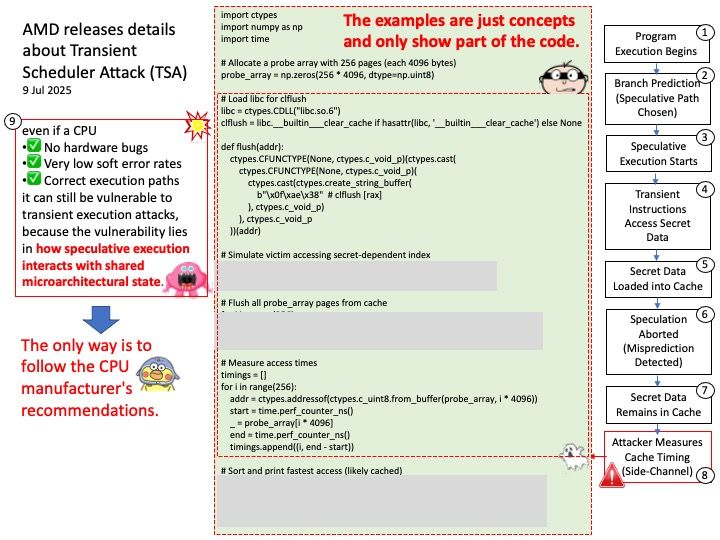
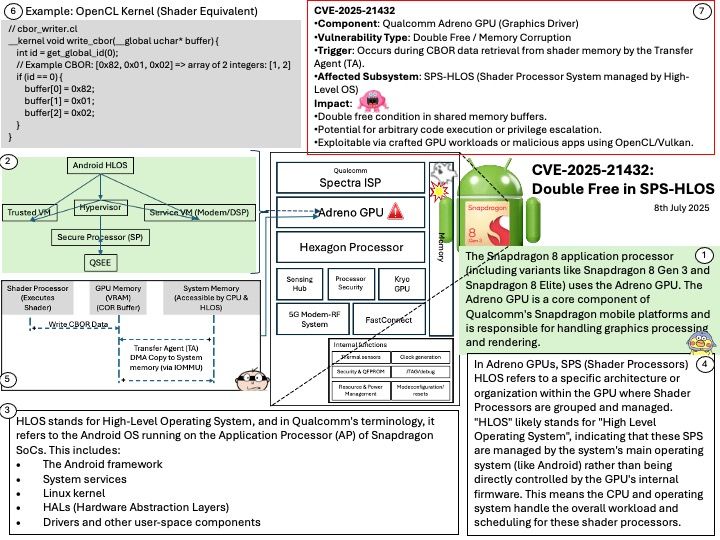
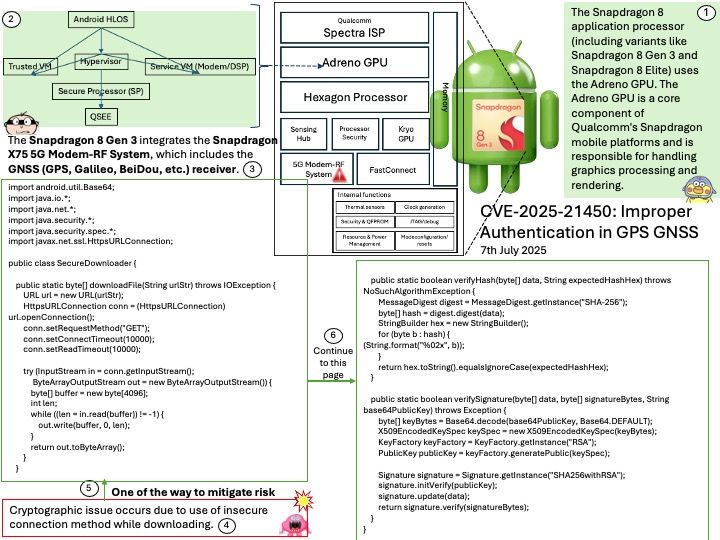
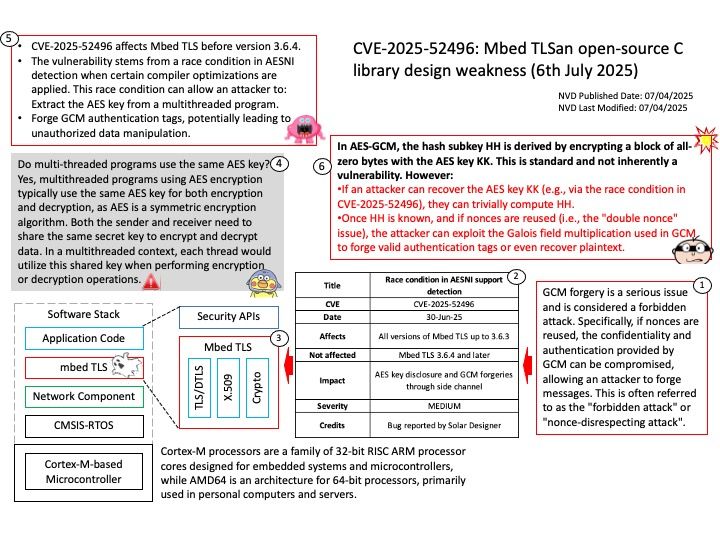
Preface: Glibc is a fundamental component of many embedded systems, which are small, specialized computer systems found in vehicles for tasks like engine control, braking, and infotainment.
Background: The regcomp function in Linux is used to compile a regular expression pattern into a form that can be efficiently used by regexec for matching. A good example of its usage involves validating user input. For instance, you might want to ensure that a user-entered password meets certain criteria, such as containing at least one uppercase letter, one lowercase letter, one digit, and one special character.
The regcomp function in the GNU C Library’s <regex.h> is responsible for compiling a regular expression into an internal data structure that can be efficiently used for matching. Essentially, it takes a string representing a regular expression pattern and converts it into a format suitable for fast searching within other strings.
The GNU C Library (glibc) provides a consistent Application Binary Interface (ABI) across different architectures and versions, ensuring compatibility between compiled programs. Architectures define the underlying hardware instruction set, while ABIs specify how functions are called, data is passed, and objects are laid out in memory. glibc abstracts these details, allowing developers to write code once and have it run on various systems that adhere to the same ABI.
While compiling a regular expression avoids recompilation within the same program execution, a system shutdown will erase the in-memory compiled representation. When the system restarts and the program is run again, the regular expression will need to be re-compiled if the performance benefit of pre-compilation is desired. The ABI does not change this behavior; it merely dictates how the compiled code interacts with other system components.
Vulnerability details: The regcomp function in the GNU C library version from 2.4 to 2.41 is subject to a double free if some previous allocation fails. It can be accomplished either by a malloc failure or by using an interposed malloc that injects random malloc failures. The double free can allow buffer manipulation depending of how the regex is constructed. This issue affects all architectures and ABIs supported by the GNU C library.
Ref: A double free error occurs if free() is called multiple times with the same memory address. Calling free() twice on the same value causes a memory leak. If a program calls free() twice with the same arguments, it corrupts the program’s memory management data structures.
Official announcement: Please refer to the URL for details –