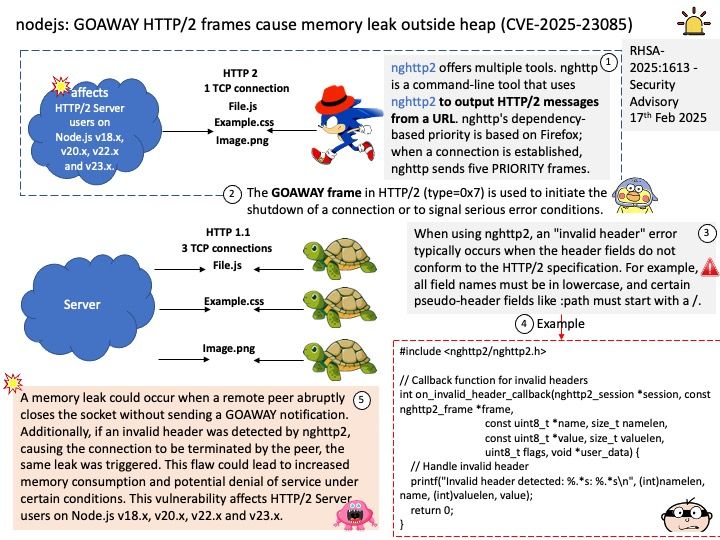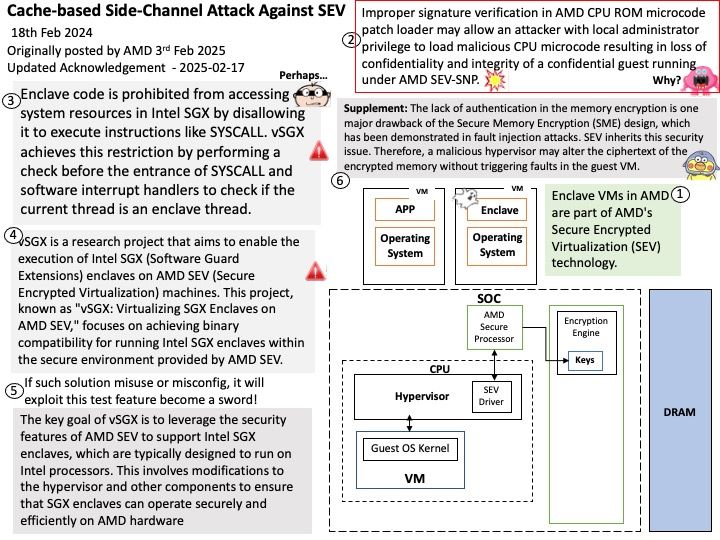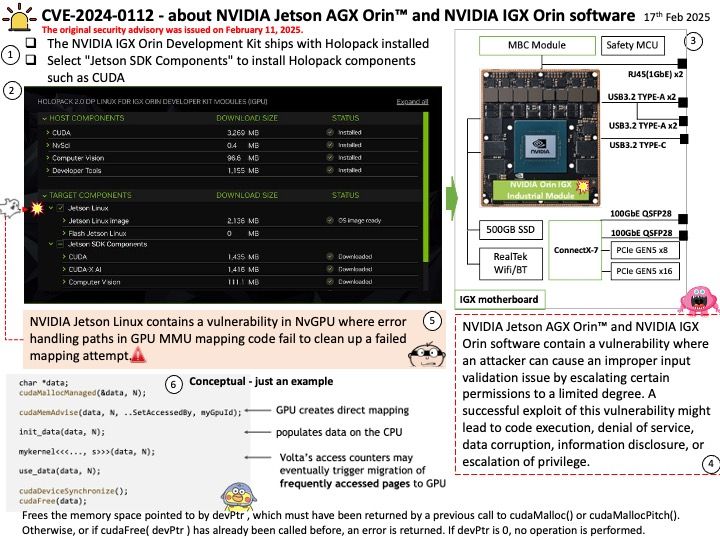
Preface: Regarding its use in HPC clusters, the Radeon PRO V710 is indeed suitable. It is supported by AMD’s ROCm platform, which is optimized for HPC and AI workloads. Additionally, it is used in Azure’s NVads V710 v5-series virtual machines, which are designed for GPU-accelerated applications, including HPC.
Background: The global memory of the AMD Radeon™ PRO V710 is the 28 GB of GDDR6 memory. This memory is connected via a 224-bit memory interface and operates at an effective speed of 18 Gbps1. The memory is used for storing data that the GPU processes, such as textures, frame buffers, and other computational data.
The NVIDIA Container Toolkit is specifically designed to work with NVIDIA GPUs and their CUDA framework. It is not compatible with AMD GPUs. For AMD GPUs, you should use the ROCm (Radeon Open Compute) platform, which provides similar functionality for containerized environments.
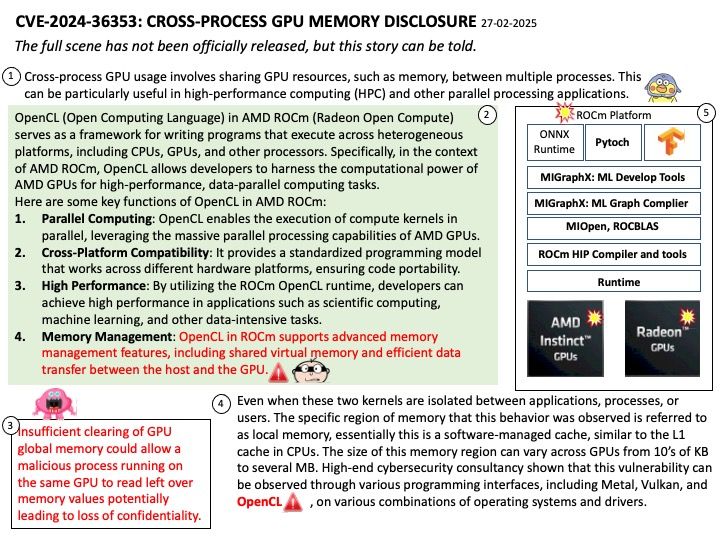
OpenCL (Open Computing Language) in AMD ROCm (Radeon Open Compute) serves as a framework for writing programs that execute across heterogeneous platforms, including CPUs, GPUs, and other processors. Specifically, in the context of AMD ROCm, OpenCL allows developers to harness the computational power of AMD GPUs for high-performance, data-parallel computing tasks.
Vulnerability details: Insufficient clearing of GPU global memory could allow a malicious process running on the same GPU to read left over memory values potentially leading to loss of confidentiality.
Official announcement: Please refer to the link for details https://www.amd.com/en/resources/product-security/bulletin/amd-sb-6019.html