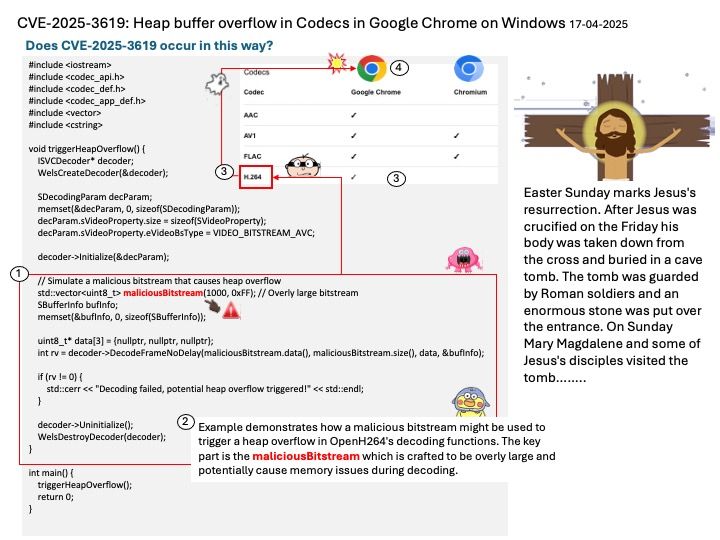
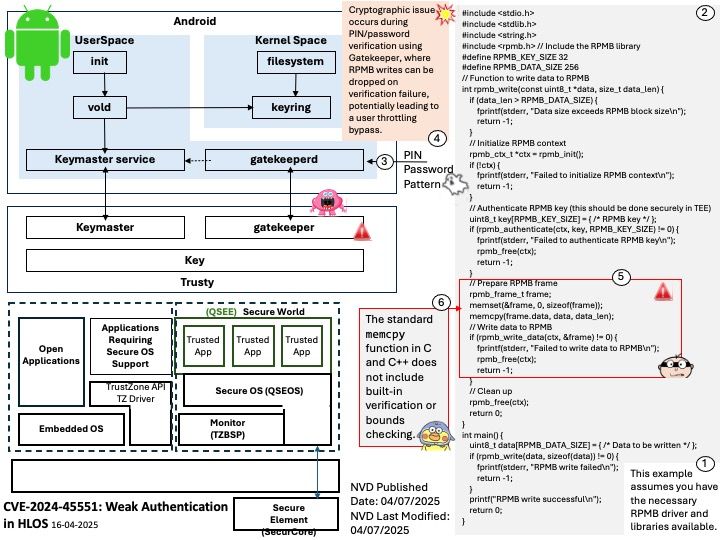
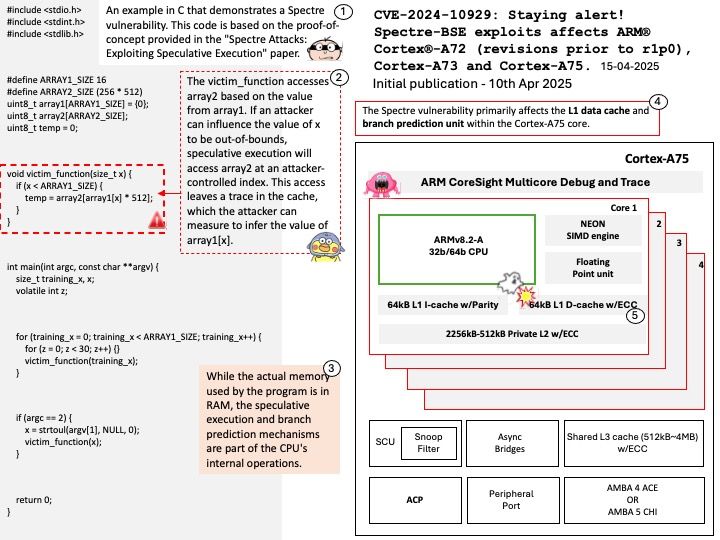
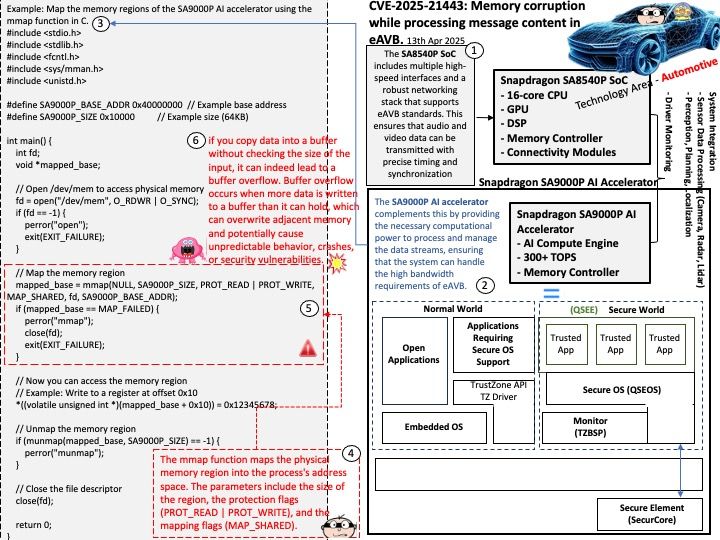
Preface: In ischemic stroke, every second counts. If TPA thrombolytic agent is used promptly in ischemic stroke, it can dissolve blood clots and reduce brain cell necrosis. But it must be used within three hours, so it is very important to grasp the golden three hours.
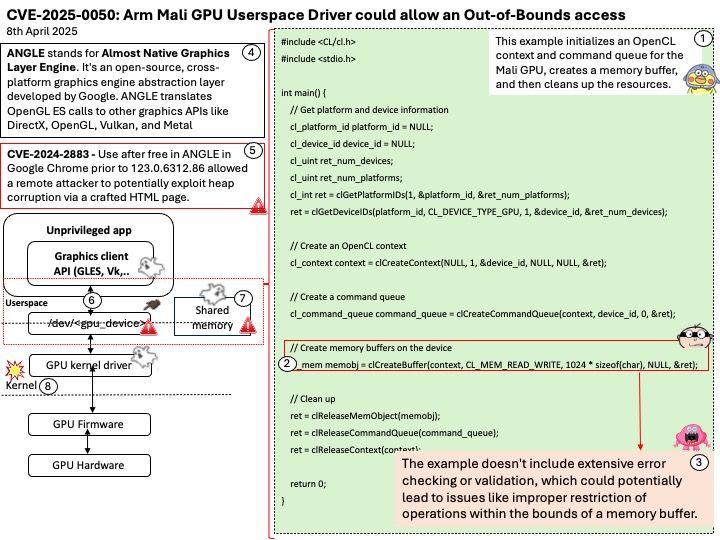
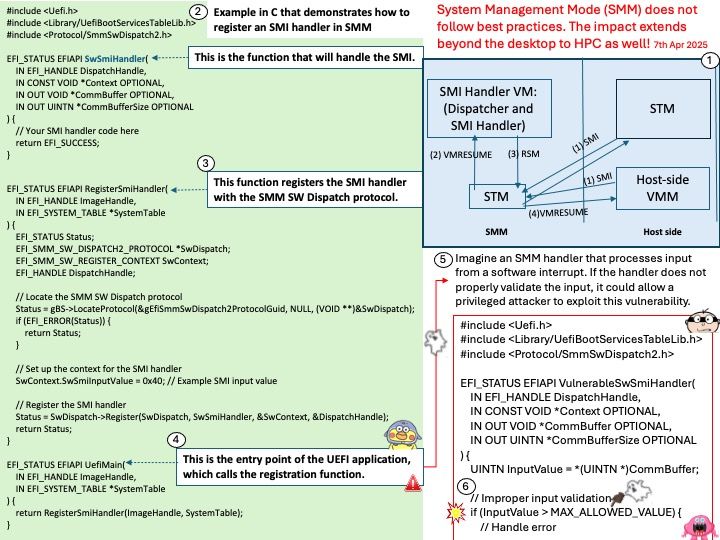
HPC systems do indeed function as a collective unit, similar to a single brain, network congestion remains a significant concern due to several technical reasons. For instance: High Data Transfer Rates, Complex Communication Patterns, Shared Resources and Latency Sensitivity.
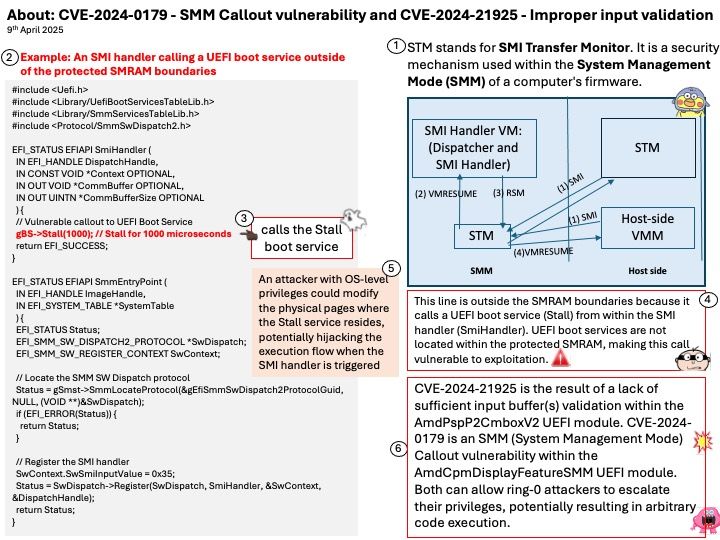
Background: HPC systems do indeed function as a collective unit, similar to a single brain, network congestion remains a significant concern due to several technical reasons:
-High Data Transfer Rates: HPC systems often involve massive data transfers between nodes. When multiple nodes simultaneously send and receive large amounts of data, it can overwhelm the network, leading to congestion.
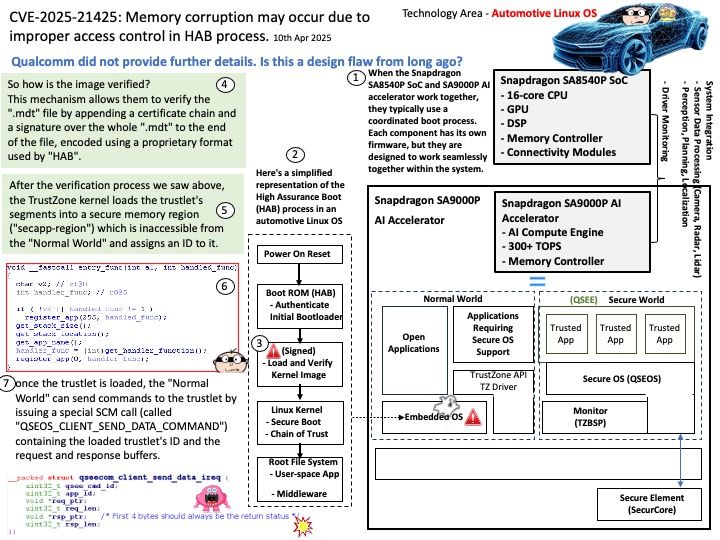
-Complex Communication Patterns: HPC workloads typically involve complex communication patterns, such as all-to-all communication, which can create bottlenecks. Even if the network is designed to handle high traffic, certain patterns can still cause congestion2.
-Shared Resources: HPC systems share network resources among many nodes. When demand for these resources exceeds capacity, it results in congestion. This can delay data transfer and impact overall system performance.
-Latency Sensitivity: Many HPC applications are sensitive to latency. Network congestion increases latency, which can significantly affect the performance of time-critical applications.
-Scalability Challenges: As HPC systems scale up, the complexity and volume of data traffic increase. Ensuring efficient communication across thousands or even millions of nodes becomes challenging, and congestion can arise if the network infrastructure isn’t robust enough.
Solution: Addressing network congestion involves implementing advanced technologies like adaptive routing, congestion control mechanisms, and scalable interconnects.