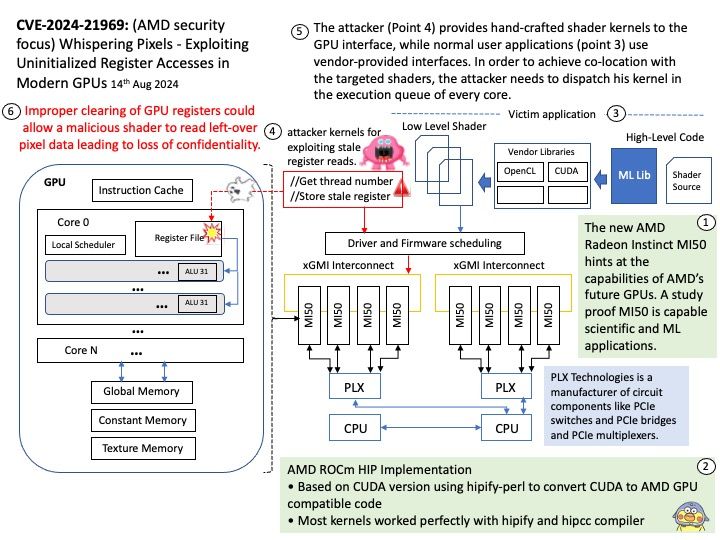
Preface: The new AMD Radeon Instinct MI50 hints at the capabilities of AMD’s future GPUs. A study proof MI50 is capable scientific and ML applications.
Background: The proliferation of graphics processing units (GPUs) has brought unprecedented computing power.
Multiple register-based vulnerabilities found across different GPU implementations.
So-called whisper pixels. The vulnerability poses unique challenges to an adversary due to opaque scheduling and register remapping algorithms present in the GPU firmware, complicating the reconstruction of leaked data.
GPU Programming: An application has to use vendor- provided libraries in order to translate a shader from its high-level source code to an architecture-dependent binary code. Vendors provide these libraries for a variety of high-level languages.
Vulnerability details: Improper clearing of GPU registers could allow a malicious shader to read left-over pixel data leading to loss of confidentiality.
Mitigation: AMD plans to create a new operating mode designed to prevent processes from running in parallel on the GPU, and to clear registers between processes on supported products.
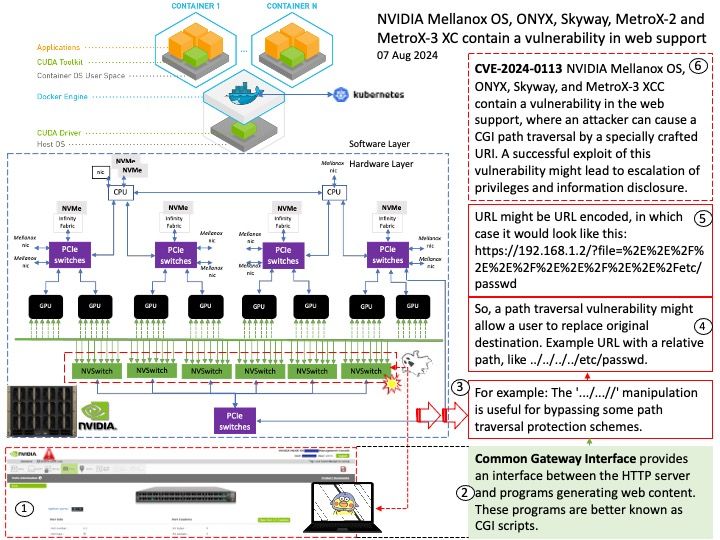
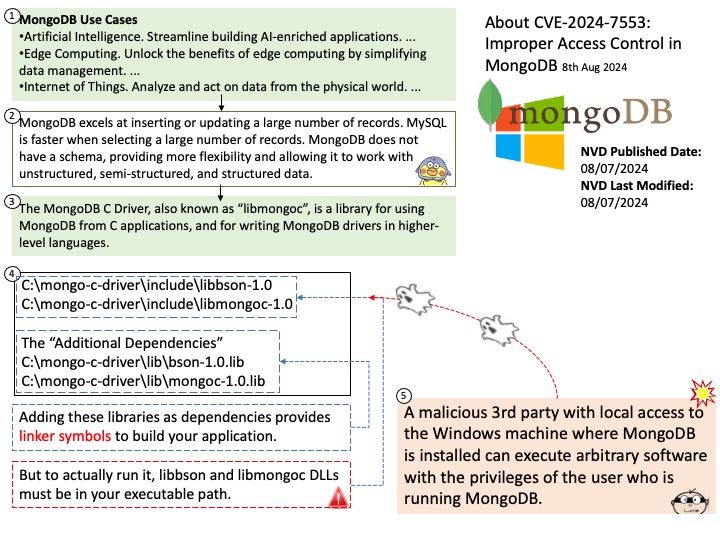
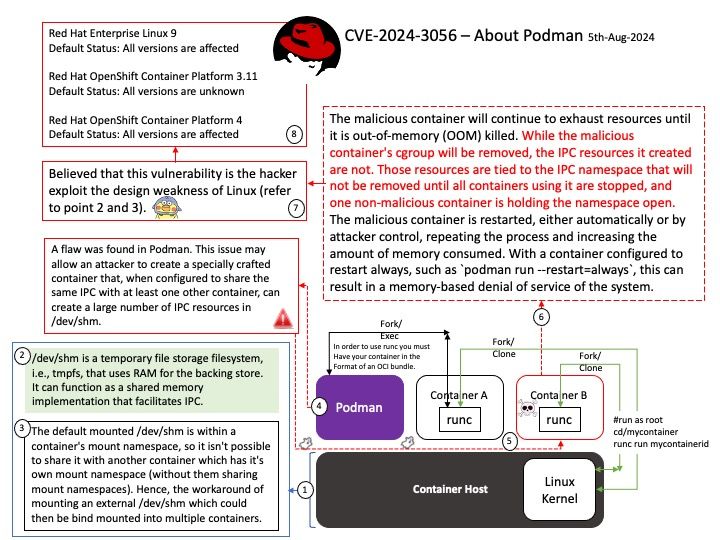
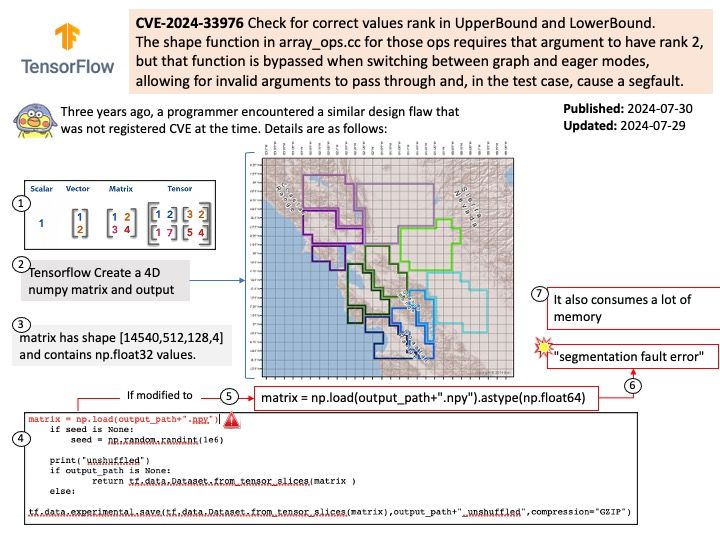
Official announcement: Please refer to the website for details – https://www.amd.com/en/resources/product-security/bulletin/amd-sb-6013.html