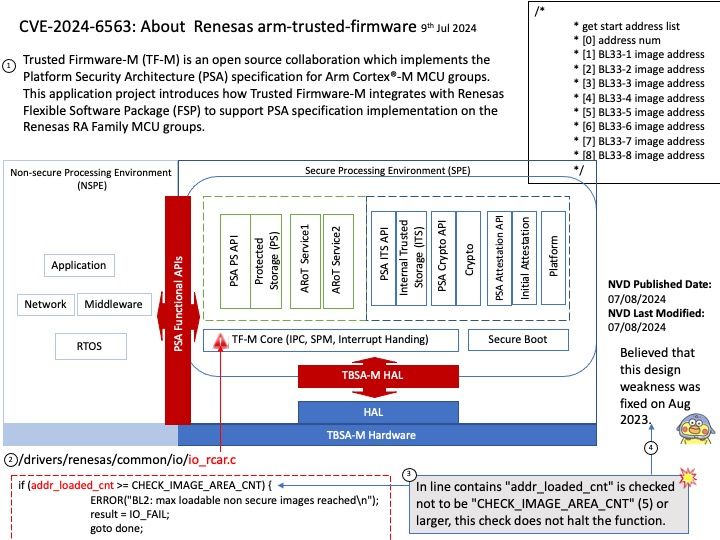
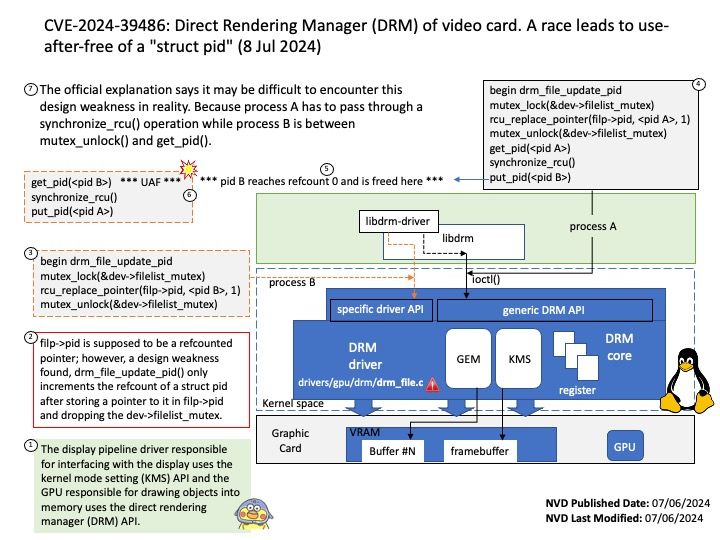
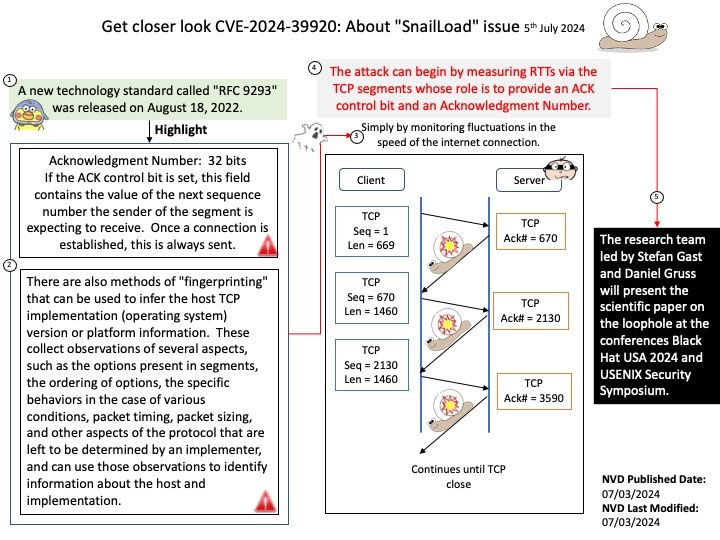
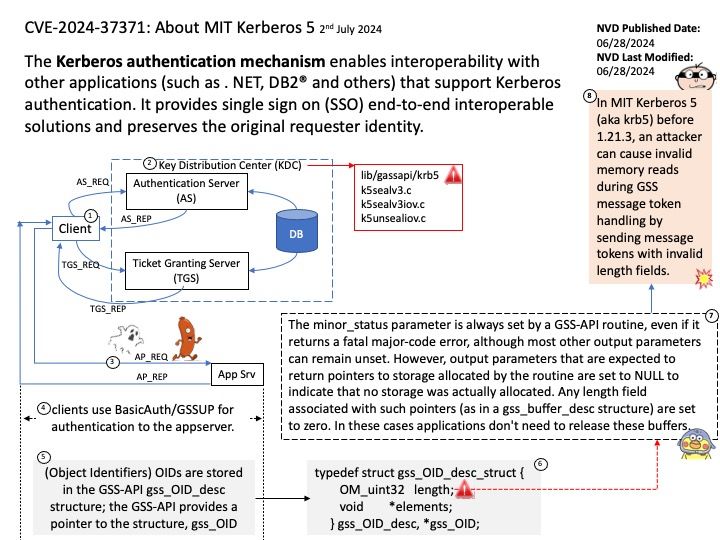
Preface: Node. js has two types of threads: one Event Loop and k Workers. The Event Loop is responsible for JavaScript callbacks and non-blocking I/O, and a Worker executes tasks corresponding to C++ code that completes an asynchronous request, including blocking I/O and CPU-intensive work.
Background: Why do we use child process in Node.js?
Node Child Process – Node is a tool that uses JavaScript and has many useful parts to it. Normally, it does work with one thread at a time, which means it can handle tasks without waiting. However, when there’s a lot of work to be done, we use the child_process module to create additional threads.
The child_process.spawn() method spawns the child process asynchronously, without blocking the Node.js event loop. The child_process.spawnSync() function provides equivalent functionality in a synchronous manner that blocks the event loop until the spawned process either exits or is terminated.
Vulnerability details: The CVE-2024-27980 was identified as an incomplete fix for the BatBadBut vulnerability. This vulnerability arises from improper handling of batch files with all possible extensions on Windows via child_process.spawn / child_process.spawnSync. A malicious command line argument can inject arbitrary commands and achieve code execution even if the shell option is not enabled.
This vulnerability affects all users of child_process.spawn and child_process.spawnSync on Windows in all active release lines.
Impact: This vulnerability affects all Windows users in active release lines: 22.x, 20.x, 18.x
Official announcement: For detail, please refer to link – https://nodejs.org/en/blog/vulnerability/july-2024-security-releases