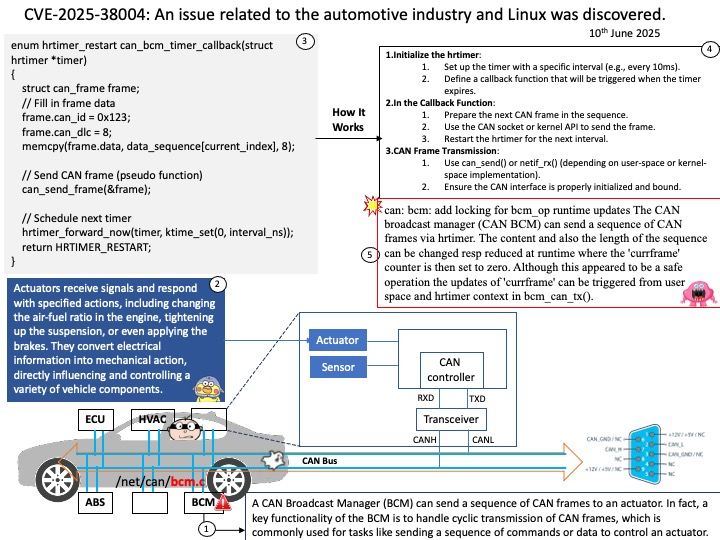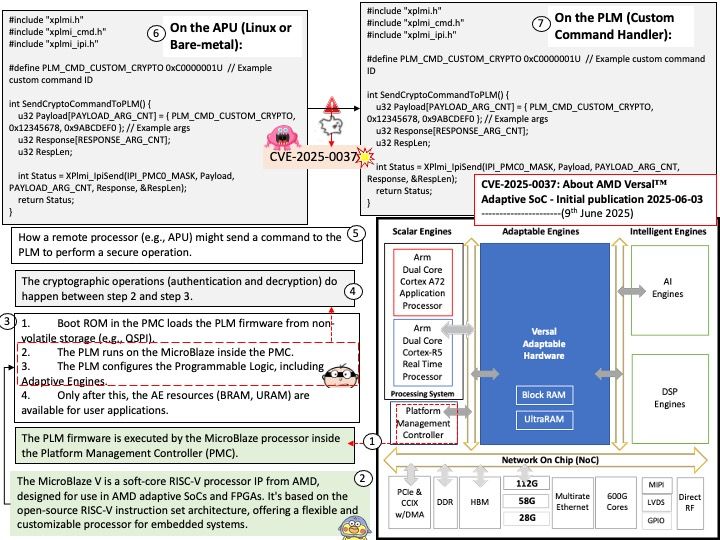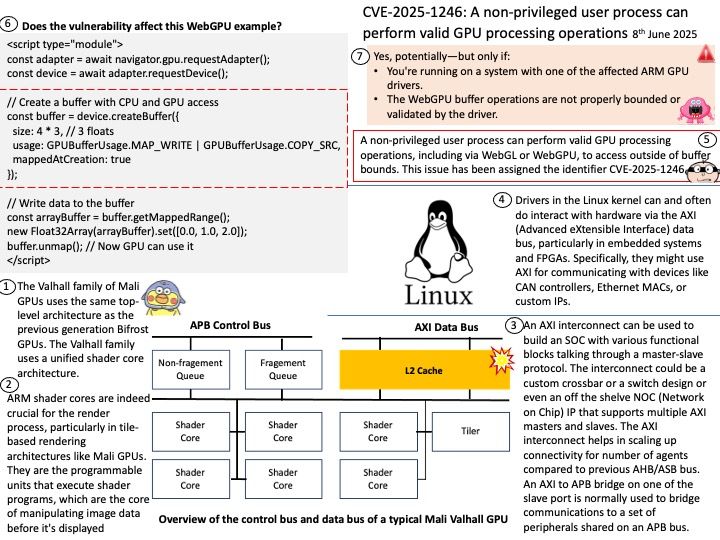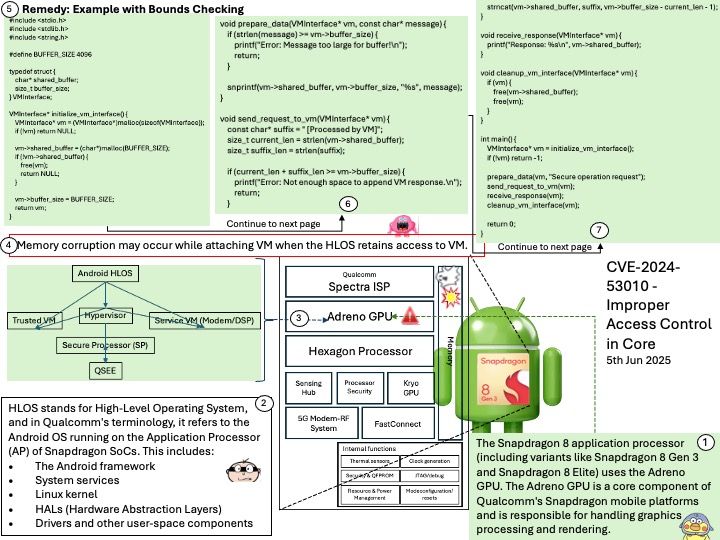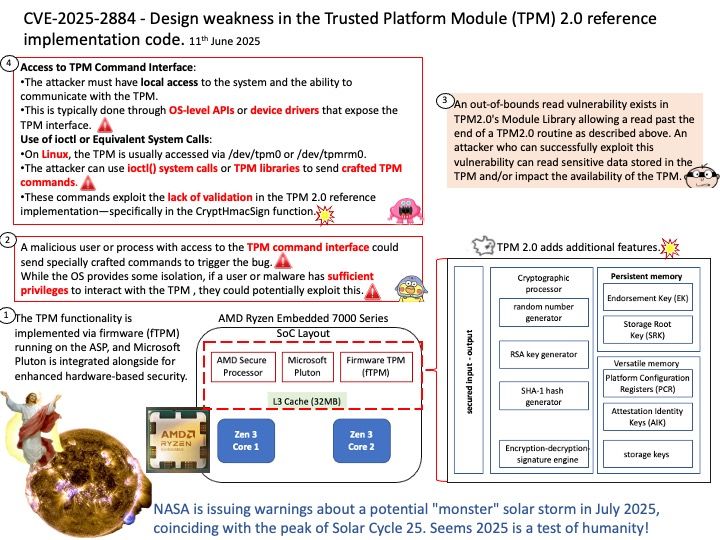
Preface: The main difference between AMD’s Trusted Platform Module (TPM) and those from other manufacturers , how it’s implemented: AMD offers a firmware TPM (fTPM), while many other manufacturers, including Intel, also offer a dedicated hardware TPM (dTPM).
Background: TPM refers to a Trusted Platform Module, which is a specialized chip that securely stores cryptographic keys used for encryption and decryption, enhancing overall system security. AMD’s approach often involves Firmware TPM (fTPM), also known as Intel’s Platform Trust Technology (PTT), which implements TPM functionality within the system’s firmware rather than using a dedicated physical chip.
The AMD Ryzen Embedded 7000 series processors indeed integrate advanced security features, including:
- AMD Secure Processor (ASP): A dedicated security co-processor embedded directly into the CPU die.
- Firmware TPM (fTPM): Implemented in firmware and runs on the ASP.
- Microsoft Pluton: A hardware-based security processor integrated into the silicon, designed to work alongside ASP and fTPM for enhanced protection.
Ref: The most common TPM is the TPM function supported by the Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) of Intel Core i series or AMD Ryzen series CPU in the motherboard UEFI firmware. fTPM can be used in all processors after Intel Broadwell (5th generation) and AMD Ryzen series. This is the most common method because you can easily use the TPM function without purchasing a separate module.
Vulnerability details: An out-of-bounds read vulnerability exists in TPM2.0’s Module Library allowing a read past the end of a TPM2.0 routine as described above. An attacker who can successfully exploit this vulnerability can read sensitive data stored in the TPM and/or impact the availability of the TPM.
Official announcement: Please see the link for details – https://www.amd.com/en/resources/product-security/bulletin/amd-sb-4011.html