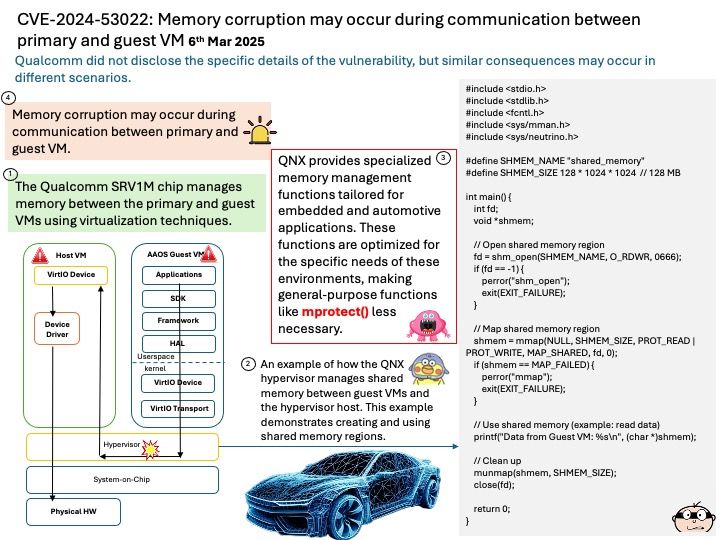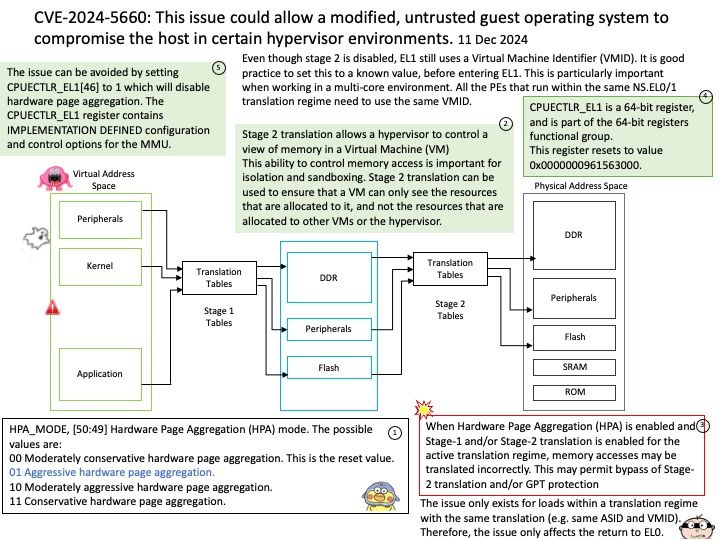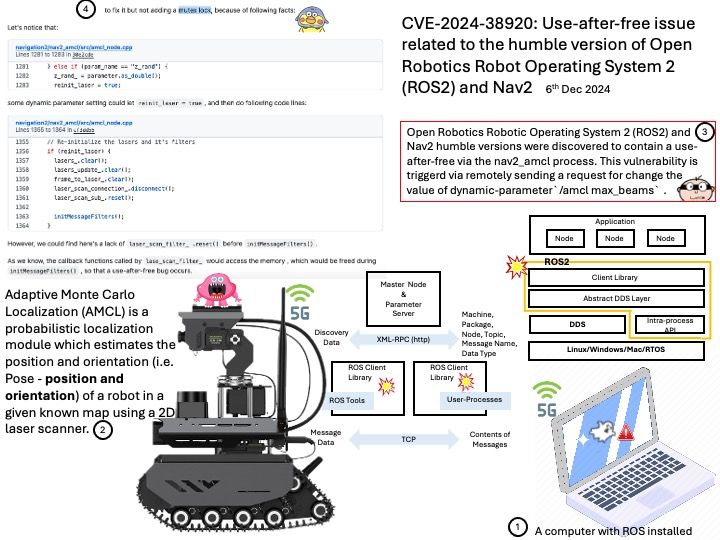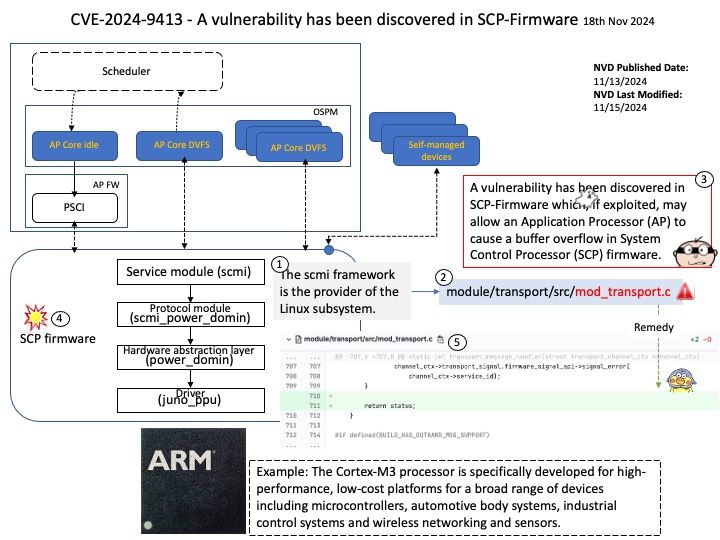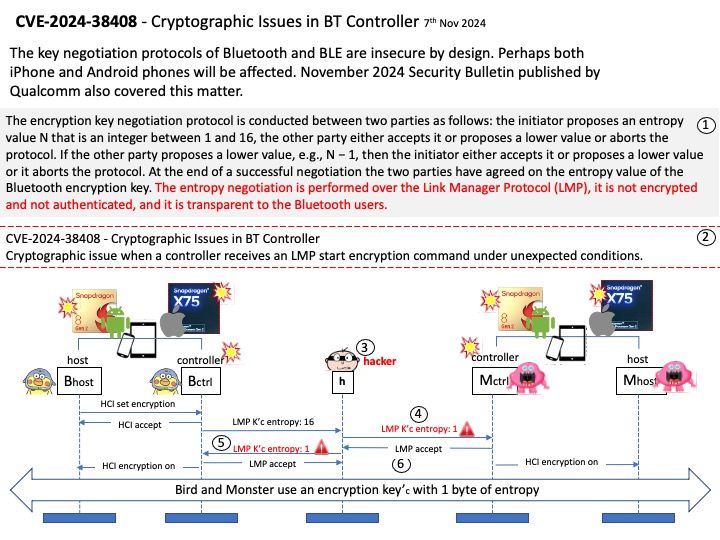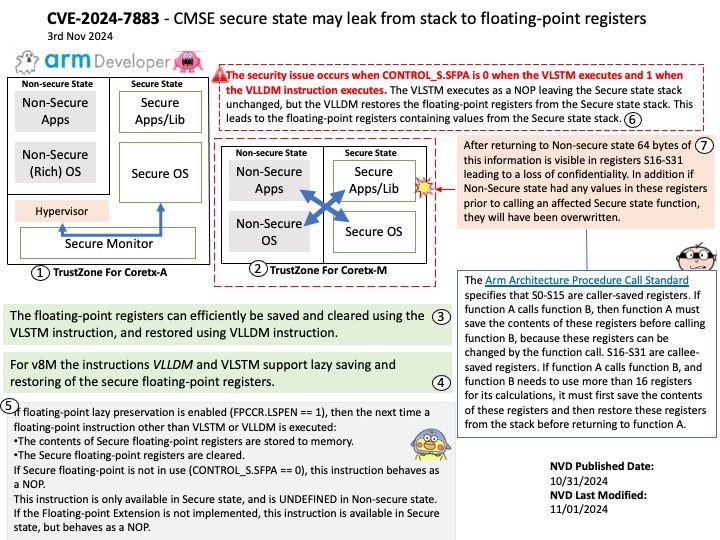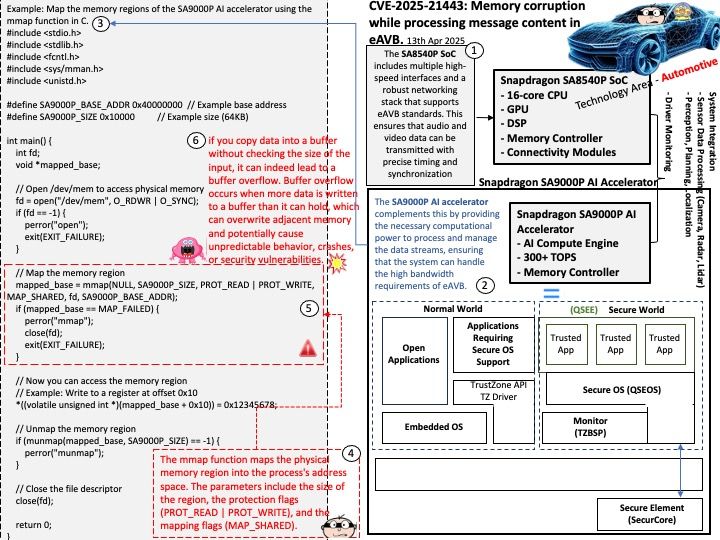
Preface: The Snapdragon SA8540P SoC and SA9000P AI accelerator are designed to work together seamlessly, particularly in advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) like GM’s Ultra Cruise. The buffer sharing design between these components is crucial for efficient data processing and low-latency performance. In automotive Ethernet Audio Video Bridging (eAVB), processors handle various types of message content to ensure efficient and reliable communication within the vehicle’s network.
Background: In Automotive Ethernet Audio Video Bridging (eAVB), processors handle the content of various types of messages to ensure efficient and reliable communication within the vehicle network.
Synchronization: eAVB ensures that audio and video streams are synchronized across different devices in the vehicle, providing a seamless infotainment experience.
Low Latency: Messages are designed to be transmitted with minimal delay, which is crucial for real-time applications like advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and infotainment
Fault Tolerance: The system is built to handle faults and ensure continuous operation even in the presence of network issues
High Bandwidth: eAVB supports high-speed data transmission, which is necessary for handling large amounts of audio and video data
Vulnerability details: in Automotive Vehicle Networks. Memory corruption while processing message content in eAVB. Found that Buffer Copy Without Checking Size of Input (‘Classic Buffer Overflow’).
Official announcement: Please refer to the link for details – https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2025-21443